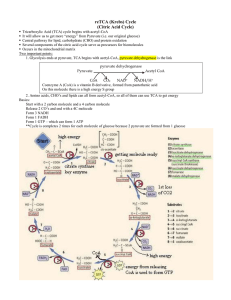
The krebs cycle The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) GROUP 9 THE KREB CYCLE PRESENTATION BY: NELONDO 219073627 NANGOLO 219147132 NASHONGO 220074836 NDARA 220033765 NEHALE 219151679 NEKANDU 219024766 What is a kreb cycle? The kerb cycle is known as a series of chemical reactions that are used by all aerobic organisms to generate energy through the oxidation of acetate. • derived from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins—into carbon dioxide. • The Krebs cycle is the second stage of cellular respiration. The kreb cycle process • The Krebs cycle is aerobic and takes place in the mitochondrial matrix. • It starts by breaking down three-carbon molecules from glycolysis • https://images.app.goo.gl/v8Liyj7BpPsVmc9y7 The process • Each pyruvate loses one carbon and makes a two carbon molecule called acetyl CoA. • The lose carbon joins with the oxygen that we breath in and forms a carbon dioxide. • The Acetyl Co-A then diffuses into the matrix of the mitochondria. • In the matrix, the pyruvate is modified in series of the following steps: The steps of the pyruvate oxidation in the matrix Step 1 A carboxyl group is snipped off of pyruvate and released as a molecule of carbon dioxide, leaving behind a two-carbon molecule. Step 2 The two-carbon molecule from step 1 is oxidized, and the electrons lost in the oxidation are picked up by NAD+ to form NADH. Step 3 The oxidized two-carbon molecule, (an acetyl group highlighted in green)is attached to Coenzyme A( CoA). An organic molecule derived from vitamin B5, to form acetyl CoA. Acetyl is sometimes called a carrier molecule, and its job here is to carry the acetyl group to the citric acid cycle. The steps above are carried out by a large enzyme complex called the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex, which consists of three interconnected enzymes and includes over 60 subunits