Marwa Aly - The Six International Conference of ESES 2014
advertisement

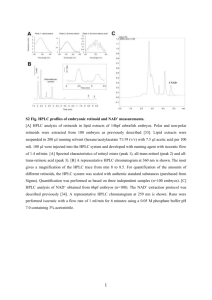
The overall aim of this Project Development luminescent lanthanide nanobioprobes for detection of N-acetyl aspartate(NAA) . EX OF N-Acetyl Amino acids N-acetyl aspartate(NAA) C6H9NO5 HO O O HO O N H The interest in N-acetylaspartate determination is due to it present in high concentration in the brain and their possible direct impact on the human as : Decreased levels of NAA 1- Alzheimer’s disease 2- AIDS 3- schizophrenia 4- Huntington’s disease 5- amyotrophic lateral or multiple sclerosis 6- traumatic brain injury high levels of NAA : causes Canavan’s disease 1-Magnetic resonance spectroscopy The major advantage of 'H NMR spectroscopy is that this technique can be applied to in vivo studies of brain The major disadvantage of NMR is its low sensitivity, allowing only metabolites present at relatively high concentration to be measured. 2-Chromatographic techniques HPLC , Gas and Liquid chromatography Advantages of HPLC •Sensitivity •Accuracy •Automation •High resolution Disadvantages of HPLC •Complexity • The analysis time is long •A further principal drawback of these methods is the requirement of (sometimes harmful) organic solvents of HPLC grade quality, whereby the costs for their purchase and disposal has to be taken into consideration development of an inexpensive, fast and sensitive method for the determination of NAA is of primary interest . One of the most convenient and simplest detection method is based on the change in absorption or luminescence in the presence of an analyte. The lanthanide complexes, with characteristically narrow excitation and emission bands, intense luminescence, and long excited-state lifetimes, have drawn considerable interest for their potential application as luminescence imaging agents and sensors. Luminescence is a highly sensitive analytical method nowadays, its interest for medical analysis and diagnosis.