Chemistry 125: Lecture 73
April 28, 2010
Benzoin, Claisen, Robinson
(Ch. 19)
Two Un-Natural Products
This
For copyright
notice see final
page of this file
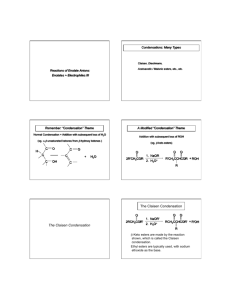
The Benzoin Condensation (prob. 19.90)
CN “reverses the
polarity” of O=C+
to C- (“umpolung”)
also an
-activator
(benzylic)
OH
like C=O an
what we have:
Ph C C N -activator
leaving
N
C
H
O
H C
H Ph
group
C N base
Ph C C N
not basic enough O
C N nucleophile
C N
pKa > 30
H C Ph
OH
where we’re going:
O
need Ph-C
to attack O=CH-Ph
H+
The Claisen Condensation (sec 19.8)
The Claisen Condensation (sec 19.8)
Driving Force
Nature’s Claisen (sec 19.6)
Fatty Acids have even numbers of C atoms!
Driving
Force
Robinson Annulation (sec 19.11)
REVIEW 1:
The Synthesis of Two
Unnatural Products
(in order to settle a question in the
theory of organic chemistry)
Is cyclobutadiene antiaromatic (4n)?
O
O
h
O
(must be disrotatory)
O
h
Make it and see.
Presumptive Evidence.
Spectroscopy?
(2 +2 forbidden thermally)
DielsAlder
(2 +2 forbidden thermally, but
it happens anyway)
+ O=C=O
very strained
Make one molecule
per cage
Making & Studying
“antiaromatic”
Cyclobutadiene
mouth
O
CH
CH2
CH2
(for solubility)
Ph
Cram, Tanner, and Thomas (1991)
Preparing
Dihydrocinnamaldehyde
O
O
O
CH
CH
CH2
CH
CH2
CH
O
Ph
Ph
CH
CH
CH3
Ph
1) “Br+” / -H+ (3 moles)
by
SN2
2 bonds
mixture
with
tetra2)(asO-CH
-
Ar-O withand
CH2two
BrCl
substituted
disubstituted analogues)
-
Cl
BrCH2
-
Br
Br
Start with Hemisphere
Br
How to
form the
C16 ring?
(by chromatography; 5% from tetramer)
Resorcinol
Hydrocinnamaldehyde
(from benzaldehyde
see above)
H+
OH
H+
+
(OH activating
etc. etc.
o,p-directing)
The electrophilic aromatic
substitution is reversible, and
ultimately the desired “tetramer”
stereoisomer precipitates from the
equilibrating mixture in 69% yield
based on hydrocinnamaldehyde.
Lucky!
1) Br+/-H+ (3 moles)
2) O-CH- 2 bonds by SN2
Ar-O with CH2BrCl
3)
Joining Hemispheres
exchange
BuLi (halogen-metal
more stable “Ar- anion”)
-
-
Li
Br
OH
B(OR)2 Br
Li
OH
B(OR)2
~40%
HO
- -overall)
HO(1%
HO
O
O-B(OR)
2
O-Li
Br
OH
B(OR)
2
4) B(OR)3
(add “Ar- ” to B ; lose RO-)
5) HOO-
(insert O between C and B.
Cf. hydroboration/oxidation;
lose most stable ArO- anion)
Note: the purpose of 1,3,4,5 is to “hide” an OH group
between the OH groups of resorcinol, and then reveal it.
6) O-CH- 2 bonds by SN2
Ar-O with CH2BrCl
CHCl3
CHCl3
Stereo Pair
X-Ray View
JACS, 113, 7717 (1991)
(easier to see without a
viewer if you make it small)
CH3CN
CH3CN
CH3CN
CH3CN
CHCl3
CHCl3 &
CH3CN are
held between
molecules in
crystal
O
HC-N(CH3)2 held
within molecule.
but lost with
t1/2 = 34 hrs
at 140°C.
CHCl3
Replace DMF
by -Pyranone
O
O
. . O
. .O
. .
. .
O
O
. .
. .
Most
shift comes from
Antiaromatic
other rings, still ~1.5
upfield
ppm above shift?
benzene
.
Proton NMR
Normal
Benzene as guest
above center of 8 benzene rings
.
.
.. .
.
..
End of Lecture 73
April 28, 2010
Copyright © J. M. McBride 2010. Some rights reserved. Except for cited third-party materials, and those used by visiting
speakers, all content is licensed under a Creative Commons License (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0).
Use of this content constitutes your acceptance of the noted license and the terms and conditions of use.
Materials from Wikimedia Commons are denoted by the symbol
.
Third party materials may be subject to additional intellectual property notices, information, or restrictions.
The following attribution may be used when reusing material that is not identified as third-party content:
J. M. McBride, Chem 125. License: Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 3.0
These last six frames are left over
from a previous year
(and a different textbook).
Instead of discarding them,
I left them here in case they
might be useful as you review.
Hydrocinnamaldehyde
Starting Material for “Clamshell” Synthesis
(Cf. p. 1068)
Ph-CH2-CH2-CHO
H2 / cat (see frame 13)
H
H
acetaldehyde
Cinnamaldehyde
(prepared by this
method in 1884)
,-unsaturated carbonyl Aldol
*
Ester Enolate (Ch. 22)
C nucleophile
*
“Claisen” or “Acetoacetic Ester” Condensation (pp. 1072-1075)
Why not use OH-?
substitution at ester
Equilibrium position?
Biological Claisen
X = SR = coA
(sec. 22.6, pp. 1081-1083)
Biological Claisen
X = SR = coA
(sec. 22.6, pp. 1081-1083)
Acid Derivatives :
A/D Substitution at C=O
O-
O
Y
X-
X
O
O
Y
X
YEquilibrium favors the more stable anion:
O
OROH
Cl- > -O-C-R > -OR > NR2pKa -2.2
4.8
16
35
How to go “wrong” way? (e.g. R-CO-OH R-CO-Cl) Trick with SOCl2.
O
O
O
O
O
O
SO2
O O
O
O S
ClCl
S
S
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
Cl
ClX = Cl ; Y = Cl + stable SO2