5. Interior Accessories
advertisement

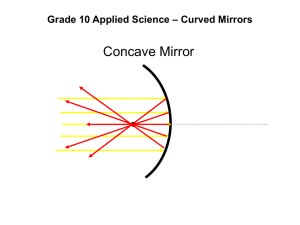
INTERIOR ARCHITECTURE INTERIOR ACCESSORIES Group 8 B02/53525/2012: Shiraz Shareen Aziz Din. B02/0903/2012: Wambua Sarah Mwende. INTRODUCTION Accessories are added elements that have various effects to the original element. Once the layout, furniture, lighting, artwork, electronics, accessories, paint and other elements have been established, accessories are then used to finalize the design. These accessories include: -Ceramics (Vases) -Mirrors -Art and Pictures -Sculptures -Clocks and Candles -Indoor Plants 1. CERAMICS Ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic solids prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling TYPES OF CERAMIC PRODUCTS Structural- eg bricks, floor and roof tiles Refractories- eg kiln lining, gas fire radiants, steel and glass making crucibles. White wares- eg tableware, cookware, wall tiles, pottery products and sanitary ware. POTTERY TYPES 1.Earthenware – often made from clay, quartz and feldspar It is, or can be, fired at relatively low temperatures and vitrification does not take place, leaving the body slightly porous(if not glazed) . After firing the body is porous and opaque, and depending on the raw materials used will be colored from white to buff to red. Earthenware is also less strong, less tough and more porous than stoneware, but is less expensive and easier to work. 2. Stoneware- a vitreous or semi-vitreous ceramic ware made primarily from nonrefractory fire Stoneware, which, though dense, impermeable and hard enough to resist scratching by a steel point. differs from porcelain because it is more opaque, and normally only partially vitrified. It is usually coloured grey or brownish because of impurities in the clay used for its manufacture, and is normally glazed." 3. Porcelain- (also known as China or Fine China) is a ceramic material made by heating materials, generally including clay in the form of kaolin, in a kiln to temperatures between 1,200 °C (2,192 °F) and 1,400 °C (2,552 °F). The toughness, strength, and translucence of porcelain arise mainly from the formation of glass and the mineral mullite within the fired body at these high temperatures. HOW ARE CERAMIC PRODUCTS MADE? SHAPING AND FORMING METHODS 1. HAND BUILDING This is the earliest forming method. Wares can be constructed by hand from coils of clay, combining flat slabs of clay, or pinching solid balls of clay or some combination of these. Parts of hand-built vessels are often joined together with the aid of slip, an aqueous suspension of clay body and water. Some studio potters find hand-building more conducive to create one-of-akind works of art. 2.THE POTTERS WHEEL In a process called "throwing“, a ball of clay is placed in the centre of a turntable, called the wheelhead, which the potter rotates with a stick, with foot power or with a variablespeed electric motor. During the process of throwing, the wheel rotates while the solid ball of soft clay is pressed, squeezed and pulled gently upwards and outwards into a hollow shape. Wares produced by this method have high artistic merit though reproducibility is poor 3.ROLLER HEAD MACHINE This machine is for shaping wares on a rotating mould, as in with a rotary shaping tool. The rotary shaping tool is a shallow cone having the same diameter as the ware being formed and shaped to the desired form of the back of the article being made. Roller head machines remain the dominant method for producing flatware. 4. SLIPCASTING A figurine made by slipcasting This is ideally suited to the making of wares that cannot be formed by other methods of shaping. A slip, made by mixing clay body with water, is poured into a highly absorbent plaster mould. Water from the slip is absorbed into the mould leaving a layer of clay body covering its internal surfaces and taking its internal shape. Excess slip is poured out of the mould, which is then split open and the moulded object removed. Slipcasting is widely used in the production of sanitary wares and is also used for making smaller articles, such as intricately detailed figurines. POTTERY DECORATION TECHNIQUES 1. Impressed surface details Making impressions in the damp clay surface can be used to create any number of freehand impressions and marks, limited only by your own imagination and patience. 2.Use of slips A slip is a suspension in water of clay and/or other materials used in the production of ceramic ware. Decoratively its placed onto a wet or leather-hard clay body surface by dipping, painting or splashing. Slipware may be carved or burnished to change the surface appearance of the ware. Colored slips can be used to create pieces of ceramic art by techniques similar to paint in other media. 3. Glazing Glaze is a layer or coating of a vitreous substance which has been fused to a ceramic object through firing. Glaze can serve to color, increase gloss, decorate, strengthen or waterproof an item. Ceramic glaze raw materials generally include silica, which will be the main glass former. Colorants, such as iron oxide, copper carbonate or cobalt carbonate, and sometimes opacifiers such as tin oxide or zirconium oxide, are used to modify the visual appearance of the fired glaze. CERAMISTS ABOUT ODUNDO’S POTTERY •Odundo's best-known ceramics are hand built, using a coiling technique. •She mostly uses terracotta to make her pieces •Each piece is burnished, covered with slip, and then burnished again. •The pieces are fired in an oxidizing atmosphere, which turns them a red-orange. •A second firing in an oxygen-poor (reducing) atmosphere causes the clay to turn black; this is known