What are igneous rocks - El Molino High School
advertisement

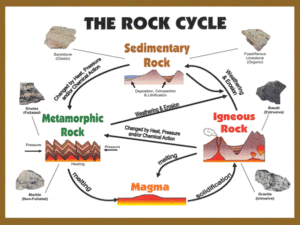
Essential Questions • How do igneous rocks form? • How can the composition of magma be described? • What are the factors that affect how rocks melt and crystallize? Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Vocabulary Review New • • • • • • silicate Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education lava igneous rock partial melting Bowen’s reaction series fractional crystallization What are igneous rocks? Igneous Rock Formation • Lava is magma that flows out onto Earth’s surface. • Igneous rocks form when lava or magma cools and minerals crystallize. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Igneous Rock Formation Composition of magma • The type of igneous rock that forms depends on the composition of the magma, which is often a slushy mix of molten rock, dissolved gases, and mineral crystals. • Magma is classified as basaltic, andesitic, or rhyolitic, based on the amount of silica it contains. Silica affects melting temperature and impacts how quickly magma flows. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Igneous Rock Formation Magma formation • Magma can be formed either by melting of Earth’s crust or by melting within the mantle. • The four main factors involved in the formation of magma are temperature, pressure, water content, and mineral content. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Igneous Rock Formation Magma formation • Temperature generally increases with depth in Earth’s crust. This temperature increase is known as the geothermal gradient. • Temperature in Earth’s crust increases 30°C every 1 km in depth. At just over 3 km it is how enough to make water boil (100°C). Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Igneous Rock Formation Magma formation • Pressure also increases with depth as a result of the weight of overlying rock. The increased pressure on a rock also increases the rock’s melting point. • Rocks and minerals often contain small percentages of water, which changes the melting point of the rocks. As water content increases, the melting point decreases. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Igneous Rock Formation Mineral content • Rocks melt at lower or higher temperatures because their component minerals have lower or higher melting points. In general, rocks that are rich in iron and magnesium melt at higher temperatures than rocks that contain higher levels of silicon. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Igneous Rock Formation Partial melting • The process whereby some minerals melt at relatively low temperatures while other minerals remain solid is called partial melting. • If temperatures are not high enough to melt the entire rock, the resulting magma will have a different composition than that of the original rock. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Bowen’s Reaction Series • Canadian geologist N. L. Bowen demonstrated that as magma cools and crystallizes, minerals form in predictable patterns in a process now known as the Bowen’s reaction series. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Bowen’s Reaction Series Iron-rich minerals • The left branch of Bowen’s reaction series represents the iron-rich minerals, which undergo abrupt changes as magma cools and crystallizes. Feldspars • The right branch of Bowen’s reaction series represents the plagioclase feldspars, which undergo a continuous change of composition as magma cools. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Fractional Crystallization • When magma cools, the first minerals that crystallize are the last minerals that melted during partial melting. This process is called fractional crystallization. • Under certain conditions, newly formed crystals can be removed from magma, ending the chemical reactions between the magma and the minerals. Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Fractional Crystallization Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education What are igneous rocks? Review Essential Questions • How do igneous rocks form? • How can the composition of magma be described? • What are the factors that affect how rocks melt and crystallize? Vocabulary • lava • igneous rock • partial melting Copyright © McGraw-Hill Education • Bowen’s reaction series • fractional crystallization What are igneous rocks?