1-3-Butadiene
advertisement

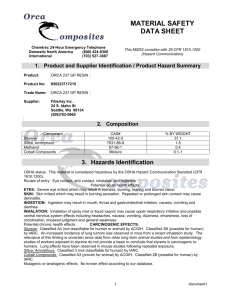
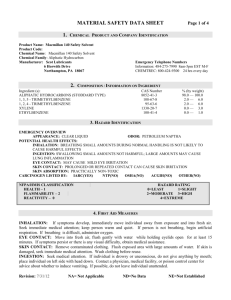
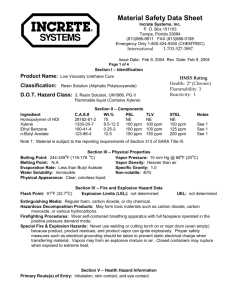
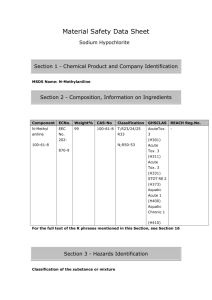
1,3Butadiene 1,3-Butadiene (BD) in our workplace Where and how BD is used How it is stored Potential for it to be released 1 BD’s physical hazards Flammable gas Explosive peroxides Fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or strong oxidizers Release of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide during a fire 2 BD’s health hazards Exposure from inhalation of gas or contact with liquid Overexposure can cause respiratory and eye irritation Contact with liquid BD can cause burns and frostbite 3a BD’s acute (short term) health hazards Central nervous system effects Blurred vision Nausea Fatigue Headache Decreased blood pressure Decreased pulse rate Unconsciousness 3b BD’s chronic (long term) health hazards Cancers of the lymphohematopoietic system Lymphoma Leukemia Potential reproductive toxicity 3c OSHA regulation of 1,3Butadiene Written hazard communication program Informed employees Labeled containers MSDSs available 4a OSHA regulation of 1,3Butadiene Time-weighted average (TWA) permissible exposure limit (PEL) is 1 part per million (ppm) Short-term exposure limit (STEL) is 5 ppm 4b OSHA regulation of 1,3Butadiene Action level is 0.5 ppm as an 8hour TWA Meeting or exceeding action level requires additional standards to be followed Access to BD standard 4c Material safety data sheets (MSDS) Where they are kept What information is included 5 Labeling requirements for containers of BD All BD containers must have legible labels and contain the following information 6 Exposure monitoring to determine employee exposures Monitoring is required unless objective data demonstrates that BD will not be released in levels at or above the action level or above the STEL 7a Exposure monitoring to determine employee exposures Affected employees and their representatives have the right to observe any exposure monitoring Affected employees must be informed of monitoring results within 5 working days of receipt 7b Exposure monitoring to determine employee exposures Within 15 working days of receipt of results, employees must be informed of the corrective actions being taken to reduce any exposures to below the PEL or STEL 7c Engineering controls limit exposure to BD Examples of engineering controls used in our workplace 8 Work practices and procedures Never eat, drink, or smoke where BD is used, stored, or handled Do not keep food, beverages, or smoking materials in these areas 9a Proper storage and handling Tightly close cylinders and containers Protect cylinders from damage Outside or detached storage is preferred Inside storage should be in a cool, dry, well-ventilated, noncombustible area 9b Proper storage and handling BD in storage should be checked for proper inhibitor content, for self-polymerization, and for formation of peroxides when in contact with air and iron Avoid contact with copper and copper alloys. Explosive copper compounds can form 9c Proper storage and handling Store away from flammables, combustible materials, and oxidizing materials Store away from sources of ignition Store cylinders vertically 9d Work practices and procedures All electrical installations and equipment used in areas where BD is present must be rated for a Class I hazardous location Waste BD is classified as a hazardous waste due to its flammability characteristics Other safe work practices at our facility 9e Regulated area An area where the exposure or potential exposure to BD exceeds 1 ppm as an 8-hour TWA or 5 ppm as a 15-minute STEL 10 Signs posted to mark regulated areas Limit entry into regulated areas Prohibit drinking smoking, eating, and 11a Signs posted to mark regulated areas Warn of BD’s potential cancer hazard 11b Signs posted to mark regulated areas Alert employees that respiratory protection is required when exposure may exceed the PELs for 8-hour TWA or STEL 11c Personal protective equipment (PPE) requirements Necessary if the use of engineering and work-practice controls does not reduce exposure to levels at or below BD’s PELs Employees are required to use it properly Our PPE requirements 12 Respiratory protection required When exposure exceeds 1 ppm as an 8-hour TWA or 5 ppm as a 15-minute STEL During installation or set up of engineering and work-practice controls 13a Respiratory protection required During non-routine, infrequent operations when exposures are limited in duration In operations where engineering and work-practice controls are not sufficient to reduce exposures to or below the PELs 13b Respiratory protection Types Care of respirator we use of respirators 13c Medical screening and surveillance program schedule When exposure to BD is at or above the action level on 30 or more days a year When exposure to BD is at or above the PELs for 10 days or more a year Following an emergency situation 14a Medical screening and surveillance program schedule Annual health questionnaire and complete blood count (CBC) Initial physical examination if 12 months have elapsed since the last physical conducted as part of a BD exposure 14b Medical screening and surveillance program schedule Physical examination before assuming duties with BD exposure Every three years after the initial physical Whenever the physician or licensed medical professional reviewing the annual health questionnaire and CBC deem an exam necessary 14c Medical screening and surveillance program schedule Upon reassignment to an area where BD exposure is below the action level and employee’s history does not meet the criteria for continued medical screening and surveillance At termination of employment if 12 months or more have elapsed since the last physical examination 14d Medical screening and surveillance program schedule Within 48 hours of an emergency situation Periodical determination of fitness to wear respirator and perform the job when respirators are required 14e Medical screening components Baseline health questionnaire, which is updated annually Complete physical examination with special emphasis on the liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and skin 14f Medical screening components CBC Tests deemed necessary by the examining physician or licensed health care professional 14g Medical screening written evaluation Occupationally pertinent results A medical opinion on whether BD exposure would place the employee’s health at increased risk Recommended limitations on the employee’s exposure to BD 14h Medical screening written evaluation Statement that the employee has been informed of the results of the medical evaluation Retained for the employee’s length of employment plus 30 years 14i Emergency situations Written plan Evacuation Emergency response duties 15 First aid procedures Eye contact – Flush the eyes with large amounts of water Skin contact – Remove all contaminated clothing and flush the affected area with large amounts of warm water 16a First aid procedures Inhalation – Move the person to fresh air immediately (if you can do so without endangering yourself). • If breathing has stopped, summon emergency medical assistance and perform cardiopulmonary resuscitation (if you are trained) 16b First aid procedures In all cases, obtain prompt medical attention for serious injuries 16c BD exposure goal program Leak prevention, detection, and repair Maintenance ventilation of local exhaust The use of pump exposure control technology 17a BD exposure goal program The use of gauging devices Unloading devices that limit employee exposure Other engineering controls 17b