as reduction-firing. •Many of the vessels she creates are reminiscent of the human form, often following the curves of the spine, stomach, or hair. •Her work may be found in museum and private collections worldwide. WHERE CAN I BUY POTTERY PIECES? Kazuri beads and pottery center in karen Earthworks pottery in westlands Kenya clay products limited Llesi pottery group 2. MIRRORS A mirror is flat or curved surface usually produced of glass that has a reflective coating applied to it. Brief History o o Man first got reflections from rivers, ponds and other natural entities The earliest man made mirrors from polished stone and mirrors made from black volcanic glass obsidian - Found in Turkey dating back to at least 6000 years. o Also found in Ancient Egypt - polished copper with the round face of the mirror embellished with ornamentation, Mesopotamia polished metal, Central and Southern America - polished stone, o China - made from metal alloys, a mixture of tin and copper called speculum metal that could be highly polished to made a reflective surface as well as mirrors made of polished bronze. o Metal alloys or precious metals mirrors were very valuable items in ancient times only affordable to the very wealthy. During the period of the Renaissance in Europe, mirrors were made by a method of coating glass with a tin and mercury amalgam. In the sixteenth century, Venice became the centre of manufacture for such mirrors. A factory for manufacturing mirrors called Saint-Gobain was established in France. Mirrors were still expensive luxuries and only the very rich owned it. In 1835 Justus von Liebig, a German chemist, developed the silveredglass mirror where a thin layer of metallic silver put onto glass by the chemical reduction of silver nitrate. This enabled mirrors to be manufactured on a much larger scale, and that is when ordinary people could buy a mirror. TYPES OF MIRRORS There are two main types: - Silvered and Non-Silvered Silvered Mirrors Concave Mirror: Glass is curved inward, and then coated, creating enlarged reflections. Useful as a grooming aide. Convex Mirror: The glass curves outward, creating reduced reflections. It can be either decorative or a useful tool in parking garages or busy corridors to help people see around the corner Silvered tinted Mirrors: Tinted mirrors are produced using the methods described above. The silver coating is applied to one of the various tinted glass substrates available on the market. Tinted mirrors are generally used in decorative applications where color and diminished light reflection are desirable. Non-Silvered Mirrors - Pyrolytic Mirrors: These are highly reflective coated glass mirrors with performance characteristics like that of silvered mirrors. They are used in shower doors and other areas where moisture can affect the substrate of silvered mirrors. Transparent/Two-way Mirrors: They are designed to permit vision through one direction while giving the appearance of a standard mirror from the opposite side. Their major application is to permit undetected observation for study or surveillance in interior conditions such as learning centers in schools and universities, medical and psychiatric clinics, and security stations in casinos or high-traffic retail stores. HOW A SILVERED MIRROR IS MADE All mirrors for interior use are manufactured by the conveyor, wet deposition method: 1. Glass Cleaning: Annealed or fully tempered glass is thoroughly cleaned by the application of cleaners and passing contact with oscillating scrub brush units and then rinsed. 2. Surface Treatment: The surface of the glass is sensitized with a diluted solution of tin chloride. This allows for the deposition of silver. Silver nitrate is sprayed onto the sensitized surface of the glass along with other chemical configurations; this forms a uniform silver layer on the glass. 3. Protection of Silver Layer: A layer of copper is deposited directly onto the silver. It can be applied in two ways: chemically or galvanically. Recent technological advances have lead to the development of copper free protective films, which also prevent silver oxidation. 4. Protective mirror Application: Once the metal layers are attached to the glass, they are covered by a protective mirror backing paint. They protect the metal layers from corrosion and from mechanical scratching. The paint can be applied either by passing the glass through a curtain of paint or by passing glass in contact with a roller paint coater. They can be applied as a single coat or double coat which are both effective. APPLICATIONS OF MIRRORS IN INTERIOR DESIGN 1. To reflect light Mirrors brighten a room, and therefore are placed near lamps or light fixtures or in places where they’ll reflect natural light. They also improve the inside lighting of a room. For instance, a room that’s painted in a dark color may seem smaller as well as feel oppressive. Adding mirrors to a number of walls can counteract the darkness and boost the color of wall space. The best method to improve a room’s lighting without needing more electricity would be to place mirrors reverse windows. The mirrors may reflect natural sunlight streaming with the windows and brighten the entire room. Some homeowners actually report a cost savings in energy costs simply by reflecting the free light in the sun. Use a large, full-length mirror in entrance ways to instantly give a person a sense of increased space when they enter. 