Safety Presentation on Fiberglass
advertisement

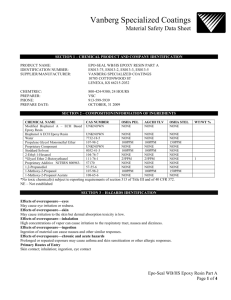
Health hazards in the ME labs Anca Bejan (ab4@vt.edu, 1-2509) Environmental, Health and Safety Services Outline Routes of exposure Exposure control Limits of exposure Epoxy resins/systems Fiberglass Personal Protective Equipment selection Respirator use at VT Routes of exposure Inhalation Ingestion Skin/eye contact Exposure controls Engineering controls (ventilation, enclosures, substitution of material) Administrative controls (work practices) Personal Protective Equipment (eye protection, gloves, foot protection, respirators) Exposure limits Are there any “safe” limits of exposure? YES Susceptibility to effects also depends on: pre-existing medical conditions, age, gender, lifestyle choices, genetic factors, medications, physical exertion, etc. OSHA – enforcement (most limits are from early 1970s) ACGIH, AIHA, NIOSH – recommended limits based on most recent studies on animal or human health effects Limits are set as 8 h TWA, 15 min TWA, Ceiling (ppm, mg/m3) Excursion limits Limits are intended to protect “nearly all workers” from adverse health effects while working 40 h weeks for about 40 years Health effects Adverse health effects Acute (immediate or delayed reaction) Chronic Nature and intensity of effects depends on: Intensity of exposure Duration of exposure Type of exposure Health condition Additive effect, chemical mixtures, etc Determining contaminant concentration in air Personal sampling Pumps Specific filters Sampling tubes Clorimetric tubes Portable instruments Determining contaminant concentration in air Your nose is NOT a reliable instrument Olfactory fatigue Odor treshold vs PEL, STEL, Ceiling Acetone: 16-600 ppm (OSHA PEL: 1000 ppm ACGIH TLV: 500 ppm) Styrene: 0.04-0.32 ppm (PEL: 100 ppm, TLV: 20 ppm) Methylene Chloride: 25-320 ppm (PEL: 25 ppm, STEL: 125 ppm, TLV: 50 ppm) Fiberglass: no OT; TLV: 0.1 f/cc Epoxy systems Used in composite materials Cure at room temperature Have two parts: epoxy resin and curing agent Epoxy resin: epichlorohydrin and bisphenol-A Curing agent: a combination of amine compounds Epoxy systems Epoxy systems- Health effects of the components Epichlorohydrin- skin sensitizer, URT irritant, affects male reproductive system; known animal carcinogen Bisphenol A- endocrine disruptor Amines- may induce asthma and URT sensitization; some are carcinogens Solvents- 2 ethoxyethanol (EGEE) and 2- methoxyethanol (EGME) affect the male reproductive system and may produce embrio/fetal damage Solvents- affect CNS and PNS Epoxy use in the WARE lab MAS Epoxies www.masepoxies.com, look for MSDS info MSDS Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS) Contains information about chemical composition of the product, hazard information, first aid measures, storage, handling and PPE requirements, fire fighting measures, accidental release measures, etc. Every product used in the WARE lab must have an MSDS on file YOU MUST BE FAMILIAR WITH THE MSDSs OF THE PRODUCTS YOU ARE USING!!! KNOW WHERE THEY ARE LOCATED IN THE LAB AND HAVE A COPY WITH YOU IF YOU NEED TO GO TO THE HOSPITAL MAS- Low viscosity epoxy resin MAS -resin So what is the chemical composition of this resin? - DGE-BPA (diglycidyl ether of bis-phenol A) - Novolak - Two-step resins made by reacting epichlorohydrin with phenol formaldehyde condensates (has more than just 2 groups of epoxy per molecule) (http://composite.about.com/library/glossary/e/bldef-e2003.htm) - epoxy diluents (solvents) MAS- medium hardener More info Working safely with epoxy resins A. Avoid all direct skin contact with resin, hardeners and mixed epoxy by wearing gloves and other clothing. Clean any uncured epoxy off the skin with waterless soap immediately after contact. NEVER use solvents to remove epoxy from the skin. Always wash thoroughly with soap and water immediately after contact. B. Protect your eyes by wearing protective eye wear. If contact should occur, flush eyes immediately with running water for 15 minutes. If discomfort continues, seek medical attention. C. Avoid breathing vapors. Use epoxy only in areas with good ventilation. In small areas, be careful have a supply of fresh air and to exhaust any fumes. Wear a respirator with an organic vapor cartridge. Wear a dust mask when you sand the epoxy. If it has cured for less than a week, use a respirator with the organic vapor in combination with a dust pre-filter. D. Avoid ingestion. Wash thoroughly after each use and especially before eating or drinking. http://masepoxies.com/mas8.htm Fiberglass Used as filler (fibers of different sizes and composition) Used as woven material Fiberglass exposure Occurs when the fibers become airborne: Sanding Polishing Shearing/cutting Mixing Routes of exposure: inhalation, skin/eye contact, ingestion Fiberglass-health effects Depend on the physical dimensions and composition of the fiber (in addition to the factors mentioned previously) Irritation and infection of nasal mucuous membrane Lung fibrosis Skin irritation Exposure control Use appropriate ventilation! Do NOT dry sweep. Vacuum or wet the dust before cleaning! Exposure control Always use gloves Wear long sleeves shirts, long pants and shoes (NO sandals) Do NOT take contamination home!! Always wash hands and face before leaving Change in “work clothes” when you are in the lab When taking them home use a closed bag Launder them separately What kind of gloves? Very few gloves are suitable for use with all the chemicals you might encounter in the lab Know where to find info about the right kind of glove (MSDS, glove manufacturer charts, etc) Epoxy – manufacturer recommends neoprene glove Acetone – butyl glove ONLY Disposable latex gloves are NOT intended for protection against chemicals and may induce sensitization to the latex protein Glove selection chart Respirators Recommended ONLY when engineering and administrative controls are not sufficient to minimize exposure Last line of defense Can be a health hazard to the user Have several limitations that must be understood BEFORE you decide to wear them Do NOT fit everybody, don’t work with beards, and don’t work at all if you are using an inappropriate filter ALWAYS consult with EHSS before you purchase ANY dust mask or cartridge respirator Respirators Where can I find more info? - - - Manufacturer websites www.osha.gov http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/ http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/homepage.html http://www.iarc.fr/ http://www.bestglove.com/ http://www.ansell.com VT EHSS : www.ehss.vt.edu