SBI4U Kreb`s Cycle
advertisement
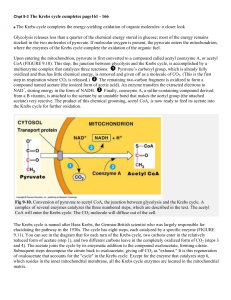
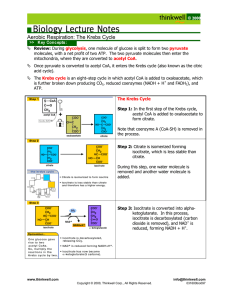
The energy in the pyruvate molecules produced in glycolysis can only be released using oxygen in a process called the Krebs Cycle. • Before pyruvate can enter the Krebs Cycle, it is oxidised in the Link Reaction. • Pyruvate molecules are actively transported into the mitochondrial matrix. The Link Reaction • Carbon dioxide is removed from the pyruvate • Hydrogen atoms are removed and transferred to NAD. • The reactions are carried out by a collection of enzymes known as the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex. • A 2 carbon compound called an acetyl group is formed which is attached to a cofactor called coenzyme A. • The resulting acetyl CoA can enter the Krebs Cycle. Pyruvate (3C) NAD NADH/H+ CO2 Acetyl CoA (2C) Extension – the Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Complex The Krebs Cycle • Acetyl CoA from the Link Reaction is combined with a 4C compound called oxaloacetate, forming 6C citrate. • Citrate undergoes a series of decarboxylation and dehydrogenation reactions which result in the regeneration of oxaloacetate. The Krebs Cycle Krebs Cycle animation Products of the Krebs Cycle • Each turn of the Krebs Cycle produces: 3 molecules of reduced NAD 1 molecule of reduced FAD 1 molecule of ATP 2 molecules of CO2 • The Krebs Cycle turns twice for every glucose molecule broken down, so per glucose molecule the yield is doubled: 6 NAD; 2 FAD; 2ATP and 4 CO2