The Atom and the Periodic Table
advertisement

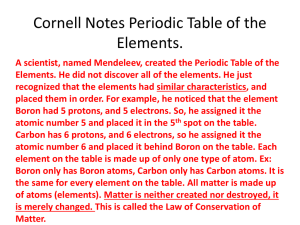
Unit: The Atom and The Periodic Table Evolution of the Structure of an Atom Dalton’s Atomic Theory • All elements are composed of indivisible particles called atoms • Atoms of the same element are identical. The atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element. • Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or chemically combine with one another in simple whole number ratios to form compounds.(law of definite composition) • Chemical rxns occur when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element, however, are never changed into atoms of another element as a result of a chemical reaction.(law of conservation of mass) J.J. Thomson • discovered the electron • plum pudding model Rutherford • discovered the nucleus • Proposed electrons surround the nucleus in a cloud The Atom Today • The atom is the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element • Atoms can only be seen with proper instrumentation • Dalton’s Atomic Theory wasn’t completely correct • Atoms can be broken down into subatomic particles • Atoms of the same element are not identical Properties of Subatomic Particles Particle Electron Proton Nuetron Symbol Relative Charge Relative Mass Actual mass (g) Distinguishing Between Atoms Atomic Number • Number of protons in the nucleus of an atom • Identifies the element • Elements are listed on periodic table according to atomic number Atomic Number Atomic Number Atomic Number • atoms are electrically neutral • # protons = # electrons Mass Number • total number of protons and neutrons in an atom • It is not found on the periodic table but can be estimated Shorthand Notation Fill in the following table Isotopes • Atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons • Differ in their mass number Isotopes • the existence of isotopes was not predicted by Dalton, who said atoms of the same element are the same Isotopes • identified by their mass # , write the name of the element then a hyphen with the mass number Isotopes Uses of Isotopes • C-14 = archeological carbon dating • Am-241 = smoke alarms • I-131 = treating thyroid disorder • Co –60 = cancer treatment Atomic Mass (atomic weight) • weighted average mass of the atoms in naturally occurring samples of the element Atomic Mass • reflects the mass and the relative abundance of isotopes as they occur in nature Atomic Mass • To calculate the atomic mass of an element multiply the atomic mass of each isotope of the element by its relative abundance, then add the results atomic mass = mass1relabd.1 + mass2rel.abd.2+... 1. Calculate the % abundance of fictitious element Nv 2. If the mass of 293Nv is 293.15 amu (red)and that of 295Nv is 295.15 amu (blue), what is the atomic mass of Nv? . Periodic Table • _______________ was the first person to find a way to list elements in order of increasing atomic mass Periodic Table • He constructed the first periodic table in 1869, an arrangement of the elements according to similarities in their properties. Mendeleev’s Periodic Table Periodic Table • In 1913, ______ determined the atomic number of atoms and arranged the modern periodic table according to atomic number . Modern Periodic Table Modern Periodic Table • Each element is identified by its symbol placed in a square Modern Periodic Table • The horizontal rows of the periodic table are called _____ • There are ___ Modern Periodic Table Modern Periodic Table • Each vertical column is called a ____ or ____ • There are ____. Modern Periodic Table Periodic Table • A periodic law means that physical and chemical properties of elements are functions of their atomic numbers • Elements in the same group on the periodic table have similar properties Modern Periodic Table • Group A elements are called the representative elements because they have a wide range of chemical and physical properties • Name the groups in Group A Modern Periodic Table • Group B elements are called the ______________ • The inner transition elements are the ______ and _____ Modern Periodic Table Modern Periodic Table • The representative elements can be divided into three broad classes; Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids • What are some characteristics of each? Modern Periodic Table Niels Bohr • credited for a model of the atom that states that electrons are at specific distances from the nucleus of an atom Bohr Models Energy Level # ELECTRONS 1 2 3 4 Bohr Models Exception: Outermost energy level can only hold up to 8eYou need to be able to diagram Bohr models for 1-36; excluding transition elements Bohr Models Do you notice any trends with the group or period of the periodic table? Bohr Models Trends: 1. Group numbers (1-8A) predict valence electrons (electrons in the outmost level). 2. The period tells you how many energy levels you have in the atom.