metabolism of nucleotides
advertisement

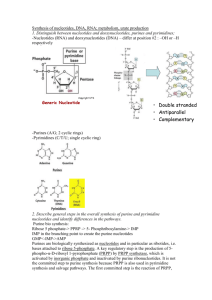
Metabolism of purines and pyrimidines - exercise - Vladimíra Kvasnicová Purine nucleotides a) include an aromatic cycle in the structure b) can contain either adenine or thymine c) include N-glycosidic bond d) are composed of a nucleoside bound to phosphoric acid by an anhydride bond Purine nucleotides a) include an aromatic cycle in the structure b) can contain either adenine or thymine c) include N-glycosidic bond d) are composed of a nucleoside bound to phosphoric acid by an anhydride bond PURINE BASES Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 ribonucleoside deoxyribonucleoside N-glycosidic bond Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 ribonucleotide deoxyribonucleotide ester bond Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Pyrimidine nucleotides a) include an imidazol ring in the structure b) include thymidine- and cytidine monophosphate c) contain an ester bond d) can include 3 phosphate groups in their structure Pyrimidine nucleotides a) include an imidazol ring in the structure b) include thymidine- and cytidine monophosphate c) contain an ester bond d) can include 3 phosphate groups in their structure PYRIMIDINE BASES Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 ribonucleosides deoxyribonucleoside Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Ribonucleotides * N-glycosidic bond * ester bond * anhydride bond Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides can be used a) as nucleoside triphosphates for nucleic acid synthesis b) in energetic metabolism of cells c) for activation of metabolic intermediates of saccharides and lipids d) in enzymatic reactions: some coenzymes are nucleotides Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides can be used a) as nucleoside triphosphates for nucleic acid synthesis b) in energetic metabolism of cells c) for activation of metabolic intermediates of saccharides and lipids d) in enzymatic reactions: some coenzymes are nucleotides Synthesis of nucleotides a) uses products of pentose cycle b) includes phosphoribosyl diphosphate (PRDP = PRPP) as a substrate c) needs derivatives of folic acid d) proceeds in a cytoplasm only Synthesis of nucleotides a) uses products of pentose cycle b) includes phosphoribosyl diphosphate (PRDP = PRPP) as a substrate c) needs derivatives of folic acid d) proceeds in a cytoplasm only H4 –folate (THF) pentose cycle PRPP = PRDP Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Synthesis of purine nucleotides a) uses ammonia as a nitrogen donor b) proceeds in a cytoplasm c) can start from nucleosides produced by degradation of nucleic acids d) includes uric acid as an intermediate Synthesis of purine nucleotides a) uses ammonia as a nitrogen donor b) proceeds in a cytoplasm c) can start from nucleosides produced by degradation of nucleic acids d) includes uric acid as an intermediate uric acid is the end product of purine ring degradation Synthesis of purine nucleotides C Y T O P L A S M Obrázek převzat z http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/mwking/nucleotide-metabolism.html (leden 2007) IMP GMP AMP Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides a) starts by the reaction: PRDP + glutamine b) proceeds only in a cytoplasm of cells c) includes orotic acid as an intermediate d) includes inosine monophosphate as an intermediate Synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides a) starts by the reaction: PRDP + glutamine b) proceeds only in a cytoplasm of cells c) includes orotic acid as an intermediate d) includes inosine monophosphate as an intermediate Synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides C Y T O P L A S M mitochondrion Obrázek převzat z http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/mwking/nucleotide-metabolism.html (leden 2007) Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Synthesis of 2-deoxyribonucleotides enzyme: ribonucleotide reductase + small protein „thioredoxin“ Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 Synthesis of thymidine monophosphate Obrázek je převzat z učebnice: Devlin, T. M. (editor): Textbook of Biochemistry with Clinical Correlations, 4th ed. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York, 1997. ISBN 0-471-15451-2 In a regulation of nucleotide synthesis participate: a) 5´-phosphoribosyl-1´-diphosphate (PRDP) b) feed back inhibition c) enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (synthesis of pyrimidines) d) enzyme xanthine oxidase (synthesis of purines) In a regulation of nucleotide synthesis participate: a) 5´-phosphoribosyl-1´-diphosphate (PRDP) b) feed back inhibition c) enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase II (synthesis of pyrimidines) d) enzyme xanthine oxidase (synthesis of purines) = enzyme of purine degradation Regulation of nucleotide synthesis regulatory enzyme activation glutamine-PRPP amidotransferase (purines) PRPP carbamoylphosphate synthetase II PRPP ATP (pyrimidines) = cytosolic inhibition IMP, GMP, AMP (allosteric inhibition) UTP In a degradation of purine nucleotides a) ammonia is released b) CO2 is produced c) the enzyme xanthine oxidase participates d) uric acid is produced as the end product In a degradation of purine nucleotides a) ammonia is released b) CO2 is produced c) the enzyme xanthine oxidase participates d) uric acid is produced as the end product Degradation of purines = „uric acid“ In a degradation of pyrimidine nucleotides a) -amino acids are produced b) the enzyme xanthine oxidase participates c) orotic acid is formed d) ammonia is produced In a degradation of pyrimidine nucleotides a) -amino acids are produced b) the enzyme xanthine oxidase participates c) orotic acid is formed d) ammonia is produced Degradation of pyrimidines Principal differences between metabolism of purines and pyrimidines purines formation of N-glycosidic bond in 1st step of their biosynthesis location of biosynthesis cytoplasm products of degradation (PRDP is the 1st substrate) uric acid (poor solubility in H2O), NH3 pyrimidines a heterocyclic ring is formed first, then it reacts with PRDP cytoplasm + 1 enzyme is in a mitochondrion CO2, NH3, -AMK (soluble in H2O)