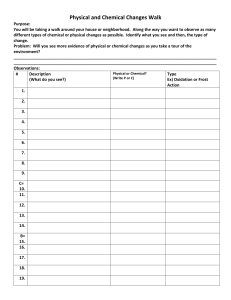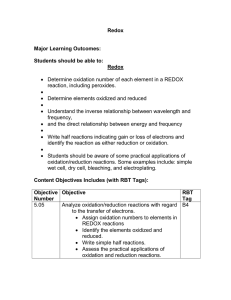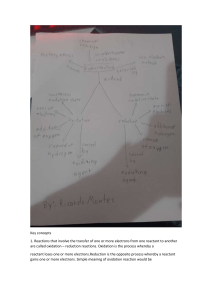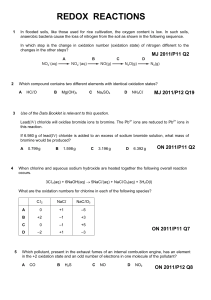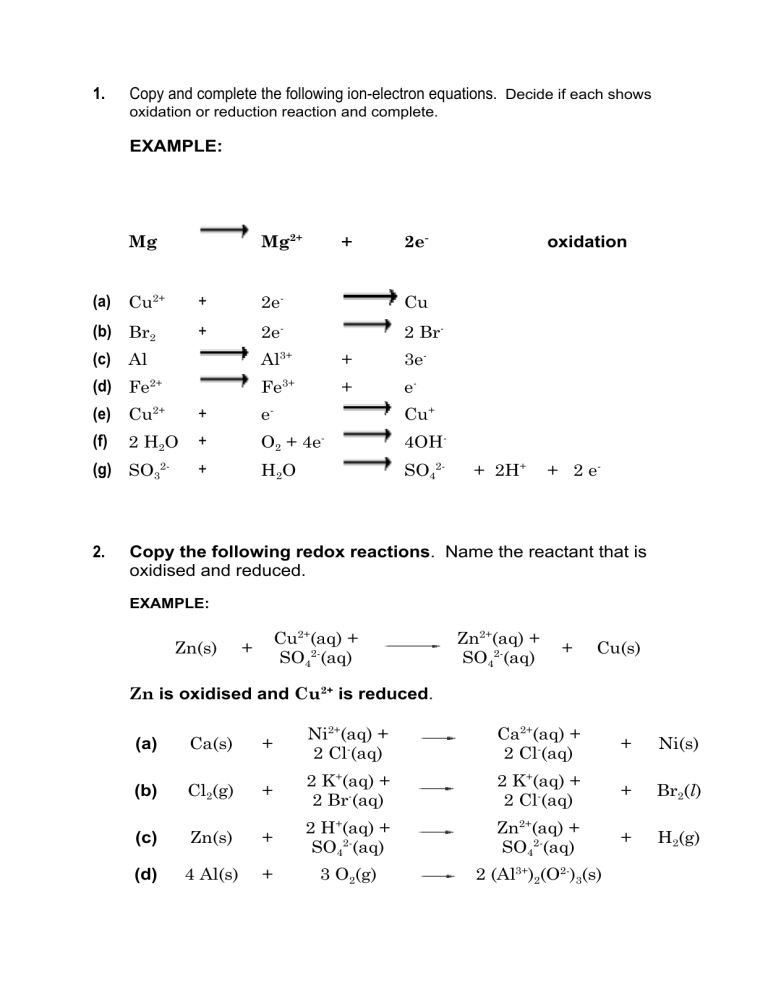
1. Copy and complete the following ion-electron equations. Decide if each shows oxidation or reduction reaction and complete. EXAMPLE: Mg Mg2+ + 2e- (a) Cu2+ + 2e- Cu (b) Br2 + 2e- 2 Br- (c) Al Al3+ + 3e- (d) Fe2+ Fe3+ + e- (e) Cu2+ + e- Cu+ (f) + O2 + 4e- 4OH- + H2O SO42- 2 H2O (g) SO32- 2. oxidation + 2H+ + 2 e- Copy the following redox reactions. Name the reactant that is oxidised and reduced. EXAMPLE: Zn(s) Cu2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Zn2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu(s) Zn is oxidised and Cu2+ is reduced. (a) Ca(s) + Ni2+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) Ca2+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) + Ni(s) (b) Cl2(g) + 2 K+(aq) + 2 Br-(aq) 2 K+(aq) + 2 Cl-(aq) + Br2(l) (c) Zn(s) + 2 H+(aq) + SO42-(aq) Zn2+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + H2(g) (d) 4 Al(s) + 3 O2(g) 2 (Al3+)2(O2-)3(s) (e) 3 Mg(s) + (Fe3+)2(O2-)3(s) 3 Mg2+O2-(s) + 2 Fe(l) (f) Identify any spectator ions in the reactions (a) – (e) and circle them.