Physical Properties of Matter: Viscosity, Density, & More
advertisement

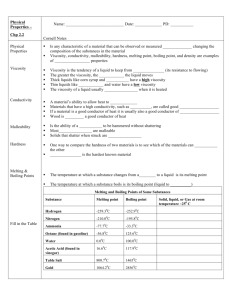
2.2 PHYSICAL PROPERTIES n Vocabulary: n n n n physical property viscosity conductivity n n n malleability melting point boiling point n n n filtration distillation physical change Objectives: n n n n n Describe physical properties of matter. Identify substances based on their physical properties. Describe how properties are used to choose materials. Describe methods used to separate mixtures. Describe evidence that indicates a physical change has taken place. Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 1 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES v physical property - any characteristic of a material that can be observed or measured WITHOUT changing the composition of the substances in the material v examples of physical properties: v viscosity v melting point v density v conductivity v boiling point v hardness v malleability Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 2 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: VISCOSITY v viscosity - tendency of a liquid to keep from flowing (its resistance to flowing) v greater viscosity, slower liquid moves v usually decreases when heated Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 3 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: CONDUCTIVITY Which spoon should you use to stir a pot of soup heating on a stove: a metal spoon or a wooden spoon? Why? Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 4 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: CONDUCTIVITY Answer: The wooden spoon Why? Because wood is not a good conductor of heat. A metal spoon is a good conductor of heat. Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 5 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: CONDUCTIVITY v conductivity - material s ability to allow heat to flow v if a material is a good conductor of heat, it is usually also a good conductor of electricity. Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 6 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: MALLEABILITY v malleability - ability of a solid to be hammered without shattering v most metals are malleable (e.g. gold) Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 7 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: MALLEABILITY v not malleable (instead brittle) - ice, glass Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 8 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: HARDNESS v hardness v one way to compare hardness of 2 materials is to see which can scratch the other v diamonds are hardest known material Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 9 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: MP & BP v melting point - temperature at which a substance changes from solid to liquid v boiling point - temperature at which a substance boils v example: water s melting point is 0°C & its boiling point is 100°C. Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 10 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: MP & BP Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 11 EXAMPLES OF PHYSICAL PROPERTIES: DENSITY v density - ratio of the mass of a substance to its volume Mass (g) Density = Volume (cm3) how heavy a substance is compared to its size v example: v can density of silver is 10.5g/cm3 be used to test the purity of a substance Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 12 USING PHYSICAL PROPERTIES physical properties are used to: v identify a material v choose a material for a specific purpose (look at How it Works: Making a Sculpture on page 49) v separate a substance in a mixture (basis for lab on Thursday) Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 13 USING PHYSICAL PROPERTIES TO SEPARATE A MIXTURE 2 common separation methods are: v filtration - process that separates materials based on the size of their particles Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 14 USING PHYSICAL PROPERTIES TO SEPARATE A MIXTURE 2 common separation methods are: v filtration - process that separates materials based on the size of their particles Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 15 USING PHYSICAL PROPERTIES TO SEPARATE A MIXTURE 2 common separation methods are: v distillation - process that separates substances in a solution based on their boiling points Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 16 SEPARATION OF MIXTURES Methods based on physical properties Filtra$on – based on size Dis$lla$on – based on boiling point Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 17 RECOGNIZING PHYSICAL PROPERTIES v physical change - change that occurs when some of the properties of a material change, but the substances in the material remain the same. v some physical changes can be reversed while others cannot v e.g. water changing states, melting butter, cutting food, cutting hair Chapter 2 Properties of Matter 18