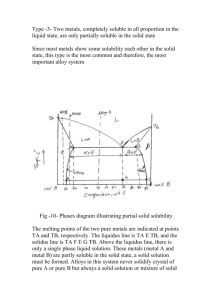
09 PHASE DIAGRAM 1 2 3
advertisement
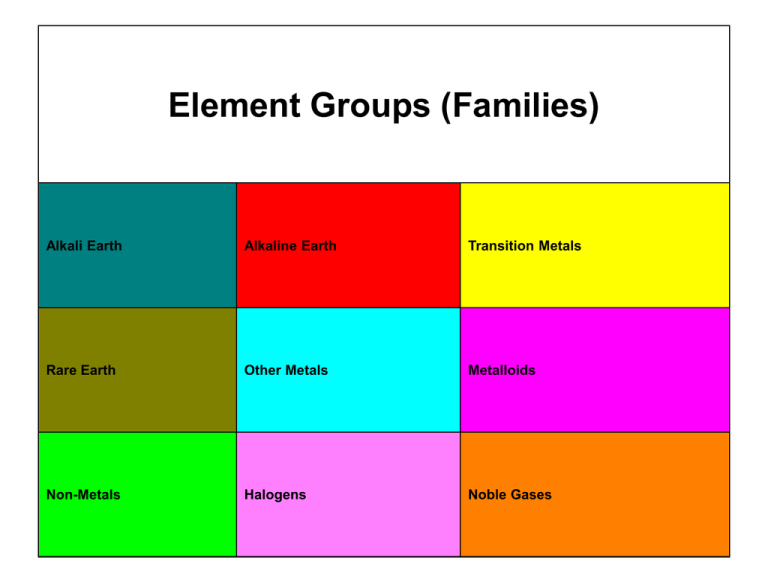
Element Groups (Families) Alkali Earth Alkaline Earth Transition Metals Rare Earth Other Metals Metalloids Non-Metals Halogens Noble Gases 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 H He 252.87 -268.6 Li Be B C N O F Ne 1347 2970 2550 4827 -195.8 -183 188.14 -246.1 Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar 552.9 1107 2467 2355 280 444.6 -34.6 -186 K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 774 1484 2832 3287 3380 2672 1962 2750 2870 2732 2567 907 2403 2830 613 684.9 58.78 -153.4 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe 688 1384 3337 4377 4927 4612 4877 3900 3727 2927 2212 765 2000 2270 1750 989.8 184 -108.1 Cs Ba * Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn 678.4 1140 5400 5425 5660 5627 5027 4527 3827 2807 356.58 1457 1740 1560 962 337 -61.8 Fr Ra Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt Uu n Uu u Uu b 677 1737 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 3469 3257 3127 3127 ? 1900 1597 3233 3041 2562 2720 2510 1727 1466 3315 Ac Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr 3200 4790 ? 3818 3902 3235 2607 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ** 7 * ** PHASE DIAGRAMS • STUDY OF PHASE RELATIONSHIPS IMPORTANT IN KNOWING PROPERTIES OF MATERIALS • MAP OF TEMPERATURE, PRESSURE AND COMPOSITION BETWEEN PHASES IN EQUILIBRIUM IN A SYSTEM GIBBS PHASE RULE P+F=C+2 Eg: states of matter- gas, liquid and solid – single phase Liquid mixture- oil and water- 2 phases In solid , several phases depending on crystal structure • STUDY IMPORTANT IN ALLOYS • ALLOY- SUBSTANCE COMPOSED OF 2 OR MORE CHEMICAL ELEMENTS • MAIN CONSTITUENT- BASE METAL AND OTHERS ALLOYING ELEMENTS FUSION LINE ALMOST VERTICALVARIATION IN PRESSURE –NO EFFECT ON M.P. OF ICE Phase Rule FUSION P r e s s u r e WATER ICE 76cm B 30 cm WATER VAPOUR T A 0 Temperature o C 100 50 • • • • • • • • • • At ‘A’ , water vapour - 1 phase At ‘B’ , water and water vapour co exist -2 phases At ‘T’ , ice, water and water vapour exist – 3 phases At ‘A’ 1 + F = chemical compound H2O + 2 F = 2 …. BIVARIANT At ‘B’ 2+ F = 1 +2, F = 1… UNIVARIANT At ‘T’ All three phases P = 3, 3 + F = 1 + 2; F = 0 INVARIANT Equilibrium Diagram Case 1: Binary Alloy with COMPLETE SOLUBILITY IN BOTH LIQUID AND SOLID PHASES in all compositions Eg: Ag-Au Cu-Ni Ge-Si Al2O3-Cr2O3 Sb-Bi Silver-Palladium Co-Ni Cu-Pt Fe-Pt Ni-Pt Ta-Ti HUME ROTHERY’S RULE- FICK’S LAWS OF DIFFUSION FIRST LAW SECOND LAW Cooling Curves & Phase Diagram Elements A and B in a Binary Alloy Phase (Equilibrium) Diagram Temperature, T (ºC) Liquid Liquidus curve L+α T1 Solidus curve 0 20 40 60 Composition, C (% wt of B) 80 100 LEVER RULE • With Fulcrum at P, weights WA and WB at the end of a lever, for equilibrium, the lever rule states: WA / WB = b/a WA WB P a b Liquid P1 P X Y Liquid + Solid 16 37 47.5 Solid 58 For P: SS/LS = (37-16)/(58-37)= 1/1 For P1: SS/LS = 31.5/ 10.5= 3/1 Liquid P1 P X Y Liquid + Solid Solid 31.5/ 