Chapter 3
advertisement

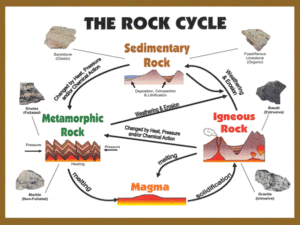
Chapter 3 - Rocks Notes January 2013 3-1 What are rocks? • Rocks in Earth’s Crust 1. Petrologists study rocks & minerals. 2. Rocks are made of minerals (2000). • Classification of Rocks 1. Classification is the grouping of things that are alike. 2. Petrologists classify rocks & minerals. • Classes of Rocks 1. Petrologists classify rocks by the way they form. 2. The THREE classes of rocks are: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic. Section 3-2 How are igneous rocks formed? • Heat Inside Earth 1. The deeper you dig, the hotter it gets 2. Molten rock is made of melted minerals. • Magma and Igneous Rock 1. When molten rock cools and hardens, igneous rock is formed. 2. Igneous rock can take thousands of years to form from magma inside Earth. • Lava and Igneous Rock 1. Igneous rocks form quickly from lava above Earth’s crust. Section 3-3 How are igneous rocks classified? • A Combination of Minerals 1. The SIX most common minerals in igneous rocks are Quartz, Mica, Amphibole, Feldspar, Olivine, & Pyroxene • Crystal Size 1. Crystal size depends on the amount of time it takes the molten rock to cool. 2. Magma = large crystals; Lava = small or none • Texture 1. Texture can be used to identify rocks. 2. Large crystals are coarse; small crystals are fine; no crystals are glassy 3-4 How are sedimentary rocks formed? • Sediments 1. The heaviest sediment sinks first. • Natural Cement 1. As more layers form, water is squeezed out. 2. Dissolved minerals act as cement. • Sedimentary Rock From Living Things 1. Rock can be formed from the remains of living things. 3-5 Classifying Sedimentary rocks • Groups of Sedimentary Rocks 1. Clastic rocks are made from rock particles. 2. Nonclastic rocks are made from dissolved minerals or the remains of living things. • Particle Size 1. Sandstone and Shale are clastic rocks • Dissolved Minerals 1. Limestone and halite are nonclastic rocks. • Plants and Animals 1. Coals are nonclastic rocks formed from the remains of plants. 3-6 How are metamorphic rocks formed? • Changed Rocks 1. Heat & pressure inside Earth change rocks over time. • Heat and Pressure 1. Too much heat will melt a rock or mineral. 2. Extreme pressure will cause flattening (layers). • Magma 1. All rock types can be changed into metamorphic rocks. 3-7 How are metamorphic rocks classified? • Classifying Metamorphic Rocks 1. Metamorphic Rocks can be foliated or nonfoliated depending on their mineral crystal bands. • Banded Metamorphic Rocks 1. Foliated rocks have crystals arranged in bands. 2. Gniess (from granite) and schist (from shale) are examples of foliated rocks. • Metamorphic Rocks Without Bands 1. Nonfoliated do not have minerals arranged in bands. 2. Quartzite is an example (from sandstone).