Chemical Equations & Changes: Chemistry Presentation
advertisement

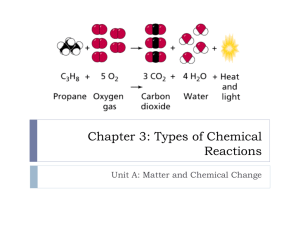
Chemistry 11.1 “Describing Chemical Changes” Review A. Reactants Products B. Dalton’s Theory… “As reactants are converted to products, the bonds holding the atoms together are broken and new bonds are formed.” C. Law of Conservation of Mass… “Mass is neither created nor destroyed.” II. Equations A. Word Equations 1. Def – words used to describe a chemical reaction. -no #’s are involved 2. Ex: Iron + Oxygen Iron (III) Oxide 3. Ex: Hydrogen Peroxide Water + Oxygen 4. Ex: Methane + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + water 5. What is the word equation for…Pure copper can be produced by heating copper (II) sulfide in the presence of diatomic oxygen from the air. Sulfur dioxide gas is also a product in this reaction. Copper II Sulfide + Oxygen Copper + Sulfur Dioxide B. Chemical Equations 1. Def – Using chemical symbols to write a chemical formula. - #’s are involved 2. Ex: Fe + O2 Fe2O3 -this is a skeleton equation b/c it is not balanced C. Balanced Chemical Equations 1. Follows the Law of Conservation of Mass. 2. 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3 III. Symbols used in chemical equations + Used to separate reactants or products “Yields” separates products and reactants (s) (l) (g) (aq) Solid state of matter ∆ / heat Pt, H2SO4 Liquid state of matter Gaseous state of matter Aqueous solution – dissolved in water Heat is supplied in the reaction A formula written above or below the yield sigh indicates it is a catalyst