2. To Increase space A wall of a mirror or mirrors in a small space, such as a bedroom or dining room or hallway that is really squashed opens it up and creates a sense of flow and increased area. 3. To create warmth Placing a mirror on a mantle can make the fireplace area, which can often feel cramped and dark, more inviting. A mirror can also be placed next to a fireplace to reflect the glow and flames of the fire 4. For an artistic effect This can be achieved by hanging a series of mirrors on a wall. They can be the same or vary in size and shape. They can be arranged in symmetrical or asymmetrical patterns depending on the tone of the room. Many mirrored surfaces will reflect the beauty of whatever room it is mounted in, and the jumbled style will add its own personality. Each of the separate mirrors reflects a slightly different perspective, so there is experience of a burst of color and shapes wherever the mirrors are placed. 5. Accessorize using decorative mirrors. You can use simple frames, add mosaic tiles to the border, or use other materials to make a mirror fit the room’s theme. 6. Vanity Mirrors In Bathrooms Since full-length vanity mirrors are standard, embellishments and thoughtful staging can be applied to make the bathrooms stand out. 6. In designing Group small mirrors together in different shapes and sizes to create an interesting feature on a wall but also bring light to the room. Glue mirrored tiles to your kitchen cabinet doors so reflect the whole room to create a mosaic look in your kitchen. Fit a mirror behind your stove, this is traditionally a rather dark area in your kitchen so add a mirror to bounce any available light around the room. This will also give you more light for when you’re cooking a meal. Place a big mirror beside your dining room table, this adds to the mood of a dining room and keeps it light and bright. Suppliers In Kenya Milways Interiors and Households - Along Argwings Khodhek Road, Hurlingam Next to Malik Motors. Furniture Palace International – Mombasa Rd. Antarc – Mombasa Rd, Opposite Airtel Ltd. Essajee Amijee – Lusaka Rd. Impala Glass Husseini Glass MPPS Tripple M Kidoz Kenya 3. SCULPTURES Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions and one of the plastic arts. Durable sculptural processes originally used carving (the removal of material) and modelling (the addition of material, as clay) but since modernism, shifts in sculptural process led to an almost complete freedom of materials and process. MATERIALS USED Metals especially bronze Stone Wood Bone Precious materials such as gold, silver, jade, and ivory are often used for small luxury works terracotta and other ceramics Wax Stained glass TYPES OF SCULPTURE sculpture in the round- free-standing sculpture that is meant to be viewed on all sides, and is surrounded entirely by space free-standing sculpture, such as statues, not attached (except possibly at the base) to any other surface • Relief- at least partly attached to a background surface. Relief is often classified by the degree of projection from the wall into low or bas-relief, high relief, and sometimes an intermediate mid-relief. Apart from their obvious decorative qualities, sculptures are used as expressive pieces. They may be used to express one’s culture, religion, beliefs, ambitions and likes. SCULPTERS IN KENYA; Akamba handicrafts They have their showroom in Mombasa and deal with a wide range of handcrafted products. 4. PAINTINGS, ART AND PICTURES Paintings or any artwork makes a living space more pleasant and intriguing. They often well with other colors, shapes and textures you choose to put in a certain area. They are included in an interior precisely because they are complementary to almost any room. Inside a house, in particular, the normal entryways and hallways often are the new display location for paintings, photos or any artwork like sculptures. A beautiful large abstract painting can spark some interesting conversation with your guests in your office or living area. Heart display of photos on wall Canvas Printing on wall in Arabic Paintings high up on the living room wall In the bathroom, attention to the naturally high humidity is important. A well-protected piece of abstract wall art or whimsy and color that will make the room come alive can therefore be used. Displaying a lot of small, framed art can be a fun way to add interest to a bathroom, especially in small spaces. Frame works on paper behind acrylic or plexiglass (a transparent acrylic plastic often used in place of glass), which can hinder condensation build up. Bathroom doors hand-painted with Italian-style frescos (a painting that is done on wet plaster) in a bathroom inside the Castello di Amorosa Winery in Calistoga, California, Thick mats can make artwork look nicer and add an extra layer of protection by keeping it further away from the plexiglass In Bedrooms Painting behind a bed inspired by nature. Painting on a dark wall. Photos can be used to fill up empty corners, hallways and walls for a lively feel. INDOOR PLANTS WHY USE INDOOR PLANTS? They are a quick decorating tool They have an air-purifying quality that can absorb and strip toxins like formaldehyde from materials in the home like carpets. Some like the aloe have medicinal value NOTE; Different plants require different care and lighting conditions. Enough research should therefore be made before purchasing any new plant. 5. CLOCKS AND CANDLES Clocks are used on walls for time as well as to accessorize the walls. Candles on the other hand provide more lighting, enhance the mood and can produce a good scent in the atmosphere of a room. Clocks on shelf with indoor plants, pictures and candles. Clock on wall above fireplace Candle, painting and indoor plant on a fireplace Large clock on wall from floor. Candle stands Candles in a fireplace THANK YOU