10.5= 3 16 37 47.5 58 = (37-16)/(58-37) 1453 1083 The structures shown are at NON EQUILIBRIUM CONDITIONS There are Three variables, one of these can be chosen as independent If fl and fs are the liquid and solid fractions, Case 2: Binary Alloy with COMPLETE SOLUBILITY IN LIQUID STATE in all compositions, but COMPLETELY INSOLUBLE IN THE SOLID • • • • STATE A very doubtful situation in practice, since most solid metals appear to dissolve small quantities of other metals In Bismuth-Cadmium, mutal solid solubility is negligible. Bi- heavy, brittle- positioned near to non metals in periodic table- Rhombic type structure-covalent bond Cadmium- HCP- Bismuth- Cadmium Equilibrium Diagram Te 40Cd/60Bi When two metals show complete solubility in liquid state, and complete insolubility in the solid state,they do so by crystallising out as alternate layers of the two pure metals. This laminated structure termed as EUTECTIC INVARIANT REACTION Te (EUTECTIC Temperature) 40Cd/60Bi When two metals show complete solubility in liquid state, and complete insolubility in the solid state, they do so by crystallising out as alternate layers of the two pure metals. This laminated structure termed as EUTECTIC A: Molten homogeneous alloy – 1 phase with 2 components, Bi and Cd 1+F = 2 +1 (only temperature is the variable, not pressure) , F=2 •B: 2 + F = 2 + 1, F= 1 •C: 3 + F = 2 + 1, F=0 At E, solid Cadmium (40%) and solid Bismuth(60%) co-exist EUTECTIC Eutectic is considered as an intimate mixture of two metals Phase Rule applied, P+F = C+ 1 3 + F = 2 +1, F = 0 Cooling curve for Eutectic (similar to pure metal) Temperature o C Time For compositions to left /right of Eutectic HUME ROTHERY’S RULE Gold- Silver, Copper- Nickel, Germanium- Silicon, Antimony- Bismuth, Aluminium Oxide- Chromium Oxide etc. are examples FICK’S LAWS OF DIFFUSION Mass Flow Process by which atoms (molecules) change their positions relative to their neighbours in a given phase under the influence of thermal energy and gradient : FICK’S LAWS OF DIFFUSION FIRST LAW dn/dt = no. of moles of B atoms crossing per unit time D= Diffusion coefficient A= Planar area dc/dx= concentration gradient If J = flux flow / unit area per unit time, SECOND LAW If D is independent of concentration, INVARIANT REACTIONS Case 3: Two metals completely soluble in all proportions in liquid state, but partially soluble in solid state • • • • • • • Melting Point of Lead:3270C Melting Point of Tin: 2320C Eutectic Temperature: 1830C Eutectic Composition: 62% Sn, 38%Pb Max. solid solubility tin in lead at 1830C: 19.5% tin Max. Solid solubility of lead in tin at 1830C: 2.6% lead Eutectic of two solid solutions α and β (instead of two metals) form Melting Point of Tin (Pb) : 2320C Melting Point of Lead (Sn) :3270C Eutectic Temperature: 1830C Eutectic Composition: 38%Pb, 62% Sn Max. solid solubility tin in lead at 1830C: 19.5% tin Max. Solid solubility of lead in tin at 1830C: 2.6% lead Liquid solubility of salt in water & partial solid solubility of one metal in another( (similarity schematically represented)