Air quality monitoring
advertisement

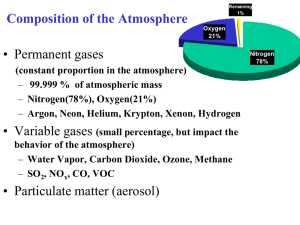
Air quality monitoring Air and meteorological monitoring parameters Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Classification of air pollutants • Primary pollutants (emitted directly to the atmosphere) • Secondary pollutants (formed by reactions involving primary pollutants and other constituents within the atmosphere) Classification of sources of air pollutants • Stationary sources • Mobile sources Sources • Natural sources • Anthropogenic sources • Urban sources Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Primary air pollutants Secondary air pollutants are formed from sunlight that results in photochemical reactions of O2 with one or more of the primary air pollutants. Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Legislation regarding the concentration limits Order no. 592/2002 revized by Order 448/2007 for establishing the limit values and the evaluation methods of several primary pollutants in the environmental air (imisii) Pollutant Hourly limit value (average 1 h) Daily limit value (average 24 h) Annually limit value for human health protection (average 1 year) Annually limit value for vegetation protection (average 1 year) SO2 350 μg/m3 125 μg/m3 - 20 μg/m3 NO+NO2 200 μg/m3 - 40 μg/m3 30 μg/m3 Particulate Matter (PM10) - 50 μg/m3 20 μg/m3 - Lead - - 0.5 μg/m3 - Benzene - - 5 μg/m3 - CO - 10 mg/m3 - - Ozone 120 μg/m3 - 18.000 μg/m3h - Arsenic* - - 6 μg/m3 - Cadmium* - - 5 μg/m3 - Nickel* - - 20 μg/m3 - *Added by Order 448/2007 Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Legislation regarding the concentration limits Order no. 592/2002 for establishing the limit values and the evaluation methods of several primary pollutants in the environmental air (imisii) Reference methods for concentration measurement SO2 Fluorescence in ultraviolet NO+NO2 Chemiluminescence Particulate Matter (PM10) Collection of PM10 on filters and mass measurement (gravimetric) or TEOM method Lead Collection of lead on filters and AAS Benzene Aspiration on a filter cartridge and gas chromatography CO Nondispersive infrared spectrophotometry (NDIR) Ozone UV photometry Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring National Network for Air Quality Monitoring (RNMCA) www.calitateaer.ro Air quality monitoring Romanian legislation regarding the concentration limits Order no. 462/1993 regarding emissions from stationary sources (emisii) Refers to emissions produced by • Stationary sources • Vehicles • Infrastructures designed to transportation • Burning installations • Fuel burning Measurements are mandatory for the installation owner. The results are to be registered and archived by the owner. The limits are given according to the source. If the limits are exceeded, the polluter pays. Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Order no. 462/1993 Burner supplied with liquid fuel Thermal power [kW/t] Pollutant Unit < 100 100 - 300 300 - 500 > 500 Suspended particulates mg/Nm3 50 50 50 50 CO mg/Nm3 170 170 170 170 SOx (expressed in SO2) mg/Nm3 1700 1700 1700 1700 NOx (expressed in NO2) mg/Nm3 450 450 450 450 Burner supplied with solid fuel Thermal power [kW/t] Pollutant Unit < 100 100 - 300 300 - 500 > 500 Suspended particulates mg/Nm3 100 100 100 100 CO mg/Nm3 250 250 250 250 SOx (expressed in SO2) mg/Nm3 2000 2000 400 400 NOx (expressed in NO2) mg/Nm3 500 400 400 400 Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Order no. 462/1993 Burner supplied with natural gas Thermal power [kW/t] Pollutant Unit < 100 100 - 300 300 - 500 > 500 Suspended particulates mg/Nm3 5 5 5 5 CO mg/Nm3 100 100 100 100 SOx (expressed in SO2) mg/Nm3 35 35 35 35 NOx (expressed in NO2) mg/Nm3 350 350 350 350 Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Methods and instrumentation • Passive sampling methods • Active sampling methods • Automatic methods • Remote optical - long path analyzers Any instrument measures 3 types of values: • Instantaneous value • TWA (Time Weighted Average) • STEL (Short Term Exposure Limits) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Methods and instrumentation Gas measurement using spectroscopic methods Spectrophotometry is based on the interaction of the gas molecules with light. hc Absorbtion techniques – it is measured the intensity of light after passing through a gaseous medium. Usually absorption is