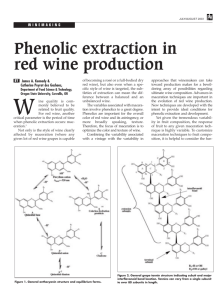
Press at 0° Brix 72 Hour Post Ferm Maceration
advertisement

Vegan Winemaking From Juice To Bottle Why Vegan? • Marketing – Vegan wines appeal to a broader range of consumers • Consumers with plant based diets often have no idea that animal products are used in some wines • Filling a much needed niche in the market • High quality wines not just for Vegans – Minimalistic winemaking – Less evasive techniques require less intervention ML- White Wine Production • Vineyard – Early pruning – early break and longer maturity before sugar accumulation – Down side – potential for frost damage – Lower sugar – lower alc and decreased effect of harsh phenolics • Juice – Hand sorting – Press options and decisions • Lighter pressing – 400 millibars or less • Separate press fractions for use in blending to add texture – complexity – Controlled phenolic levels • Most animal based fining products are for phenolic reduction – lighter press = less phenolic compounds • Address the need before it is needed • Higher quality juice from the lighter pressing – higher quality wine in the bottle ML- White Wine Production • In The Tank – Lysozyme - Animal products are not just for fining • Egg based enzyme used to prevent malolactic fermentation – Alternative • Close monitoring of the fermentation environment • Sulfur management post press – Oxidation Treatment/Prevention • PVPP and Plant based proteins – Already Vegan ML- White Wine Production Modern Day Fining “Standards” • Animal Products Used – Isinglass – Gelatins(Fish Gelatins) – Potassium Caseinate • Alternatives – Hybrids – Bentonite/PVPP/Plant protein/Silica – Plant Proteins – Winemaking Practices Red Wine Production • Animal Product Standards – Albumin • Softens wine – reduces tannins – Gelatins and Fish Gelatins • Softens wine – reduces tannins – color stabilization – Casein • Softens wine – aids in oxidation management Red Wine Production • Starts in the Vineyard – Terroir – know your fruit – know your vineyard • Fermentation management – – – – Cold Soaking Extended maceration Extraction Enzymes Oak alternatives – Enological tannins • Trials • Analysis Estate Cabernet Cold Soak Trial (No extended maceration) 24 Hour Cold Soak 72 Hour Cold Soak Catechins Before Ferm <1mg/L 1mg/L Catechins After Ferm 7mg/L 7mg/L Tannins Before Ferm 108mg/L 90mg/L Tannins After Ferm 610mg/L 719mg/L Total Anthocyanins Before Ferm 145mg/L 350mg/L Total Anthocyanins After Ferm 507mg/L 561mg/L •Longer cold soak increased tannins •Anthocyanin extraction finishes at roughly the same level • Color is drawn out at higher temps and has a potential max level •Decreasing cold soak time – can decrease tannins, astringency, bitterness •Decreased cold soak time – can decrease the need for protein fining down the road Estate Cabernet Extended Maceration Trial (No cold soak) Press at 0° Brix 72 Hour Post Ferm Maceration Catechins before Ferm 1mg/L 1mg/L Catechins after Ferm 6mg/L 6mg/L Tannins before Ferm 80mg/L 111mg/L Tannins after Ferm 731mg/L 882mg/L Anthocyanins before Ferm 268mg/L 151mg/L Anthocyanins after Ferm 998mg/L 966mg/L •Longer Maceration time results – increased anthocyanins with similar tannin extraction •Still more tannin extraction occurs during maceration •To manage tannins while maximizing color – shorter cold soak with no maceration •Color extraction plateaus like with cold soaking •Color must then be stabilized since there is reduced tannin structure to support it Red Wine Production • Utilize New Technology – Micro Oxygenation • Color stabilization • Oak tannin management • Oxidation management – Ultra Filtration – Cross Flow • Reduce tannin structure • Downside – reduce color – Instrumentation – Analysis • Extraction monitoring • Dissolved oxygen pick up Red Wine Production Balancing Act • Managing the vineyard to prevent over – ripeness : Reduced complexity from under ripe fruit. • Whole cluster press: Destem and Crush • Decreasing cold soak and maceration : decrease extraction of aromas, complexity and structure. • Micro oxygenation for color stabilization : Oxidation and Spoilage risks. • Enological tannin usage : astringent mouth feel • Cross flow filtration : damaged structure Red Wine Production • Alternatives – – – – – Plant Proteins Hybrid usage Viticultural Practices Winemaking Techniques New Technology • A need for more Alternative Research? – Malolactic fermentation control and prevention in white wines – Plant based – synthetic proteins for softening red wines – New plant based products for corrective purposes oxidation Conclusion • There is a demand to be supplied • Vineyard and Viticulture practices • Managing the production process • Managing the fermentation • Managing the aging process • Utilizing new technology • Experimentation