File
advertisement
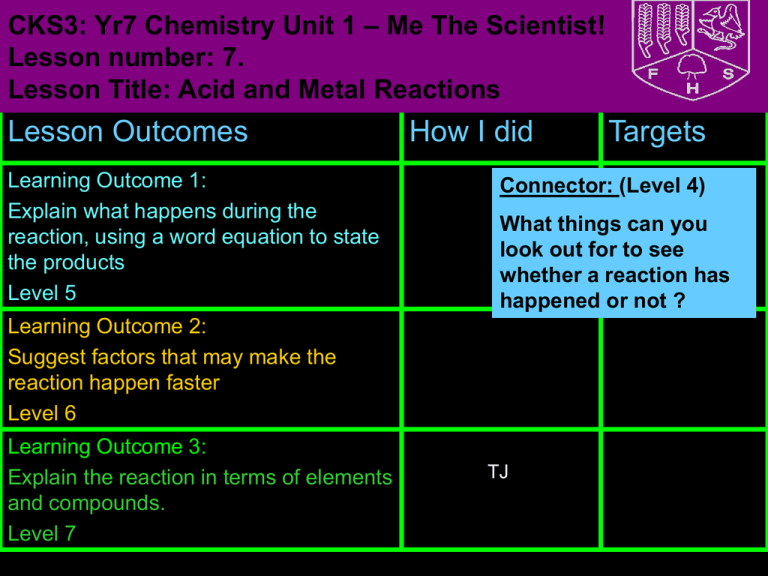
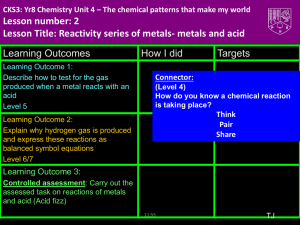
CKS3: Yr7 Chemistry Unit 1 – Me The Scientist! Lesson number: 7. Lesson Title: Acid and Metal Reactions Lesson Outcomes Learning Outcome 1: Explain what happens during the reaction, using a word equation to state the products Level 5 How I did Connector: (Level 4) What things can you look out for to see whether a reaction has happened or not ? Learning Outcome 2: Suggest factors that may make the reaction happen faster Level 6 Learning Outcome 3: Explain the reaction in terms of elements and compounds. Level 7 Targets TJ BIG picture Key Question: What is the difference between an element and a compound? • What skills will you be developing this lesson? • HSW- by planning and carrying out an investigation/ Interpreting data/ evaluating an experiment •How is this lesson relevant to every day life? Chemicals and reactions used to work machines for example, for fireworks • Literacy- by writing explanations using correctly spelt keywords and good grammar. Where does this lesson fit in to the rest of the topic? Lesson 2 • Team work- during a practical investigation •Quick Discussion: •What do you already know? • Participation- during a practical activity • Reflection- through self and peer Keywords: Create sentences using the keywords to show that you know what they mean. Put your hand up if there is any key word from the list that you don’t understand. • • • • • • • Element Compound Chemical Reaction Hydrogen Concentration Surface Area Temperature •Odour •Acid • Density • Splint • Air Odour • Pop • Density • Lighted • Air • Salt • Metal New Information for Learning Outcome 1 • Visual: Demonstration • Audio: Demonstration • Kinaesthetic: Class experiment New Information for Learning Outcome 1 (i) Ice cube melting (iii) Boiling water to make steam What happens when a physical change occurs? When a physical change happens, no new substance is made. A physical change can be easily reversed (undone). New Information for Learning Outcome 1 (i) Boiling an egg (ii) Burning a match What happens when a chemical change occurs? When a chemical change happens, a new substance is made. A chemical change cannot be easily reversed (undone). Adding acid to alkali Fireworks Ice cream melting x Driving a car Boiling the kettle x frying an egg Discuss in pairs which of The changes that are not these arex chemical reactions x chemical changes are called Lighting a matchphysical changes Burning a candle Printing x Melting candle wax Dissolving sugar in tea Making ice cubes Ironing clothes x x Baking a cake Launching a space rocket Outcome 1 • A chemical reaction is when one or more NEW chemical substances are formed from the starting material The starting substances used in a reaction are reactants. The new substances formed in a reaction are products. New Information for Learning Outcome 1 • Observations that can help you see if a chemical reaction has taken place are: 1. 2. 3. 4. Colour change Gas coming off (you see fizzing or bubbling in a liquid) A change in temperature A solid may be formed when two liquids mixed 5. 6. Some also make noise (fireworks) Some even make electricity (in batteries) Learning Activities for Outcome 1 • Your task is going to be to carry out a particular chemical reaction. The reaction between an acid and a metal. • You will also carry out a test for the reaction to show that it has taken place. Learning Activities for Outcome 1 What do you need to do to be safe when conducting this experiment? Learning Activites for Outcome 1 To investigate which metal is the most reactive metal Write the independent variable, dependent variable and the control variable Metal Bubbles Colour Temperature change of acid Temperature Rise in of acid after temperature before adding metal (C) adding metal (C) (C) Zinc (Zn) Iron (Fe) Copper (Cu) Magnesium (Mg) Extension: Write a conclusion for your observations Draw the picture of the chemical reaction in each test tube. Do all metals react with acids in the same way? sodium magnesium iron lead copper iron magnesium lead copper - -the the metal no metal -metal bubbles, the reacts reacts metal slowly, no