Addition of HX across a double bond
advertisement

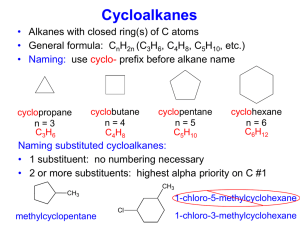
Addition of HX across a double bond And Carbocation rearrangement Addition of HX across a double bond An acid, HX, such as HCl, HBr and HI add across a double in this fashion. Cl H3C H3C Or CH3 + HCl Cl H3C CH3 CH3 This is called Markovnikov addition of HX across a double bond. Markovnikov Addition Markovnikov’s rule states that when adding something across a double bond, the anion (negative ion) will bond with the more substituted carbon. Example: CH3 H3C + CH3 Cl HCl H3C CH3 CH3 Notice how there is no distinct stereochemistry. This is because the ion can attack either side of the carbon. Quick Review: Draw the products of the following two reactions: CH3 CH3 H3C + H3C HBr CH3 H3C Br CH3 CH3 H3C H3C H3C H3C CH3 CH3 + HCl Cl CH3 CH3 Rearrangement The anion, in normal circumstances, will always attack the most substituted carbon in the molecule, not just the most substituted carbon in the double bond. Example: H3C CH3 CH3 + HCl H3C CH3 Cl CH3 Why does rearrangement occur: An intermediate is formed in the reaction between HCl and an Alkene. It follows by this mechanism: CH3 H3C H3C + + H Cl - + CH H3C H H3C CH3 H3C + C H In this intermediate, a carbocation is formed. Carbocations can easily rearrange to a more stable carbon. H3C CH3 Carbocation stability A primary carbocation is a carbocation bonded to one other carbon. A secondary carbocation is a carbocation bonded to two other carbons. It is more stable than a primary carbocation. A tertiary carbocation is a carbocation bonded to three other carbons and is more stable than a secondary carbocation. The general order is 1º< 2º< 3º What type of carbocations are these? Which are the most stable? CH3 + H3C C CH3 CH3 + H2C CH3 CH3 H3C + CH CH3 INCORRECT CORRECT