Chapter 4 Rocks: Mineral Mixtures
advertisement

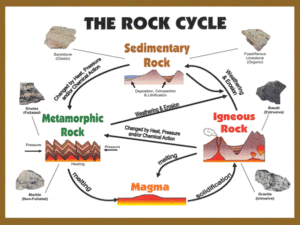
Chapter 4 Rocks: Mineral Mixtures Standard S6E5.b Investigate the composition of rocks in terms of minerals Section 1 pp.90, 95, 96 EQ: How are rocks and minerals different? • Rock • Naturally occurring solid mixture of one or more minerals and organic (living) matter EQ: How are rocks classified? • 3 Classes of Rocks 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Metamorphic Rocks are classified by: • Composition • The chemical makeup of the rock –the minerals and other materials • Texture • The size, shape and positions of the rock grains • Provides clues as to how and where the rock is formed Summary • Write a paragraph that: • Compares and contrasts minerals and rocks. • Write another paragraph that: • Compares and contrasts composition and texture. Section 2 pp.98 – 101 EQ: Where do igneous rocks come from? • Igneous Rocks • Igneous means “fire” • Begins as magma that contains many minerals • Cooled magma hardens and solidifies • Composition of Igneous Rocks • Determined by minerals • Light colored ones – less dense– made of aluminum, silicon • Dark colored ones – more dense, made of iron, calcium, & magnesium • Texture of Igneous Rocks • Size of the grains • Fast cooling lava on the surface of the volcano -fine grains or no grains Ex: pumice • Slow cooling magma inside the Earth -large grains Ex: granite • Igneous Rock Formation • Intrussive igneous rock -forms inside Earth cools slowly large grains Ex: granite • Igneous Rock Formation • Extrussive Igneous Rock -forms on Earth’s surface cools fast fine grains or no grains Ex: pumice • Igneous Rock Formation • In other words, the faster the magma or lava cools the smaller the grains of the rock • The slower the magma or lava cools the larger the grains of the rock Summary • Compare and contrast Stone Mountain’s granite and pumice from a volcano. Draw a Picture of the Formation of Igneous Rocks • Label intrusive, extrusive, magma, lava. • Show the grain size of the developing rocks. • Indicate how fast the rocks cool. • Name rock samples for each class of igneous rocks. Section 3 pp. 102 – 105 EQ: What are sedimentary rocks made of? • Sediment • Fragments of weathered rock & minerals • Strata • Layers of sed. rock on Earth’s surface that forms when the sed is deposited & cemented together by dissolved clacite & quartz • Stratification • Process in which sed. Rocks are arranged in layers EQ: What are the 3 classes of sedimentary rock? • Clastic • Made of rock fragments cemented together by dissolved calcite & quartz • May be any grain size • Examples: conglomerate, shale, sandstone • Chemical • From solutions of dissolved minerals in water • The dissolved minerals crystallize • Ex: halite—salt— NaCl Result of supersaturated salt water • Organic • Made from the remains of dead organisms • Ex: Chalk is made of tiny sea creatures • Ex: Coal forms underground when decomposed plant material is changed into coal by heat & pressure Fossil fuels are nonrenewable resources Summary • Describe the formation of the 3 classes of sedimentary rock. • Draw a picture of how each sed. rock forms • Show the rock “before” it became a sed. rock and the “after” or the resulting sed. rock. • Label each class of sedimentary rock. • Compare and Contrast Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks Section 4 pp. 106 – 111 EQ: What is metamorphism? • Metamorphism • Change shape • Metamorphic Rock • The structure, texture or composition of the rock changes because of extreme heat and/or pressure • A chemical change occurs • Deformation • Change in the shape of a rock caused by a force, like squeeze or stretch EQ: What are the 2 classes of metamorphic rock? • Foliated • Mineral grains are arranged in bands • Ex: mica, slate • Non-foliated • Random arrangement of grains • Ex: marble Summary • If I needed to make a tool from a rock, should I choose a foliated or a non-foliated metamorphic rock? Explain your answer.