very reacts reaction slowly, producing quickly with producing acid a few thestrong very bubbles acid,few producing bubbleslots of sodium --the bursts into flames, awith very reaction bubbles Learning Activities for Outcome 1 • You will be testing 4 metals • You will be looking to see if bubbles are produced, if there is a change in colour and a change in temperature • Draw a table that you would use to collect your results Keywords: Demonstrate your Learning for Outcome 1 I am working at level .... because ........... Create (L8) Evaluate (L7) Judge Justify Defend Decide Agree Value Prove Check Criticise Recommend Support Test Create Evaluate Combine construct Develop Imagine Design Change Improve Discuss Create Invent Suppose Put together Make up Synthesise Analyse (L6) Apply (L5) Use Build Execute Develop Construct Identify Plan Select Solve Organise Apply Model Analyse Apply Remember (L3) Understand Who What When Where Why Which How Match Define List Choose Name Spell Tell Describe Remember 07:38 Take apart Compare Classify Examine List Distinguish Simplify Theme Conclude Motive Discover Understand (L4) Explain what when where how Rephrase Demonstrate Summarise Contrast Show Predict Compare Clarify Illustrate Categorise Learning Outcome 1: Review Go back to your Learning Outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Learning Outcome Explain what happens during the reaction, using a word equation to state the products Level 5 How I did Met? Partly met? Not met? Targets How can I improve on Learning Outcome 1? New Information for Learning Outcome 2 • When a metal reacts with an acid, the products are a salt and hydrogen: metal acid salt hydrogen • Hydrogen is colourless, odourless gas • Hydrogen is less dense than air • Hydrogen forms an explosive mixture with air Learning Activites for Outcome 2 Place a burning splint next to the mouth of test tube. A ‘squeaky pop’ as the gas ignites shows that hydrogen is the gas produced in this reaction. hydrogen burning splint magnesium + acid Learning Activites for Outcome 2 Using the keywords opposite to explain the properties of hydrogen Keywords for Task 2: • Odour • Density • Air • Salt Explain how you would test for hydrogen gas • Metal • Acid • Splint • Pop • Lighted Learning Activites for Outcome 2 • If an acid is added to a (fairly reactive) metal what will happen to the metal? • How can we tell a reaction is happening? • Are all metals reactive? Can you give an example of an unreactive metal? Keywords: Demonstrate your Learning for Outcome 2 I am working at level .... because ........... Create (L8) Evaluate (L7) Judge Justify Defend Decide Agree Value Prove Check Criticise Recommend Support Test Create Evaluate Combine construct Develop Imagine Design Change Improve Discuss Create Invent Suppose Put together Make up Synthesise Analyse (L6) Apply (L5) Use Build Execute Develop Construct Identify Plan Select Solve Organise Apply Model Analyse Apply Remember (L3) Understand Who What When Where Why Which How Match Define List Choose Name Spell Tell Describe Remember 07:38 Take apart Compare Classify Examine List Distinguish Simplify Theme Conclude Motive Discover Understand (L4) Explain what when where how Rephrase Demonstrate Summarise Contrast Show Predict Compare Clarify Illustrate Categorise Learning Outcome 2: Review Go back to your Learning Outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Lesson Outcomes Lesson Outcome 2 Suggest factors that may make the reaction happen faster Level 6 How I did Met? Partly met? Not met? Targets How can I improve on task 2? New Information for Learning Outcome 3a • What is the difference between elements and compounds? If a solid, liquid or gas is made up of only one type of atom we say it is an element. For example, consider a tripod made up of iron: These atoms are ALL iron – there’s nothing else in here New Information for Learning Outcome 3a Compounds are different to elements. They contain different atoms. Here are some examples: Glucose Sodium chloride (salt) Methane Learning Activites for Outcome 3a In this chemical reaction, which substances are the reactants and which substances are products? magnesium copper oxide