The Periodic Table
advertisement

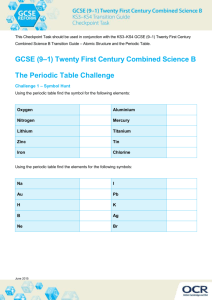
The Periodic Table Elements in the Periodic Table Groups Periods Introduction to Terminologies Groups Periods Periodic table: It is the tabular display of chemical elements. Group: A group or a family is a vertical column in the periodic table Period : The horizontal row in a periodic table is called a period. Details in the Periodic Table • Atomic Number = number of electrons = number of protons • Atomic Mass = number of (protons + neutrons) Groups • 18 groups in standard periodic table, numbered from 1 to 18, as per IUPAC standards. • Elements in a group have similar configurations of the outermost shells, leading to similar properties. Group Names • • • • • • • • • Group 1: Alkali metals Group 2: Alkaline earth metals Group 3-11 : Transition Metals Group 11: Coinage metals/Copper Family Group 12-14: Metalloids & nonmetals Group 15: Pnictogens /Nitrogen Family Group 16: Chalcogens /Oxygen Family Group 17: Halogens /Halide Family Group 18: Noble gases Periods • There are 7 periods in the table. • Elements of the same period have the same number of electron shells. • Within each group across a period, the number of electrons and protons increases, leading to increase in atomic number. • Elements within the same period do not generally show similarity in properties, except d-block and f-block (lanthanides) elements. Trends in the Periodic Table • Trends occur due to the electronic configurations of elements. • Across a period, electrons of the outermost shell, experience increased nuclear attraction due to increase in atomic number. • Down a group, nuclear attraction decreases due to “shielding effect”. Periodic Trends - Summary Classification of Elements in Periodic Table Classification depends on the difference in physical and chemical properties of elements: • Metals (yellow ) • Nonmetals (green) • Metalloids (purple) Properties of Metals • Shiny solids at room temperature, except mercury. • Good conductor of both heat and electricity. • High melting point and density. • Shiny and lustrous. • Ductile and malleable. • Metals can be alloyed. Properties of Nonmetals • • • • • Insulators of heat and electricity. Dull surface. Low density, compared to metals. Low melting temperatures. Brittle solids Element of the UP – Copper..!!! • Symbol – Cu, from the Latin word cuprum • Atomic number – 29 • Classification – Transition Metal • Appearance – Reddish, with a bright metallic luster • Position in the Periodic table: Group 11 and Period 4. • Melting Point: 1356 K (1981 oF) Alloys of Copper • • • • • • Brass – Cu and Zn Red Brass/Gunmetal – Cu, Zn and Sn Phosphor Bronze/Bronze – Cu and Sn Aluminum Bronze – Cu and Al Silicon Bronze – Cu and Si Monel – Ni and Cu Applications of Cu • • • • • • • Piping Electrical applications Architecture Household products Coinage Chemical applications Miscellaneous Cu – The Miracle Element • http://www.ebaumsworld.com/video/watch/ 80906854/