Movement Through the Cell Membrane

Movement Through the Cell
Membrane
1. Review: What are the building blocks of lipids?
2. Sketch a lipid molecule in the space below. Label your sketch!
1. Review: What are the building blocks of lipids? Glycerol and fatty acids
2. Sketch a lipid molecule in the space below. Label your sketch!
1. Review: What are the building blocks of lipids? Glycerol and fatty acids
2. Sketch a lipid molecule in the space below. Label your sketch!
Glycerol
Fatty Acids
3. What is the function of the cell membrane ?
4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer .
5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane.
a. _____________ b. _______________
3. What is the function of the cell membrane ?
Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell
4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer .
5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane.
a. _____________ b. _______________
3. What is the function of the cell membrane ?
Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell
4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer .
Double-layered sheet of lipid molecules; hydrophilic heads point out, hydrophobic tails point in
5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane.
a. _____________ b. _______________
3. What is the function of the cell membrane ?
Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell
4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer .
Double-layered sheet of lipid molecules; hydrophilic heads point out, hydrophobic tails point in
5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane.
a. proteins b. _______________
3. What is the function of the cell membrane ?
Regulate what enters and leaves the cell; protect and support the cell
4. Describe the structure of a lipid bilayer .
Double-layered sheet of lipid molecules; hydrophilic heads point out, hydrophobic tails point in
5. In addition to lipids, list 2 other types of molecules found in the cell membrane.
a. proteins b. carbohydrates http://www.sciencefriday.com/videos/watch/10210
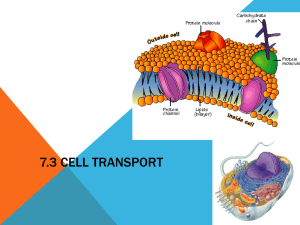
6. Label the diagram of a cell membrane shown below:
Outside of cell
Carbohydrate chains
Proteins
Cell membrane
Inside of cell
(cytoplasm)
Protein channel
Lipid bilayer
7. Define the following terms: a. solution: b. solute: c. solvent: d. concentration:
7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: c. solvent: d. concentration:
7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: substance that is dissolved in a solution c. solvent: d. concentration:
7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: substance that is dissolved in a solution c. solvent: substance in which the solute is dissolved d. concentration:
7. Define the following terms: a. solution: mixture of 2 or more substances in which molecules are evenly distributed b. solute: substance that is dissolved in a solution c. solvent: substance in which the solute is dissolved d. concentration: mass of solute in a given volume of solution
8. During the process of diffusion , molecules tend to move from to until the solution reaches equilibrium .
9. Does diffusion require energy? _______ Explain.
8. During the process of diffusion , molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to until the solution reaches equilibrium .
9. Does diffusion require energy? _______ Explain.
8. During the process of diffusion , molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the solution reaches equilibrium .
9. Does diffusion require energy? _______ Explain.
8. During the process of diffusion , molecules tend to move from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration until the solution reaches equilibrium .
9. Does diffusion require energy? __ NO __ Explain.
Molecules naturally move from HIGH concentration to LOW concentration
Example of Diffusion:
• The smell of popcorn after it ’s been popped.
• Does the smell of popcorn stay where the popcorn was popped?
Why or why not?
10. Why are biological membranes described as selectively permeable ?
11. What is osmosis ?
10. Why are biological membranes described as selectively permeable ? Some substances can pass through the membrane while other substances cannot
11. What is osmosis ?
10. Why are biological membranes described as selectively permeable ? Some substances can pass through the membrane while other substances cannot
11. What is osmosis ? Diffusion of water across a membrane
12. Label the drawing below to show how osmosis works.
water
Cell
Membrane glucose
Figure 7-15 Osmosis
Figure 7-15 Osmosis
13. Define the following terms: a. hypertonic: b. hypotonic: c. isotonic:
14. Cells are almost always __________ to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell.
Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b.
13. Define the following terms: a. hypertonic: Solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell
• Water leaves the cell, animal cells can shrink.
b. hypotonic: lower concentration of solute
• Water enters the cell, animal cells can expand and possibly burst.
• Plant and bacteria cells have their cell walls that provides provide protection from too much osmotic pressure
Isotonic
• The concentration of the solutes is the same inside and outside the cell.
• Water goes in and out at the same rate and pressure doesn ’t change
14. Cells are almost always __________ to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell.
Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b.
14. Cells are almost always
hypertonic
to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water ____ the cell.
Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b.
14. Cells are almost always
hypertonic
to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water
into
the cell.
Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a. b.
14. Cells are almost always
hypertonic
to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water
into
the cell.
Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a.
cell walls keep cell from expanding
b.
14. Cells are almost always
hypertonic
to fresh water, meaning there will be a net movement of water
into
the cell.
Describe two ways that cells keep from bursting in fresh water environments: a.
cell walls keep cell from expanding
b.
contractile vacuole pumps extra water out of cell
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OYoaLzobQmk
15. What is facilitated diffusion ?
16. Label the diagram to show how facilitated diffusion works:
15. What is facilitated diffusion ? Diffusion of molecules across a cell membrane through a special protein channel
16. Label the diagram to show how facilitated diffusion works:
Protein channel
Glucose molecules
High concentration of solute
Low concentration of solute
Cell Membrane http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_facilita ted_diffusion_works.html
17. What is active transport ?
18. Label the diagram to show how active transport works:
17. What is active transport ? Molecules pumped through special protein channels from low concentration to high concentration
18. Label the diagram to show how active transport works:
Cell Membrane
Energy
Cell Membrane
Protein channel
Molecule to be carried
Protein channel
Low concentration
High concentration http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter2/animation__how_the_s odium_potassium_pump_works.html
19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: b. phagocytosis: c. exocytosis:
19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: process of cellular ingestion by which the cell membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell. b. phagocytosis: c. exocytosis:
19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: process of cellular ingestion by which the cell membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell. b. phagocytosis: (another name for endocytosis) c. exocytosis:
19. Define the following terms: a. endocytosis: process of cellular ingestion by which the cell membrane folds inward to bring substances into the cell. b. phagocytosis: (another name for endocytosis) c. exocytosis: removal of material from a cell; membrane surrounding material fuses with cell membrane to force material out
20. Complete the following chart to compare types of movement through a cell membrane:
Diffusion
Types of molecules transported
Special channel required?
Small molecules no
Energy reguired?
no
Osmosis water
Facilitated diffusion ions, sugars
(glucose), salts
Active transport ions (H + , K + ,
Na+, Ca 2+ ) no yes yes no yes no