Rocks
advertisement

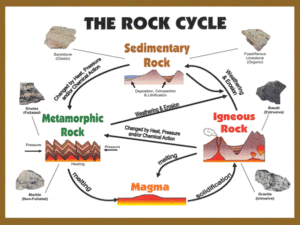
Rocks Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks ROCK CYCLE • Equilibrium • Interrelationships between – – – – – igneous rocks sediment sedimentary rocks metamorphic rocks weathering and erosion IGNEOUS ROCKS EXTRUSIVE Volcanic- Fine-grained INTRUSIVE Plutonic- Coarse-grained MAGMA • Molten Rock – Usually with dissolved gasses • Generated at depth • Eruptions if magma (lava) reaches surface • If doesn’t reach surface, Solidifies underground – – – Intrudes country or host rock Intrusive contact Xenolith- ‘foreign body’ Igneous Rocks • Names based on mineral composition reflects chemical composition of the magma and... Grain size – Very coarse-grained Pegmatitic – Coarse-grained: Phaneritic > 1 mm. – Fine-grained: Aphanitic < 1 mm. – Porphyritic- 2 crystal sizes Igneous RocksClassification • Coarse-grained• Plutonic (Intrusive) – – – – Granite (Sialic) (SIlica and ALuminum rich) Diorite Gabbro (Mafic) (MAgnesium and iron (FE) rich) Dunite & Peridotite (Ultramafic) • Fine-Grained • Volcanic (Extrusive) – Rhyolite (Sialic) – Andesite – Basalt (Mafic) Igneous Rock Identification • Granite (& Rhyolite) – – – – High in Si + O Low in Fe + Mg Mostly feldspar & Light-colored quartz • Basalt (& Gabbro) – – – – “Low” in Si + O High in Fe + Mg no quartz, abundant ferromagnesian minerals Dark colored • Andesite (& Diorite- intermediate) WEATHERING, EROSION, TRANSPORTATION • Weathering- Physical disintegration and chemical decomposition of rocks • Erosion- Physical removal • Transportation- Movement of eroded particles • Chemical vs. Physical Weathering • Effects of weathering – – – Surface alteration of outcrops Spheroidal weathering Differential weathering Physical Weathering Differential Weathering Frost Action Exfoliation Organic Action ROCK CYCLE Relative Percentages of Sedimentary Rocks SEDIMENT • Particle size – – – – – Pebbles, cobbles, boulders Gravel- > 2mm Sand- 2mm - 0.063mm Silt - 0.063mm - 0.004mm Clay- < 0.004 • Deposition Clay-sized particle vs. clay mineral TYPES OF SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • Clastic or Detrital • Chemical- inorganic precipitation or evaporation • Biochemical- Organic remains – shells, charcoal, plant fragments CLASTIC (Detrital) ROCKS • Breccia and Conglomerate (> 2mm) – Sedimentary Breccia- angular fragments – Conglomerate- rounded fragments • Sandstone (2mm - 0.063mm) – Quartz sandstone – Arkose (feldspar) – Graywacke (appreciable amounts of silt/clay) • Fine-grained Matrix • Usually from turbidity currents Quartz Sandstone • CHEMICAL SEDIMENTARY ROCKS Carbonate Rocks – Limestone- made of calcite • Inorganic varieties – micrite, oolites, travertine – Dolomite – Recrystallization • Chert- silica • Evaporites – Rock gypsum – Rock salt BIOCHEMICAL SEDIMENTARY ROCKS • Coal – Develops from peat • plant fragments – Lignite – Bituminous Coal • Carbonate Rocks – Limestone- made of calcite • organic varieties – Coquina – Fossiliferous Limestone – Chalk SEDIMENTARY STRUCTURES – – – – – Cross-bedding Graded bed Mud cracks Ripple marks Fossils Mudcracks Sedimentary Rocks as Resources • Non-Metallic – – – – Sand and gravel Limestone Clay Gypsum • Energy Resources – Oil and Gas – Coal Formation of Oil and Gas U.S. Coal Production Metamorphic Rocks • Metamorphism – Increase in Pressure; increase in Temperature • Burial • Contact • Regional • Metamorphic rock – Pre-existing rock – Parent rock Foliation Classification A- Slate C- Phyllite D- Schist E- Gneiss F- Migmatite Classification