Chapter 8 Metabolism Enzymes Notes
advertisement

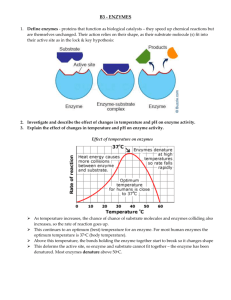
Chapter 8 An Introduction to Metabolism Metabolism • Metabolism is the sum of all chemical reactions in your body. • If a reactions breaks things down, it is catabolic • If a reaction builds things up, it is anabolic Energy • Energy is the capacity to cause change. • Energy of motion is kinetic energy • Energy that is stored is potential energy • Potential energy that is released during a chemical reaction is chemical energy Energy is released or consumed • In an exergonic reaction energy is released. • When you break things down, you release energy • All catabolic reactions are exergonic • Cellular respiration is exergonic. • These are spontaneous reactions • Delta G (a measure of free energy) is negative Energy is released or consumed • In an endergonic reaction energy is absorbed. • When you build things, you need energy • All anabolic reactions are endergonic • Photosynthesis is endergonic • These are non-spontaneous reactions • Delta G is positive Making and breaking bonds • Making bonds is called dehydration synthesis. You take away water to make a new bond. • Breaking bonds is called hydrolysis. You add water to break a bond. Introducing ATP • ATP is adenosine triphosphate • It is composed of a nitrogenous base called adenine, a ribose sugar, and a chain of 3 phosphate groups • Energy is stored in the bonds between the phosphate groups. • When a bond is broken between the Ps, it releases energy ATP to ADP to ATP • To get the energy, hydrolysis occurs to break off 1 P, turning ATP into ADP • During cellular respiration, energy from food is used to add the P back on to ADP to make more ATP Enzymes! • Enzymes are proteins. They are catalysts that speed up chemical reactions by lowering the amount of energy needed for those reactions to start (activation energy) Enzyme terms • The thing an enzyme binds to and acts on is called the substrate. • The place where the enzyme binds is the active site. • Enzymes are specific and only fit to their own substrate like a key into a lock • Enzymes are reusable and are used over and over Factors affecting enzymes • 1. Temperature • 2. pH • 3. Salinity Factors affecting enzymes • Some enzymes need helpers: • Cofactors are INORGANIC and bind to the enzymes to make them work (zinc, iron, copper, minerals) • Coenzymes are ORGANIC and bind to the enzyme to make them work (vitamins) Factors affecting enzymes • Inhibitors block enzyme action • Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of the substrate so that the enzyme can’t get in • Non-competitive inhibitors bind somewhere on the substrate, changing the shape of the active site, so enzymes no longer fit