File
advertisement

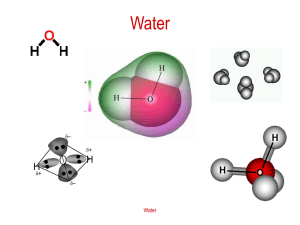
Chemical bonding and strucure 2 Objectives of this lesson: Recall what you have learned in the previous lesson specifically and the current topic in general; Bring new ideas based on what you have learned so far; Understand the forces holding particles (atoms, molecules etc.,); How these forces affect the physical properties such as boiling point and melting point of a substance; To understand the energy requirement to break holding forces (bonds) is not the same; To learn and compare electrostatic attraction between particles. What you think about the following statements? When we boil water, energy is supplied and the energy is used to break the bonds between atoms and hence water boils. The attractive force between solid particles is much higher than liquid particles and the particles in gaseous state do not attract. Ice floats in water due to the air trapped between water molecules in ice structure. Water and ethanol; both are liquids and they both boil at the same temperature. Molecules have polarity when they are formed and cannot be induced. Some questions to answer by the end of the lesson. When we boil water, do the bonds between hydrogen and oxygen break? Do inter molecular attraction exists among non polar substances? Why all liquids do not have equal boiling point? Ice floats in water. Why? Water, Ethanol and Ethanoic acid which one has highest boiling point? Why? Forces holding particles Atoms are attracted within a molecule by intramolecular attractive forces; ionic, covalent. Between molecules there is attractive force which is responsible for different states of matter. All molecules have intermolecular attractive forces and hence all substances (solids, liquids and gases)have boiling and melting points. Including inert gases. The inter molecular attractive forces include: Van der Waals force (London dispersion force) (Induced dipole) Dipole-dipole attraction (permanent or induced) Hydrogen boning Forces holding particles….. Dipole attraction can be between polar molecules-dipoledipole or polar and non-polar molecules-induced dipole-dipole attraction Van der Waals force of attraction is a kind of induced temporary dipole attraction. For Hydrogen bonding, Hydrogen atom should be joined to a highly electronegative atom such as Oxygen, Nitrogen or Fluorine. The lone pair of electrons in oxygen, Nitrogen or Fluorine are used to attract Hydrogen. The strength of inter-molecular attractive forces is represented below: Van der Waals force<Dipole-dipole<Hydrogen bonding London Dispersion Forces (Van der Waals Force) http://my.hrw.com/sh/hw5ny/0030363292/student/ch1 1/sec03/qc10/hw5ny11_03_q10fs.htm Dipole to Dipole Forces http://chemmovies.unl.edu/ChemAnime/DIPOLED/DIP OLED.html Hydrogen Bonding in Water http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/ animations/hydrogenbonds.html Hydrogen bonding in water Hydrogen bonding in HF and CO Hydrogen bonding in ammonia BP 19.0 C BP -33.0C BP 100.0C Lone pair of electrons in oxygen, fluorine or nitrogen is used to attract hydrogen H2O; HF and NH3 which one has highest bp? Explain BP 78.1C BP 118.0C BP 100.0C Which one has higher bp? Explain ICE and hydrogen bonding When temperature goes below 4 degree C in water, there is a strong tendency to form a network of hydrogen bonds, where each hydrogen atom is in a line between two oxygen atoms. This hydrogen bonding tendency gets stronger as the temperature gets lower (because there is less thermal energy to shake the hydrogen bonds out of position). The ice structure is completely hydrogen bonded, and these bonds force the crystalline structure to be very "open“ This makes the molecules kept apart with strong hydrogen bonds. So the volume increases and density decreases. In liquid water, the hydrogen bonds are more flexible and molecules can come closer at times give relatively less volume and higher density. So ice floats in water. How aquatic animals survive when the temperature is very low? Ice is an insulator to heat. Ice prevents heat loss from water below. This helps aquatic animals to stay alive in winter when the temperature is too low. Question time 1. Helium is an inert gas. Why it has melting and boiling points? 2. Which intermolecular force is present in all substances? 3. Propane C3H8 and Hexane C6H14 both are alkanes. Which one has a higher bp? Explain. 4. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest among intermolecular forces. On boiling water, why the bond between oxygen and hydrogen does not break instead of the hydrogen bonds? 5. On cooling, substances will have higher density. But when we change water to ice, density decreases. Explain. 6. Which compound contains hydrogen bonding? COCl2; PH3; H2CO; CH3OH Question time cont…. 7. Which of the following has the strongest attraction between molecules? SiH4; CH2=O; CH3-CH3; O2 8. Write reasons for: (a) Sulphur and Oxygen both are in group 6. Why water is a liquid while SO2 is a gas at room temperature? (b) Ethanol (CH3-CH2-OH) has a higher boiling point than dimethyl ether(CH3-O-CH3) (c) The boiling point of sulphur dioxide is 24 C higher than that of Chlorine gas. Answers………….. 1. Helium is an inert gas. Why it has melting and boiling points? The force of attraction among helium atoms is Van der Waals force (London dispersion). 2. Which intermolecular force is present in all substances? Van der Waals force of attraction. 3. Propane C3H8 and Hexane C6H14 both are alkanes. Which one has a higher bp? Explain. Hexane has higher boiling point. It has larger molecular mass and hence bigger number of electrons to form larger Van der Waals force of attraction. 4. Hydrogen bonding is the strongest among intermolecular forces. On boiling water, why the bond between oxygen and hydrogen does not break instead of the hydrogen bonds? Covalent bond between Hydrogen and Oxygen has much higher bond enthalpy (energy) than Hydrogen bonding between molecules. 5. On cooling, substances will have higher density. But when we change water to ice, density decreases. Explain. When we change water to ice, the Hydrogen bond between water molecules become more rigid (less movement of bond due to low energy) making the ice with larger volume. Larger the volume, smaller the density when the mass is the same. 6. Which compound contains hydrogen bonding? COCl2; PH3; H2CO; CH3OH CH3OH 7. Which of the following has the strongest attraction between molecules? SiH4; CH2=O; CH3-CH3; O2 CH2=O ; because of dipole-dipole attraction together with London force. All others have weak Van der Walls force only. 8. Write reasons for: (a) Sulphur and Oxygen both are in group 6. Why water is a liquid while SO2 is a gas at room temperature? Water has strong Hydrogen bonding together with London force and Dipole attraction. SO2 has no Hydrogen bonding. (b) Ethanol (CH3-CH2-OH) has a higher boiling point than dimethyl ether(CH3-O-CH3) Ethanol has strong Hydrogen bonding which is not in dimethyl ether. (c) The boiling point of sulphur dioxide is 24 C higher than that of Chlorine gas. Chlorine molecules have only Van der Waals force of attraction. Sulphur dioxide has Van der Waals force and diploe-dipole attraction.