Rocks - Scoil Mhuire Geography
advertisement

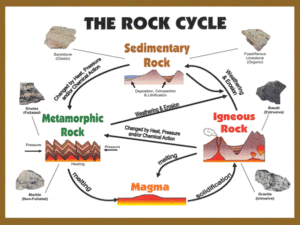
Chapter 5 Rocks • Explain the formation of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rock • Name and give examples of three different rock types. • Explain the rock cycle • Discuss human interaction with the rock cycle using a case study • Know how this topic appears on the exam paper. Rocks Before we start our chapter…. Lets have a recap on the three rock groups http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G7A WGhQynTY Key Words • • • • • • • • • • • Igneous Basalt Granite Sedimentary Sandstone Limestone Metamorphic Quartzite Marble Schist Gneiss Igneous Rock Keywords • • • • • Plutonic Rock (intrusive) Volcanic Rock Magma Crystals Solidified Igneous Rock • The two examples we are going to use are Granite and Basalt. • Read page 43 of your book. • In your groups write the characteristics of granite and the characteristics of basalt. Class Activity: Fill out the table Rock Location Crystals Colour Cools Example Sedimentary Rock • • • • • • Organically formed rock Inorganically formed rock Accumulation Strata Lithification Bedding planes Sedimentary Rock is all about layers!! • Layers of rock fragments, the remains of animals and plants are layered on top of each other. • The rock forms when these layers all made from the build up or accumulate of layers of inorganic (rock fragments) or organic sediments (once living). • Each layer is called strata and they are laid down on bedding planes. • The layers get compressed by pressure and the water and air is pushed out. • They get compacted and are cemented or stuck together by silica or calcite to form solid rock • This is called lithification (turning sediment into stone) Examples Inorganic: Sandstone, shale and conglomerates Organic: Limestone, chalk and coal. Discovery learning: Each group will be given a rock type to investigate. You will present your findings to the class. What you need to do • Name the rock and give the location. • Explain how the rock is formed • Describe the appearance. **Write down notes into your copies about what you have learnt about each of the rock types** Homework • Summarise sedimentary rocks into your copies. Metamorphic rocks • Metamorphic rocks behave just like the………. Humans changing or morphing into power rangers • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C1UtsY0uZ Vk • Metamorphic rocks are just like the power ranges. They are made from igneous or sedimentary rocks that change or ‘morph’ into new rock called metamorphic rock Movements of the Earth’s Crust cause heating and squashing of rocks Rocks are sometimes changed Limestone Marble Shale Slate And also Sandstone Quartzite Metamorphic Rocks • • • • • • • • • Igneous Sedimentary Changed Great Heat Pressure Marble Quartzite Schist Gneiss Handout: Metamorphic Rock • Lets break this handout into groups • Each group take a section. Read through it. Try to put it into your own words. • Share your explanations with the class. Activity: Read all the case study in your groups. Highlight parts you do not understand. Each group will reteach the topic again. Activity • Using the hand out create a table of metamorphic rocks. • Use the following headings 1. Rock Name 2. Type of metamorphic rock 3. Appearance 4. How it was formed 5. Location in Ireland. The Rock Cycle • The process by which each rock type can be changed into another To remember the rock cycle! • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=53lMdHzv GCQ&playnext=1&list=PLFE564A227272476F &feature=results_video Activity: Teach each other the rock cycle in your groups Activity • In your groups draw and label the rock cycle. **No Cheating!!!** put away the copies!!! Human Interaction with the Rock Cycle • Mind Map Human Interaction with the rock cycle Quarrying • Read page 48 and page 49 as a class. • In your groups summarise the main points of each heading • This is a long question so remember…. Use your own words!!!