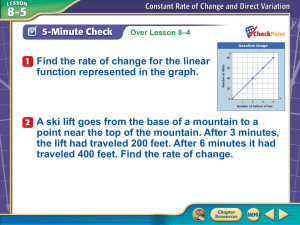
Fick`s Law: Tutorial

Fick’s Law: Tutorial
By Elizabeth Kelley Buzbee AAS, RRT-NPS, RCP
Kingwood College Respiratory Care Department
The rate of diffusion of a gas into a liquid is:
– Directly proportional to:
• the partial pressures of the gas above the liquid
• surface area of available for gas exchange
• solubility co-efficient of the gas
– Inversely proportional to:
• Gram molecular weight of the molecules
• Thickness of the membrane
Directly proportional to: the partial pressures of the gas above the liquid
Molecules diffuse from high to low concentration
Obviously, there are more molecules of blue squares than there are of green circles, so the partial pressure of the blue squares is pushing more molecules into the liquid
• The partial pressure of the 02 in an alveoli is 100 mmHg.
• The partial pressure of the 02 in the capillary is 40 mmHg
• The gradient between alveoli and capillary is 100-40 or 60 mmHg
• The 02 in the alveoli will move into the capillary until the partial pressures equilibrate in both compartments
• The partial pressure of the C02 in an alveoli is 40 mmHg.
• The partial pressure of the C02 in the capillary is 46 mmHg
• The gradient between alveoli and capillary is 46-40 or 6 mmHg
• The C02 in the capillary will move into the alveoli until the partial pressures equilibrate in both compartments
Directly proportional to: the partial pressures of the gas above the liquid
02
C02
PA02 : 100 mmHg
PAC02 : 40 mmHg
P cap 02 : 46 mmHg
P cap 02 : 40 mmHg
Directly proportional to: surface area of available for gas exchange
• Imagine you have a filter over your air conditioner intake
• If you cut a bigger hole into the wall and exchange your filter for a larger one, more air can move through the filter to
Directly proportional to: surface area of available for gas exchange
• The surface area of the average adult human lung is equal to surface area of a tennis court
• The surface area of the gills of a shark are so much smaller than the shark must swim all the time to breath or can catch so ZZZ by sleeping in a rapid current of water.
Directly proportional to: solubility co-efficient of the gas
• HENRY’S LAW states that a volume of gas will dissolve into a liquid is equal to its solubility co-efficient x its partial pressure
– Different gases have different physical properties.
– Some gases dissolve easily into liquids, while others don’t.
– A solubility co-efficient is a score based on the measurement of how much a given gas volume can dissolve in 1 ml of a given liquid at a given temperature and standard pressure
The solubility co-efficient of 02 is: .023 ml / 1 ml blood plasma
The solubility co-efficient of C02 is: 0.510 ml/ml blood plasma
.023: .510 as 1: 22 or C02 dissolves 22 x better than 02 does
Inversely proportional to:
GMW
• GRAHAM’S LAW : states that the ability of a gas to diffuse is inversely proportional to it’s Gram molecule weight
– 02 has only 2 0xygen molecules, while C02 has a carbon as well as the 2 oxygen molecules.
– 02 can move faster through a membrane than C02 can because it has less mass.
Inversely proportional to: thickness of the membrane
• Imagine you have a curtain across your window that is made of lace and on the other window you have a curtain made of velvet.
• Which of the two curtains will allow the wind to blow into the room?
• Naturally the thin lacy curtain will allow wind better than the thick heavy velvet