magnesium oxide copper Substance Reactant or Product? magnesium oxide magnesium copper oxide product reactant copper reactant product Outcome 3a METAL + ACID e.g. Sodium + hydrochloric acid SALT + HYDROGEN Sodium chloride + hydrogen Copy and complete the following reactions: 1) Iron + hydrochloric acid Iron chloride + hydrogen 2) Zinc + hydrochloric acid Zinc chloride + hydrogen 3) Copper + hydrochloric acid No reaction 4) Magnesium + hydrochloric acid magnesium chloride + hydrogen Extension: Write a word equation for the following metals with hydrochloric acid: Lead, aluminium, tin and Outcome 3b • Anything that increases the chance of effective collision increases the rate (speed) of reaction. Factors include: • Increased surface Area • Increased concentration • Increased temperature Outcome 3b • Task 3: • Using the keywords on the right to help you, write in your own words what changes could have been done to the reaction to make it go faster Keywords for Task 3: • particles • space • liquid • solid • diffuse • Use diagrams to help you • collision • energy Keywords: Demonstrate your Learning for Outcome 3 I am working at level .... because ........... Create (L8) Evaluate (L7) Judge Justify Defend Decide Agree Value Prove Check Criticise Recommend Support Test Create Evaluate Combine construct Develop Imagine Design Change Improve Discuss Create Invent Suppose Put together Make up Synthesise Analyse (L6) Apply (L5) Use Build Execute Develop Construct Identify Plan Select Solve Organise Apply Model Analyse Apply Remember (L3) Understand Who What When Where Why Which How Match Define List Choose Name Spell Tell Describe Remember 07:38 Take apart Compare Classify Examine List Distinguish Simplify Theme Conclude Motive Discover Understand (L4) Explain what when where how Rephrase Demonstrate Summarise Contrast Show Predict Compare Clarify Illustrate Categorise Task 3: Review Go back to your lesson outcome grid and fill out the ‘How I did’ and the ‘Targets’ column. Lesson Outcomes Lesson Outcome 3: Explain the reaction in terms of elements and compounds. Level 7 How I did Met? Partly met? Not met? Targets How can I improve on task 3? Review of lesson Review for Remembering • Stand up if you have met the lesson outcomes? • If not what do you need to do next in order to meet the outcome? Record this in your diary as part of your homework. • Is there any part of the lesson you think you need to go over again next lesson? • Tell the person next to you three things you have learnt this lesson. • How will you remember this for your exam? If time at the end...King Kongs Hand! EYe protection must be worn. Work over a sink - this is messy! 1 Work in pairs. You can draw ‘hairs’ on the glove to make it look like the hairy and of King Kong. 2 Use the balance to weigh out 10 g of sodium bicarbonate. One person should hold open the glove. The other person can then pour the sodium bicarbonate into the thumb section of the glove. 3 Measure out 50 cm3 of colourless vinegar using the measuring cylinder. 4 One person now holds open the glove, containing the sodium bicarbonate. Then the other person pours the vinegar via the funnel into the three fingers of the glove furthest from the thumb. 5Then one of you must VERY CAREFULLY pull together the top of the glove and hold it firmly to make an airtight seal, making sure the vinegar and sodium bicarbonate do not mix until you are ready. 6 Shake the glove so that the sodium bicarbonate and vinegar mix. Hold it for several minutes. 7 Watch what happens! Extended Learning Extended Learning task: Write a conclusion for your observations Draw the picture of the chemical reaction in each test tube of the experiment we will be conducting • Due date: next lesson • Criteria for Level 5: Write a conlusion of what happened. • Criteria for level 6: Finish a detailed conclusion and include diagrams • Criteria for level 7: Finish a detailed conclusion, include diagrams and include a detailed report of how the experiement was conducted Science Department Lesson plan Teacher information Technicians list: A variety of metals Zinc, Iron, Copper, Magnsium HCL Test tubes Splint Provision: 1) EAL: 2) SEN: Role of TA: 1) 2) 3)