Lesson 31&32
advertisement

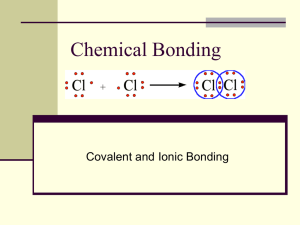
CHEMICAL BONDS Aims: to learn basic vocabulary used when talking about chemical bonding TABLE SALT SILVER ATOMS A WATER MOLECULE OXYGEN MOLECULES A SODIUM ATOM TRANSFERS AN ELECTRON TO A CHLORINE ATOM TO CREATE TABLE SALT Chemical bonding What kinds of chemical bonds are there? Covalent Ionic Metallic TYPES OF CHEMICAL BONDING KEY WORDS: bond = veza attractive forces = privlacne sile interact = medjusobno delovati valence electron = valentni elektron electron shell = elektronska ljuska, omotac positively charged = pozitivno naelektrisan negatively charged = negativno naelektrisan oppositely charged = suprotno naelektrisan particle = cestica repel = odbijati attract = privlaciti share = deliti properties = karakteristike, osobine crystalline = kristalni dissolve = rastvoriti solution = rastvor acid = kiselina row = red outermost = spoljni core = jezgro diverse = razlicit READ THE TEXT AND FIND THE WORDS WHICH HAVE THE SAME/OPPOSITE MEANING AS THE FOLLOWING WORDS. bond, link, connection = t_______ are located in = r_____ remember = r________ attract ↔ r________ happen = o________ get = g________ characteristics = p__________ think about = c______ stinking, unpleasant = f_________ happen = t____ p____ spring up, jump up = b________ different = d_________ READ THE TEXT AND FIND THE WORDS WHICH HAVE THE SAME/OPPOSITE MEANING AS THE FOLLOWING WORDS. bond, link, connection = tie are located in = reside remember = recall attract ↔ repel happen = occur get = gain characteristics = properties think about = consider stinking, unpleasant = foul Happen = take place spring up, jump up = bounce different = diverse COVALENT BONDS Explain what a covalent bond is. What is a covalent bond compared to? What is the shared electron compared to? Which molecules were mentioned as examples of: a) a single covalent bond b) a double covalent bond c) a triple covalent bond How can you predict if the bonds are covalent or not? READ THE TEXT AND FIND THE WORDS WHICH HAVE THE SAME MEANING AS THE FOLLOWING WORDS. breathe out = e______ separate, distinct = d_______ give = d_________ part = p________ element = c_________ guess = p_________ join together = s_______ t______ READ THE TEXT AND FIND THE WORDS WHICH HAVE THE SAME/OPPOSITE MEANING AS THE FOLLOWING WORDS. breathe out = exhale separate, distinct = discrete give = donate part = portion element = component guess = predict join = stick together IONIC BONDS KEY WORDS get over = preboleti, pomiriti se sa necim saltshaker = slanik strip = skinuti, uzeti charge = naelektrisanje Opposites attract. = Suprotnosti se privlace. lose = izgubiti loss = gubitak unlike = za razliku od exist = postojati solid = cvrsta supstanca READ THE TEXT CAREFULLY AND ANSWER THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS. Which example of ionic bond is given in the text? What holds two oppositely charged atoms together? What’s the difference between sodium chloride and barium chloride? What kinds of elements usually form ionic bonds? What other examples of ionic bonds are mentioned? POLAR COVALENT BONDS KEY WORDS playground = igraliste preschoolers = predskolac on average = u proseku determine = odrediti measure = meriti draw = vući corresponding = koji odgovara value = vrednost devise = smisliti, napraviti increase = povecati se toddler = dete koje tek uci da hoda tug = vući CHOOSE THE WORD WHICH BEST COMPLETES THE SENTENCE. 1. This means that sometimes in a covalent bond the electrons are not _____equally between the two atoms. a) sharing b) shared c) share 2. Electronegativity is a _______ of an atom's ability to draw its bonding electrons to itself. a) measure b) determine c) calculate 3. Electronegativity ________ from left to right going across a period. a) decreases b) bigger c) increases PROGRESS TEST QUESTIONS A 1. Atoms are the building blocks of all substances. But what is it that keeps atoms connected together? They are held together by _____________ (CHEMISTRY) BONDS, strong ______________ (attract) forces between atoms. 2. An IONIC BOND occurs when one atom gains a valence electron from a ______________ (difference) atom, forming a negative ion (ANION) and a positive ion (CATION), respectively. B 1. A molecule that has oppositely charged ends is called a P _ _ _ _ MOLECULE. 2. In the formula H2O, the number 2 is a S _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _. A 1. 2. Atoms are the building blocks of all substances. But what is it that keeps atoms connected together? They are held together by CHEMICAL BONDS, strong attractive forces between atoms. An IONIC BOND occurs when one atom gains a valence electron from a different atom, forming a negative ion (ANION) and a positive ion (CATION), respectively. B 1. A molecule that has oppositely charged ends is called a POLAR MOLECULE. 2. In the formula H2O, the number 2 is a SUBSCRIPT. COMPONENT EXIST FORM SHARE MADE UP Oxygen does not _________ as a single oxygen atom, but as a molecule of two oxygen atoms. These two oxygen atoms _________ two pairs of valence electrons (four valence electrons total) between them, forming a DOUBLE COVALENT BOND. This is true of any double covalent bond; four valence electrons are shared between two atoms. Another _________ of air is nitrogen. Like oxygen, nitrogen does not exist as a single nitrogen atom, but as a molecule ___________of two nitrogen atoms. The two nitrogen atoms in a molecule of nitrogen share three pairs of valence electrons (six valence electrons total) to _________a TRIPLE COVALENT BOND. Oxygen does not exist as a single oxygen atom, but as a molecule of two oxygen atoms. These two oxygen atoms share two pairs of valence electrons (four valence electrons total) between them, forming a DOUBLE COVALENT BOND. This is true of any double covalent bond; four valence electrons are shared between two atoms. Another component of air is nitrogen. Like oxygen, nitrogen does not exist as a single nitrogen atom, but as a molecule made up of two nitrogen atoms. The two nitrogen atoms in a molecule of nitrogen share three pairs of valence electrons (six valence electrons total) to form a TRIPLE COVALENT BOND.