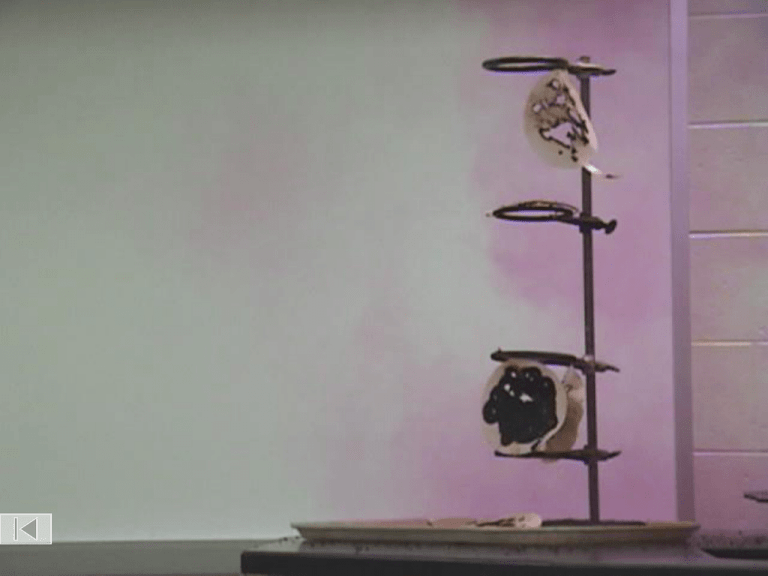
Decomposition of
Nitrogen Triiodide
N2
NI3
2 NI3(s)
I2
N2(g) + 3 I2(g)
Exothermic Reaction
Reactants Products + Energy
10 energy
=
8 energy
+ 2 energy
Energy of reactants
Energy
Energy of products
Reactants
-DH
Products
Reaction Progress
Endothermic Reaction
Energy + Reactants Products
Energy
Activation
Energy
Reactants
Products
+DH Endothermic
Reaction progress
Effect of Catalyst on Reaction Rate
WhatCatalyst
is a catalyst?
does it do
duringfor
a chemical
reaction?
lowers What
the activation
energy
the reaction.
No catalyst
Energy
activation energy
for catalyzed reaction
reactants
products
Reaction Progress
An Energy Diagram
Ea
activation
energy
energy
reactants
products
course of reaction
Animation by Raymond Chang
All rights reserved
Formation of a solid AgCl
AgNO3(aq) + KCl(aq) KNO3 (aq) + AgCl(s)
Single and Double Replacement
Reactions
Single-replacement reaction
Mg
+
CuSO4
General form:
A
+ BC
MgSO4
AC
+
+
Cu
B
Double-replacement reaction
CaCO3
+
General form:
AB
+
2 HCl
CaCl2
+
H2CO3
CD
AD
+
CB
Single displacement is a type of a reaction when a metal
reacts with a compound containing a metal, where the
single metal in the reaction is more reactive replaces the
less reactive metal in the compound.
Single-replacement reaction
Mg
+
CuSO4
General form:
A
+ BC
MgSO4
AC
+
+
Cu
B
DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS: In a double
displacement reaction (ionic reaction) the ions of two
compounds exchange places in an aqueous solution to
form two new compounds.
Double-replacement reaction
CaCO3
+
General form:
AB
+
2 HCl
CaCl2
+
H2CO3
CD
AD
+
CB
Double Replacement Reaction
Synthesis Reactions - when two compounds or elements
combine to make one molecule or compound.
A+ B --> AB
2 H2 + O2 -------> 2 H2O
Decomposition Reactions - a compound or molecule
breaks down into simpler elements or compounds
AB - -> A + B
CO2 ------> C + O2
Important Chemical Reactions
Oxidation Reactions
Reactant + Oxygen -------> Products
Oxidation reactions are fundamental to our existence
Definition: A chemical change involving oxygen
Oxidation reactions can occur more rapidly in the presence of
humidity in the air, or in the presence of light
GALVINIZATION – coating iron materials with zinc to prevent
the formation of rust.
Combustion
Combustion – Form of oxidation that releases a large amount of
energy (HIGHLY EXOTHERMIC).
Three requirements for a combustion:
Fuel – reacts with oxidizing agent to release energy
Oxidizing agent – substance that causes a fuel to react (usually oxygen)
Ignition temperature – the required temperature needed to combust
the fuel
Three types of combustions:
Rapid – Release a lot of energy in a short period of time
Spontaneous – Fuel ignites without the need for outside energy
Slow – Occurs of long period of time
A Combustion reaction usually looks like:
Fuel + oxygen ------> CO2 + H2O + Energy
CH4 + O2 -------> CO2 + H2O
Other important Chemical
Reactions ...
Cellular Respiration
Glucose + Oxygen -----> Carbon Dioxide + Water + Energy
Photosynthesis
Light + Carbon Dioxide + Water-----> Oxygen + Glucose












