Chemical and Physical Changes
advertisement

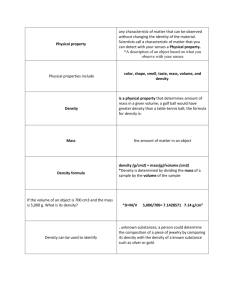
Physical and Chemical Changes Physical Property Observable traits that do not change the identity of the substance Include color, shape, smell, taste, mass, volume and density Also include ductility, malleability, conductivity and solubility Can be determined without changing a substance Physical Property Density - mass/volume Ductility – ability to be pulled into wire Malleability – ability to be hammered Conductivity – ability to pass electric current Solubility – ability to dissolve Physical Change Any change in size, shape, form, or state where the identity of the matter stays the same Ex. - Cutting a watermelon into slices Often easy to reverse with filtration, magnetism, evaporation, distillation, and centrifuge Physical Change Evidence includes: same substance no new substances color change state change same smell, taste, texture different volume, mass same density Chemical Property The characteristic of a substance that allows it to change into something different Includes flammability, reactivity with oxygen, and acidity Testing for chemical properties causes a change in the substance Chemical Property Flammability – able to be burned; combustion Reactivity with oxygen Acidity pH level scale from 1 to 14 1 being most acidic 14 being least acidic (most basic) Water is a 7 (neutral) on the pH scale Chemical Change Happens when a substance undergoes a change that causes it traits to change Ex. - digestion, photosynthesis, paint drying, and oil burning. New materials are formed that are different from the starting materials Chemical Change NOT easily reversed Evidence includes: Release of energy – light, heat, sound Formation of gas or solid that is NOT the results of simple state change Chemical Change Evidence includes: new substance Example of Chemical Change Chlorine Added to swimming pools and drinking water Causes acidity Prevents reproduction, growth and development of algae, bacteria, protists and insects. Types of Chemical Reactions Synthesis Decomposition Acids and Bases Acids Sharp smell, sour taste Corrode metals, harmful to organisms pH between 0 and 7 Ex. - citrus fruits contain acids. Bases Feel slippery, taste bitter May also be harmful to organisms pH of between 7 and 14 Ex. - a bar of soap is basic Salts Salts are compounds of metal and nonmetal Formed when acids and bases react Ex. – table salt and chalk Energy… …is required for both types of changes