Brenda Trujillo`s TALA powerpoint presentation
advertisement
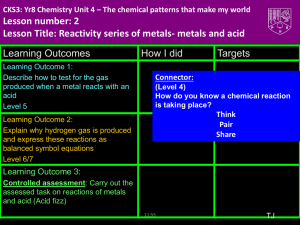
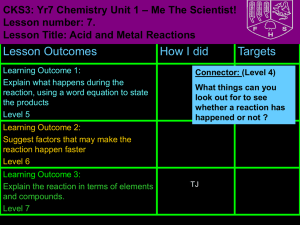
Unit: Chemical Reactions Types of Chemical Reactions: Single Replacement After today you will be able to… • Identify a single replacement reaction • Predict the products in words for single replacement reactions Predicting Products 3. Single Replacement: An element and compound react to form a different element and compound Common form: Element + Compound Element +Compound A + BC AC + B Predicting Products • These reactions do not always occur. • You must use the “activity series” sheet • “Like will replace like” – metals always replace metals, etc. Examples of single replacements: Activity Series of Metals (and Hydrogen) Listed in order of decreasing activity. lithium (1) A metal in a compound is replacedpotassium by a more barium strontium active metal calcium ? Must use the activity series! sodium cesium beryllium magnesium aluminum zinc chromium gallium iron cobalt nickel tin lead hydrogen copper mercury silver lithium + zinc acetate zinc + lithium acetate (Metal) (Metal) Lithium is more reactive than zinc. Examples of single replacements: Activity Series of Metals (and Hydrogen) Listed in order of decreasing activity. ? lithium potassium barium strontium calcium sodium cesium beryllium magnesium aluminum zinc chromium gallium iron cobalt nickel tin lead hydrogen copper mercury silver copper + aluminum sulfate NO REACTION (Metal) (Metal) Copper is lower on activity series and therefore is less reactive than aluminum. Examples of single replacements: Activity Series of Metals (and Hydrogen) Listed in order of decreasing activity. ? lithium potassium barium strontium calcium sodium cesium beryllium magnesium aluminum zinc chromium gallium iron cobalt nickel tin lead hydrogen copper mercury silver + lead lead (II) carbonate + barium barium carbonate (Metal) (Metal) No Roman Numeral necessary! Activity Series of Metals (and Hydrogen) Examples of single replacements: Listed in order of decreasing activity. lithium potassium barium strontium calcium sodium cesium beryllium magnesium aluminum zinc chromium gallium iron cobalt nickel tin lead hydrogen copper mercury silver (2) Hydrogen in water is replaced by a more active metal hydrogen hydroxide sodium + water sodium hydroxide + hydrogen Tip: Change water into “hydrogen hydroxide.” Activity Series of Metals (and Hydrogen) Examples of single replacements: Listed in order of decreasing activity. lithium potassium barium strontium calcium sodium cesium beryllium magnesium aluminum zinc chromium gallium iron cobalt nickel tin lead hydrogen copper mercury silver (3) Hydrogen in acid is replaced by a more active metal hydrogen phosphate calcium + hydrogen calcium + phosphoric acid phosphate Tip: Change acid names into their ionic name. Examples of single replacements: (4) A non-metal in a compound is replaced by a more active non- metal Activity Series of Non-Metals Listed in order of decreasing activity. magnesium + iodine fluorine fluorine + magnesium iodide fluoride chlorine (Non-metal) (Non-metal) bromine iodine Tip: Watch your endings! Make sure nonmetals replace non-metals!