Design and Simulation of MANET Architecture over ZigBee Protocol
advertisement

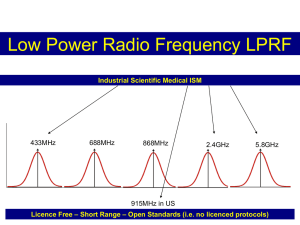
Design and Simulation of MANET Architecture over ZigBee Protocol Suite with Layer ColaborativeEnergy aware design for Performance Optimization Rupam Das Under the Guidance of Prof Rekha Patil HOD , CSE, PDACE, Gulbarga Problem Statement • To adapt 802.15.4 ZigBee standard for Adhoc Network and to improve the performance by using layer collaborative model and Energy Optimization Contribution • ZigBee is adapted standard for Sensor network having low data rate but supports energy conservation. • This is the first known architectural proposal for integrating and adapting ZigBee for Mobile adhoc network • We have proposed the architecture, layer wise protocol adaptation, and shown that even ZigBee can easily be adopted with improved network life but for low data rate in MANET MANET and Conventional Infrastructured Network Conventional MAC 802.11 for MANET ZigBee Characteristic • Dual PHY (2.4GHz and 868/915 MHz) • Data rates of 250 kbps (@2.4 GHz), 40 kbps (@ 915 MHz), and 20 kbps (@868 MHz) • Optimized for low duty-cycle applications (<0.1%) • CSMA-CA channel access: Yields high throughput and low latency for low duty cycle devices like sensors and controls • Low power (battery life multi-month to years) • Multiple topologies: star, peer-to-peer, mesh • Addressing space of up to: • 18,450,000,000,000,000,000 devices (64 bit IEEE address) • 65,535 networks • Optional guaranteed time slot for applications requiring low latency • Fully hand-shaked protocol for transfer reliability • Range: 50m typical (5-500m based on environment) Supported Topologies Communication Mode MAC Primitive for ZigBee • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • MAC Data Service MCPS-DATA – exchange data packets between MAC and PHY MCPS-PURGE – purge an MSDU from the transaction queue MAC Management Service MLME-ASSOCIATE/DISASSOCIATE – network association MLME-SYNC / SYNC-LOSS - device synchronization MLME-SCAN - scan radio channels MLME- COMM-STATUS – communication status MLME-GET / -SET– retrieve/set MAC PIB parameters MLME-START / BEACON-NOTIFY – beacon management MLME-POLL - beaconless synchronization MLME-GTS - GTS management MLME-RESET – request for MLME to perform reset MLME-ORPHAN - orphan device management MLME-RX-ENABLE - enabling/disabling of radio system ZigBee Protocol Overview Adopted ZigBee Topology for MANET Algorithm • • • Start the transmission and continue for t seconds. Random waypoint: For i=1:1:N – – – – • • • • • • • • Pause for pt milliseconds.// pt=pause time Goto (a) End update the co-ordinate values. End At MAC layer: Estimate the Received power of the packet PRx. – • • • • • • • Select a position P1[i] Move towards P1[i] with persistent speed v m/s. Update P[i] If(P[i]==P1[i]) If(MAC has the contention) Forward the packets that are been sent by routing layer Else i) Store the packets in Queue ii) wait for the channel access. End 4) At Network Layer: • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Bypass MAC and calculate Energy Directly and store in variable Ecur. a) Generate beacon Packets to Neighbors b) Receive beacon packets forwarded by the Neighbors c) Prepare Routing table (ID, Hops, Energy) d) update Neighbors table e) if receiving node is coordinator if coordinator has finished receiving all beacons generate coordinator beacon end else increase the hop field value forward the packets. end e) If (RREQ is received) Current Node has Eneough Energy? Yes: Forward RREQ Update Route Information No: Drop RREQ End • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • if(RREP is received) update route information. Forward to precursor node.// previous nodes Notify PAN Coordinator End if (a data packet is received for Application) forward to MAC layer Update Energy end if( Packet is received from MAC) forward to application layer end If( Control Message is received from the MAC) Generate RERR. Update Energy End 5.At Physical Layer: As the packet is received, Find type of packet Change the Energy level according to equation (1). 6. At the end of simulation, calculate throughput, latency, control overhead, packet delivery ratio. Simulation Parameters Results Conclusion • Results show that ZigBee can be easily integrated with the existing MANET architecture without compromising the performance significantly. • Findings of Simulation also show that 802.11 is better for the delay sensitive communication network. But this MAC adaption leads to fast energy losses in the nodes which leads to low network lifetime. • Proposed technique stands out against the conventional ZigBee adaptation and 802.11 in Network lifetime improvement. Thus this adaption is more suitable for the networks where communication is required to be for extended period of time. • Result also depicts that the proposed work is more suitable for networks with lower mobility as packet loss is observed under high mobility. The performance can be further improved by controlling the sleep mode of the devices through measured parameters.