Chapter 5: Rocks
advertisement

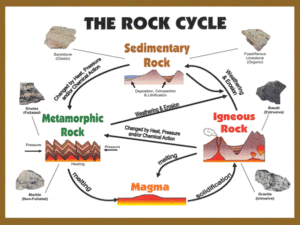
CHAPTER 5: ROCKS Section 6: The Rock Cycle BASICS Forces deep inside Earth and at the surface produce a slow cycle that builds, destroys, and changes the rocks in the crust. Rock cycle: series of processes on Earth’s surface and in the crust and mantle that slowly change rocks from one kind to another A CYCLE OF MANY PATHWAYS JOURNEY OF A ROCK 1. Granite (igneous) formed beneath the surface 2. Pushed upward into mountain through plate tectonics 3. Granite is eroded 4. Particles become sand and are carried by streams into ocean 5. Settle on ocean floor and layers build up 6. Becomes sandstone (sedimentary) 7. Sandstone buried deeply 8. Heat and pressure change into quartzite (metamorphic) CHECKPOINT 1 Begin with igneous rock and explain how it could change through two more steps in the rock cycle. CHECKPOINT 1 Begin with igneous rock and explain how it could change through two more steps in the rock cycle. Possible answer: the igneous rock is buried, exposed to heat and pressure, and becomes a metamorphic rock, which eventually is uplifted and eroded to form sediment and then sedimentary rock. THE ROCK CYCLE AND PLATE TECTONICS Plate movements start the rock cycle by helping to form magma, the source of igneous rocks. Plate movements also cause faulting, folding, and other motions of the crust that help to form sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Igneous Rocks Oceanic plates move apart magma rises and fills gap with new igneous rock Oceanic plate subducts under continental magma forms and rises volcano made of igneous rock Collision of continental plates may push rocks so deep the melt to form magma cools and hardens to form igneous rock THE ROCK CYCLE AND PLATE TECTONICS Sedimentary and Metamorphic Rocks Collision between continental plates range; erosion sedimentary rock Collision between continental plates deep into mantle (heat & pressure) rock mountain push rocks metamorphic CHECKPOINT 2 How can the collision of plates lead to the formation of sedimentary rock? CHECKPOINT 2 How can the collision of plates lead to the formation of sedimentary rock? During the collision, mountains form. Through time, the mountains are weathered and eroded to produce sediment. The sediment is compacted and cemented to form sedimentary rock. POST-LESSON QUIZ 1. How can a metamorphic rock become a sedimentary rock? a. exposure to heat and pressure b. melting c. erosion d. volcanic activity POST-LESSON QUIZ 2. How can igneous rock become metamorphic rock? a. exposure to heat and pressure b. melting c. erosion d. volcanic activity POST-LESSON QUIZ 3. How can metamorphic rock become igneous rock? a. exposure to heat and pressure b. melting and recrystallization c. erosion d. deposition POST-LESSON QUIZ 4. What is the driving force behind the rock cycle? a. the Sun b. plate tectonics c. human impact d. ocean tides POST-LESSON QUIZ 5. A metamorphic rock can become which of the following types of rock? a. a different type of metamorphic rock b. an igneous rock c. a sedimentary rock d. all of the above