measured at several frequencies in order to avoid offests and interferences with other species. There are 4 principles: • Differential Optical Absorption Spectroscopy (DOAS) • Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) • Non-Dispersive Infrared (NDIR) • Tunable Laser Diode Absorption Spectroscopy (TLDAS) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Methods and instrumentation Gas measurement using spectroscopic methods Emission techniques – excite molecules of the gas and then examine the light emitted as they return to their ground state. The signal is passed through a narrowband filter and measured with a photomultiplier tube. • Flame photometry • Chemiluminescence • UV fluorescence Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of carbon monoxide (CO) by IR photometry Beer’s law A = log(I/Io) = abC I0 λ 4,61μm A = absorbance a = absorbtion coefficient b = path length C = concentration I Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of carbon monoxide (CO) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of carbon monoxide (CO) by IR photometry Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of carbon monoxide (CO) by IR photometry Schematic of a NDIR head Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of nitric oxides (NOx) by chemiluminescence Chemiluminescent reaction NO + O3 ==> NO2+ O2 + hv (0.6 – 3 μm) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of sulphur dioxide (SO2) by UV fluorescence Excitation S0 + hνex → S1 Fluorescence (emission) S1 → S0 + hνem + heat Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of sulphur dioxide (SO2) by UV fluorescence Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of sulphur dioxide (SO2) by UV fluorescence Teledyne 100E UV Fluorescence SO2 Analyzer Ranges: 0-50 ppb to 0-20,000 ppb full scale, user selectable or autoranging Units: ppb, ppm, µg/m3, mg/m3 Zero noise: < 0.2 ppb (RMS) Span noise: < 0.5% of reading (RMS) above 50 ppb Lower Detectable Limit (LDL): 0,4 ppb Linearity: 1% of full scale Precision: 0.5% of reading above 50 ppb Analog outputs: 10V, 5V, 1V, 0.1V, selectable Serial outputs: Serial Port 1: RS-232 (DB-9M) Serial Port 2: standard RS-232 or optional Environmental monitoring RS-485 (DB-9F), Ethernet Air quality monitoring Gas chromatography Gas chromatography (video clip) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) Photo-Ionization Detector (PID) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOC) Photo-Ionization Detector (PID) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of suspended particles (particulate matter – PM) Fraction Size range PM10 (thoracic fraction) ≤ 10 μm PM2.5 (respirable fraction) ≤ 2.5 μm PM2.5 – PM10 (coarse fraction) 2.5 - 10 μm PM1 (fine fraction) ≤ 1 μm Ultrafine (UFP or UP) ≤ 0.1 μm Aerosol = particles + gas Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of suspended particles (particulate matter – PM) Gravimteric method Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of suspended particles (particulate matter – PM) Beta Attenuation Method Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of suspended particles (particulate matter – PM) Beta Attenuation Method Model: BAM-1020 EnviroTechnology Technical specifications Source Carbon-14 (C-14), < 3.7 MBq Measurement Range 0 to 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 5.0, 10.0 mg/m3 0 to 100, 1,000, 2,000, 3,000, 5,000, 10,000 μg/m3 Minimum Detection Limit 6 μg/m3 (1/2 hour), 4 μg/m3 (1hour) 3 μg/m3 (3 hour), 1 μg/m3 (24-hour) Resolution 0.1 μg/m3 Precision ±2.0 μg/m3 < 80 μg/m3, 4-5 μg/m3 > 80 μg/m3 (24-hour average) Accuracy (for mass measurement) ± 5% using NIST-traceable mass foil set Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of suspended particles (particulate matter – PM) Optical method Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of suspended particles (particulate matter – PM) Tapered Element Oscillating Microbalance (TEOM) Environmental monitoring Air quality monitoring Measurement of gaseous pollutants using electrochemical sensors O2 SnO2-x R A [C ] O2 Gaz O2 SnO2-x SnO2-x SnO2-x R = resistance A, α = constants E eV în aer C = gas concentration Metallic oxide E eV în prezenţa gazelor de reducere Detected gases TiO2, Fe2O3, CoO, ZnO, ZrO2, SnO2, La2O3 O2 Cr2O3, NiO, ZnO, ZrO2, SnO2, In2O3 CO Fe2O3, Fe3O4, Co3O4, ZnO CH4 SnO2, VO NOx ZnO, Al2O3, SnO2 halogens Environmental monitoring