anaerobic respiration, link reaction and Krebs cycle
advertisement

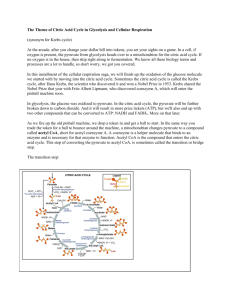
F214 RESPIRATION 3: ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION, THE LINK REACTION AND THE KREBS CYCLE Complete the notes sheets below. Where you see a blank (…………………..), decide which word/phrase is most appropriate. ………………………. (which takes place in the ……………………) produces …… molecules of pyruvate. The fate of the pyruvate depends on …………………… availability. In the absence of oxygen, alcoholic fermentation or lactic fermentation takes place. 2 x PYRUVATE (….C) 1. Alcoholic fermentation: When there is insufficient …………………….., it is important that the reduced NAD (……………) is …………………….. back to NAD+ so that the energy yielding phase of glycolysis can continue. In yeast, pyruvate is decarboxylated to ETHANAL (…..C), releasing …………….. . The enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase then ……………….. ETHANAL to ETHANOL (…..C), at the same time ………………… NADH back to ……………. . CH3CHO + NADH C2H5OH +NAD+ Alcohol dehydrogenase 1|Page The process is summarised below: NADH NAD+ Alcohol dehydrogenase C2H5OH + CO2 What is the net production of ATP per molecule of glucose in anaerobic respiration using alcoholic fermentation? …………… ATP molecules 2. Lactic fermentation: The main aim of lactic fermentation is to ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… Pyruvate is …………………… by NADH to form ………………………… acid. As this is a redox reaction, NADH is ………………………… back to ……………. since an …… atom is donated to the pyruvate. This reaction is catalysed by lactate dehydrogenase. 1 molecule of NADH is ………………….. per pyruvate molecule. 1 molecule of glucose will produce ………… molecules of ATP in using this form of …………………………… respiration. 2|Page The process is summarised below: NADH NAD+ Lactate dehydrogenase C3H6O The link reaction In the presence of oxygen, pyruvate is ………………………. transported across the inner and outer mitochondrial membranes into the …………………… . The purpose of the link reaction is to convert ……C pyruvate into 2C acetate which can be oxidised in the Krebs cycle. DECARBOXYLATION: PYRUVATE DECARBOXYLASE removes a …………………….. group. This eventually becomes ……………………………. which ………………….. into the blood and is carried to the …………………… . DEHYDROGENATION: PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE removes …………………….. atoms. PYRUVATE (…..C) NAD+ NADH CO2 ACETATE (…..C) 3|Page Coenzyme A accepts the …………………., forming ACETYL COENZYME A (Acetyl CoA). The CoA carries the acetate to the next stage in aerobic respiration, the …………………………….. . This stage also takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. Put the symbols below into the correct order to produce an equation which summarises the link reaction: + 2acetylCoA 2CoA 2pyruvate 2NADH 2CO2 2NAD+ + ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………… During the link reaction, ………… molecules of ATP are produced. …………. molecules of …………….. NAD are produced. So far, via glycolysis and the link reaction, the following have been produced: Product ATP Reduced NAD (NADH) Carbon Dioxide Acetyl CoA 4|Page Number of molecules produced per MOLECULE OF GLUCOSE: The Krebs cycle ………………………… enters the Krebs cycle, which takes place in the ……………………… . Acetyl (…..C) is transferred from CoA to join a 4C intermediate called OXALOACETATE. CITRATE (…..C) is produced. Acetyl CoA (…..C) CoA Citrate (…..C) Oxaloacetate (…..C) This is gradually dehydrogenated (……………………………) and decarboxylated (…………………………….) over several steps until the 4C …………………………….. is reformed. ……………………….. and …………………………. are released. ………………… diffuses into the blood while …… atoms are taken up by ……………., or an alternative carrier called FAD. The carriers transport H atoms ………………………………………………………. for the final step in respiration. 5|Page to the Acetyl CoA (…..C) CoA Oxaloacetate (…..C) Citrate (…..C) Intermediate compound (…..C) Intermediate compound (…..C) Intermediate compound (…..C) Intermediate compound (…..C) What 2 processes are occurring at the points marked with a ? ………………………………………….. and …………………………………………….. The process occurring at point , where the first 4C intermediate is changed to another 4C intermediate is called SUBSTRATE LEVEL …………………………………… . At point , the 2nd 4C intermediate is ……………… to a third 4C intermediate, releasing ……….. hydrogen …………. . These are collected by ……………., which is …………………. . At point , the third …..C intermediate is …………………………. (oxidised) to reform …………………………….. . Another NAD+ molecule is ………………………… . 6|Page There is 1 turn of the Krebs cycle for each molecule of acetate. For each turn of the Krebs cycle, …... molecules of reduced NAD, …… molecules of reduced FAD, …… molecules of CO2 and …… molecule(s) of ATP are produced. Per MOLECULE OF GLUCOSE, the following are produced by the Krebs cycle: Product ATP Reduced NAD (NADH) Reduced FAD (FADH) Carbon Dioxide Number of molecules produced per MOLECULE OF GLUCOSE: ***REMEMBER*** these reactions do not use oxygen, but they will not occur without it. They are AEROBIC. So far, via glycolysis, the link reaction and the Krebs cycle, the following have been produced: Product ATP Reduced NAD (NADH) Reduced FAD (FADH) Carbon Dioxide 7|Page Number of molecules produced per MOLECULE OF GLUCOSE: A summary of the processes so far: NEXT TIME! 8|Page