Chapter 2 Lesson 3: Igneous Rocks

Chapter 2 Lesson 3: Igneous Rocks
Study and Review Guide
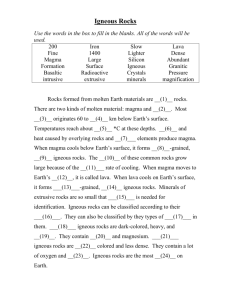
1. Igneous rocks are formed from the cooling of magma or lava.
How are igneous rocks classified?
Origin
Texture
Mineral composition
Directions: Circle the correct term that matches
.
Choose Intrusive or Extrusive.
2. Formed from lava that erupted onto Earth’s surface.
3. Granite is the most abundant
4. Basalt is the most common
5. Formed when magma hardened beneath Earth’s surface
6. Fine grained or glassy texture
7. Larger grains
8. The texture of an igneous rock depends on the ______________ and _______________
Of its mineral crystals.
What is the exception to this rule?
Igneous rocks that lack a crystal structure.
9. Rapidly cooling lava forms
____________________ grained igneous rock with _____________ crystals or
___________________ Crystals at all.
10. Slowly cooling magma forms coarsegrained rocks with large crystals such as granite.
11. Lava that is low is silica usually forms
_____________________-colored
Rocks such as _____________________.
12. Magma that is high in silica usually forms _______________
-colored rocks such as ______________.
13. Many igneous rocks are hard,___________, and durable. People throughout history have used igneous rocks for ________________________ and _______________________
Directions: Describe how each of these igneous rocks can be used.
14. granite
15. basalt
16. pumice
17. obsidian
18. perlite
16.
17.
14. Fortresses in Peru (building blocks), building materials ie. Egyptians: statues; Today: curbstones and floors
15. cobblestones, landscaping, roads
18. Mixed with soil and used for starting vegetable seeds