Chapter 30 & 31 Review
advertisement

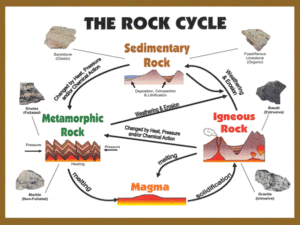
Chapter 30 & 31 Review Prepared by Mrs. Senger Can you…? 1) What are the five groups of minerals and describe their characteristics? 2) What is a mineral? 3) What are the three kinds of magma and how are they the same/different? 4) What are physical tests we can run to test a mineral during identification? 5) What are the 3 kinds of rocks and what are their origins? 6) Describe the two kinds of metamorphism. 7) What are intrusive and extrusive rocks? 8) List the three kinds of volcanoes and their characteristics. 9) What is the rock cycle (deposition, cementation, chemical weathering, physical weathering, erosion, clastic rocks, fossils, and non/foliated rocks are all words you may choose to use in the description). What is the tendency of a mineral to break along a plane of weakness? • • • • Hardness Streak Specific gravity Cleavage What is the tendency of a mineral to break along a plane of weakness? • • • • Hardness Streak Specific gravity Cleavage Metamorphism caused by both thermal and mechanical means is called Regional metamorphism Dynamic metamorphism Contact metamorphism None of these Metamorphism caused by both thermal and mechanical means is called Regional metamorphism Dynamic metamorphism Contact metamorphism None of these All minerals are Synthetic Contain sulfur Organic Crystalline solids All minerals are Synthetic Contain sulfur Organic Crystalline solids Rocks altered by heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface are Igneous rocks Metamorphic rocks Extrusive sedimentary rocks Intrusive igneous rocks Rocks altered by heat and pressure beneath the Earth’s surface are Igneous rocks Metamorphic rocks Extrusive sedimentary rocks Intrusive igneous rocks The most useful physical properties for identification of minerals are Color, cleavage and crystal form Luster, streak and color Streak, hardness and cleavage Acid test, hardness and color The most useful physical properties for identification of minerals are Color, cleavage and crystal form Luster, streak and color Streak, hardness and cleavage Acid test, hardness and color Metamorphism caused by the close proximity of magma source is called Contact metamorphism Regional metamorphism Dynamic metamorphism None of these Metamorphism caused by the close proximity of magma source is called Contact metamorphism Regional metamorphism Dynamic metamorphism None of these Moh’s scale is defined on the basis of minerals that have different Cleavage direction Hardness Shapes Colors Moh’s scale is defined on the basis of minerals that have different Cleavage direction Hardness Shapes Colors If the rock particles in a sedimentary rock are small, round & sorted, we can infer that the grains traveled a Long distance for short time Long distance for long time Short distance for a short time Short distance for a long time If the rock particles in a sedimentary rock are small, round & sorted, we can infer that the grains traveled a Long distance for short time Long distance for long time Short distance for a short time Short distance for a long time Some ___ rock is formed from minerals that were once dissolved in water. Metamorphic Igneous Sedimentary Igneous and metamorphic Some ___ rock is formed from minerals that were once dissolved in water. Metamorphic Igneous Sedimentary Igneous and metamorphic As rock is weathered it breaks down and erodes. Sedimentation begins where erosion stops. Erosion is A chemical process Disintegration and fragmentation of rock into smaller pieces Decomposition and alternation of rock material Transportation of rock particles via water, wind or ice As rock is weathered it breaks down and erodes. Sedimentation begins where erosion stops. Erosion is A chemical process Disintegration and fragmentation of rock into smaller pieces Decomposition and alternation of rock material Transportation of rock particles via water, wind or ice What is the appearance of a mineral’s surface when it reflects light? Hardness Luster Color Cleavage What is the appearance of a mineral’s surface when it reflects light? Hardness Luster Color Cleavage The majority of surface rocks are Intrusive Extrusive Sedimentary metamorphic The majority of surface rocks are Intrusive Extrusive Sedimentary metamorphic What is molten rock from the Earth’s interior called? Magma Lava Carbonate Silicate What is molten rock from the Earth’s interior called? Magma Lava Carbonate Silicate A composite volcano is formed by Alternating layers of lava, ash and mud flow debris Random piles of volcanic debris A mixture of rock and lava Flows of fluid basaltic lava A composite volcano is formed by Alternating layers of lava, ash and mud flow debris Random piles of volcanic debris A mixture of rock and lava Flows of fluid basaltic lava A mineral is a naturally formed & Has a chemical formula Has a crystal structure Is an inorganic solid All of the above A mineral is a naturally formed & Has a chemical formula Has a crystal structure Is an inorganic solid All of the above The silicon content of magma affects its viscosity. Magma with high silicon content has a High viscosity and flows quickly High viscosity and flows slowly Low viscosity and flows quickly Low viscosity and flows slowly The silicon content of magma affects its viscosity. Magma with high silicon content has a High viscosity and flows quickly High viscosity and flows slowly Low viscosity and flows quickly Low viscosity and flows slowly What is the ratio between the weight of a substance and the weight of an equal volume of water? Streak Fracture Specific gravity Hardness What is the ratio between the weight of a substance and the weight of an equal volume of water? Streak Fracture Specific gravity Hardness The most violent volcanoes that erupt but generally continue to erupt again are Shield volcano Composite volcano Cinder volcano None of these The most violent volcanoes that erupt but generally continue to erupt again are Shield volcano Composite volcano Cinder volcano None of these What is the least reliable characteristic used to identify a mineral? Color Hardness Streak Specific gravity What is the least reliable characteristic used to identify a mineral? Color Hardness Streak Specific gravity Mauna Loa (island of Hawaii) is a Shield volcano Cinder volcano Composite volcano None of these Mauna Loa (island of Hawaii) is a Shield volcano Cinder volcano Composite volcano None of these There are 5 groups that are used to classify minerals. Some examples are the carbonates, silicates and Sulfates Sulfides Oxides All are groups used to classify minerals There are 5 groups that are used to classify minerals. Some examples are the carbonates, silicates and Sulfates Sulfides Oxides All are groups used to classify minerals Plutons form from magma Below the Earth’s surface Above the Earth’s surface Ejected from volcanoes All of these Plutons form from magma Below the Earth’s surface Above the Earth’s surface Ejected from volcanoes All of these Rocks and minerals are constantly being recycled or changed, through processes such as erosion, plate tectonics & crystallization, to form one of the three kinds of rocks. Which of the following is NOT one of these classifications? Metamorphic Extrusive Igneous Sedimentary Rocks and minerals are constantly being recycled or changed, through processes such as erosion, plate tectonics & crystallization, to form one of the three kinds of rocks. Which of the following is NOT one of these classifications? Metamorphic Extrusive Igneous Sedimentary Igneous rock is formed from Solidified lava beneath the Earth’s surface High temperature and pressure Crystallization of magma Any of these Igneous rock is formed from Solidified lava beneath the Earth’s surface High temperature and pressure Crystallization of magma Any of these Rocks formed by cooling from a molten state are Sedimentary rocks Igneous rocks Precipitated rocks Metamorphic rocks Rocks formed by cooling from a molten state are Sedimentary rocks Igneous rocks Precipitated rocks Metamorphic rocks Rocks are grouped into three classes depending on how the rock was Located Discovered Shaped Formed Rocks are grouped into three classes depending on how the rock was Located Discovered Shaped Formed What do we call magma that has reached the Earth’s surface? Marble Lava Foliated Metamorphic What do we call magma that has reached the Earth’s surface? Marble Lava Foliated Metamorphic