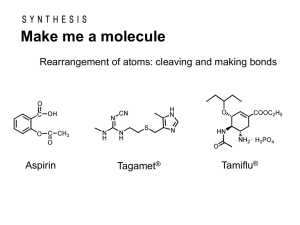
Metabolism of Xenobiotics
advertisement

ENVR/TOXC 442 Fall 2011 Metabolism of Xenobiotics II. Phase 1 Metabolism Aug 30, 2011 L.M. Ball Rosenau 158 lmball@unc.edu Phase I reactions • Chemical modification of xenobiotics • Introduces or uncovers polar functional groups that provide sites for Phase II metabolism • Major classes of reaction: – Oxidation – Reduction – Hydrolysis Overview of oxidations, reductions, hydrolyses • Oxidation –Loss of electrons M M+ + e–Gain of oxygen R + O RO Oxidation reactions Hydroxylation Epoxidation HC O HC CH2 Styrene CH2 Styrene oxide H O H Benzo[a]pyrene Benzo[a]pyrene 7,8-oxide Demethylation CH3 O OH H + O C H Anisole Phenol Formaldehyde Deethylation H2 C CH3 O OH H + C CH3 o N H N C CH3 O Phenacetin H C CH3 O Acetaminophen Acetaldehyde Overview of oxidations, reductions, hydrolyses • Reduction – Gain of electrons M+ + e- M – Loss of oxygen RO R + O – Gain of hydrogen R + H RH Reduction • Nitro to amino group NO2 NO HNOH • Chromium VI to Chromium III Cr6+ + 3 e- Cr3+ H NH Hydrolysis • Addition of water – Cleavage of R-O or R-N bond accompanied by addition of H2O R’-O-R + H2O R’-N-R + H2O H R’-O-H + R-OH R’-N-H + R-OH H Principal Phase I enzymes • • • • • • • Cytochrome P450 Flavin monooxygenase Monoamine oxidase Esterases Amidases Hydrolases Reductases, dehydrogenases, oxidases Cytochrome P450 • Heme protein • Terminal oxidase of the mixed-function oxidase (MFO) electron-transfer system • Located in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of all major organs and tissues • Uses NADPH as a source of reducing equivalents • Inducible Cytochrome P450 • Heme protein • Terminal oxidase of the mixed-function oxidase (MFO) electron-transfer system • Located in the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of all major organs and tissues • Uses NADPH as a source of reducing equivalents • Inducible Overall reaction R-H + O2 + NADPH + H+ R-OH + H2O + NADP+ Ferric protoporphyrin IX CH2 CH3 HC NCH3 H3C O C H2 C N H2 C Fe+3 N CH OH CH2 N O C OH H2 C CH2 CH3 Protoporphyrin IX Catalytic cycle of cytochrome P450 ROH H+ Fe3+ HO22- + RH H2O Fe3+-RH HO2 - [Fe2+-RH] NADH H+ + eNADPH H2O2 H+ Fe3+-RH + e- from NADPH-cytC reductase Fe2+-RH O2 +O2 [Fe2+-RH] -. O 2 P450 and reductase in endoplasmic reticulum The P450 gene superfamily • Format of nomenclature: CYPFamily/Subfamily/Gene • Family = 1, 2, …150 and counting – ~40% aa similarity • Subfamily = A, B,…H… – 55-65% aa similarity • Gene = 1, 2..10 or above – >97% aa similarity (allelic variants) • Families grouped in Clans Family Subfamily Gene CYP1 A (PAC-inducible 1 BaP hydroxylation, O-deethyl’n 2 N-hydroxylation, O-deethylation CYP2 A 1 Testosterone 7-hydroxylation 2 Testosterone 15-hydroxylation B 1 Aliphatic hydroxylation 2 O-deethylation C 1 - 20+ 2C19, mephenytoin hydroxylase Demethylation CH3 O OH H + O C H Anisole Phenol Formaldehyde Deethylation H2 C CH3 O OH H + C CH3 o N H N C CH3 O Phenacetin H C CH3 O Acetaminophen Acetaldehyde Family Subfamily Gene CYP1 A (PAC-inducible 1 BaP hydroxylation, O-deethyl’n 2 N-hydroxylation, O-deethylation CYP2 A 1 Testosterone 7-hydroxylation 2 Testosterone 15-hydroxylation B 1 Aliphatic hydroxylation 2 O-deethylation C 1 - 20+ 2C19, mephenytoin hydroxylase SubFamily family CYP2 Gene D 1 - 6+ 2D6, debrisoquine hydroxylase E 1 C- and N-hydroxylation small molecules 2 1 F CYP3 A 1-4 3A4 CYP4 A 1 Lauric acid - and -1 hydroxylation SubFamily family Gene CYP11 (mito) A 1 Steroid 11-hydroxylation CYP17 CYP21 1 Steroid 17-hydroxylation 1 Steroid 21-hydroxylation A A CYP51 A CYP52-66 A CYP71-99, 701 CYP101 A CYP102-132 A 1 (Plants, yeast) Yeasts, fungi Plants 1 Pseudomonas putida P450cam Bacteria Changes in P450 levels with age Rats M: 2C6, 2C11, 3A2 2A1 2C6 3A2 F: 2A1, 2C6, 2C12 Flavin monooxygenase • Flavoprotein • Mixed-function amine oxidase • Located in smooth endoplasmic reticulum, in human, pig, rabbit liver, guinea-pig lung, human kidney • Uses NADPH as a source of reducing equivalents • Not inducible Overall reaction R-H + O2 + NADPH + H+ R-OH + H2O + NADP+ Monoamine oxidase • Metabolizes endogenous monoamine neurotransmitters • Uses NADPH as a source of reducing equivalents • Found in the endoplasmic reticulum and in mitochondria, of nerve endings and liver Esterases • Hydrolyse esters to carboxylic acid and alcohol functional groups • Non-specific esterases in plasma, more substrate-specific forms in liver cytosol O O C H3C O H2 C Ethyl acetate + H2O CH3 H2 C C H3C OH Acetic acid + HO CH3 Ethanol Amidases • Hydrolyse amides to carboxylic acids and amines (or ammonia) • Found in plasma and in liver cytosol O H R C N H O + H2O R H + C OH H N H Hydrolases • Hydrolyse ethers H2 C H3C H2 C O Diethyl ether H2 C + H2O CH3 H3C H2 C OH Ethanol + HO Ethanol CH3 Reductases, dehydrogenases, oxidases • In cytosol, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria Alcohol dehydrogenase H H3C C Aldehyde dehydrogenase NAD + NADH + H+ OH H3C O NAD + NADH + H+ C H3C H O C OH H Ethanol Acetaldehyde Acetic acid