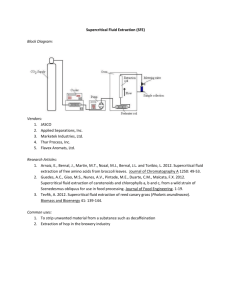
SFE Application: Extraction of Vitamin E from Olive Oil
advertisement

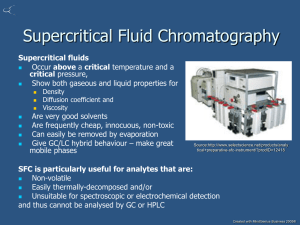
Supercritical Fluid Extraction Andrew DeMartini Brooks Hurd Chris Petry Amanda Walker Supercritical Fluids • Supercritical fluid is one that is above critical temperature and critical pressure. • Possess properties of both gases and liquids. • Density, diffusivity, and viscosity are vital properties to SCF. General Process • Basis: the more volatile component will partition into the supercritical phase • Pump liquid solvent from a reservoir and adjust to supercritical conditions – CO2 is the most common solvent • Remove solute and solvent from extractor • Separate extract from CO2 Equipment • • • • • • Heat exchanger Pump or compressor Extraction chamber Collection trap Separator Compressor Governing Equations • Liquid Extraction can be modeled as a regular stripping column – Number of Equilibrium Stages – Size of Equilibrium Stages • Solid Extraction is controlled by Mass Transfer of Supercritical Fluid through solid • Mass Transfer Equation: Ca v Ca DAB 2Ca t SFE Application: Extraction of Vitamin E from Olive Oil • Vitamin E is extracted from olive oil via counter-current supercritical extraction • CO2 is brought to supercritical state before entering the column • Fenske rings are used as the column packing • Cascade decompression takes place after the extraction to separate the CO2 from the product Olive Oil Extraction Schematic Column Schematic • Column operates at 313 K and 20 MPa • Column used is 17.6 mm I.D. and 1.8 m in height • Extraction is 50% efficient with no raffinate recycle streams Alternative Methods • Aerosol Solvent Extraction System – Solution sprayed through small nozzle – Small droplets of the solution are mixed with the supercritical fluid and the liquid droplets dissolve into the supercritical fluid • Solution Enhanced Dispersion Process – Supercritical fluid is mixed with the solution. – Then the mixture is put into a chamber and is followed by change in temperature and change in pressure. Solvent Variations • Water could be used as the supercritical fluid – Critical water works well for aqueous streams with a low concentration or organic materials, but it is a poor solvent for many inorganic compounds. • A mix of carbon dioxide and a light hydrocarbon may be used. – Ethane and propane mixtures are ones that have been used successfully. – Hydrocarbons cost more than carbon dioxide, but work better as a solvent. Pros and Cons of SFE Pros • Non-Toxic Solvent • Low Heating Cost • Inexpensive Solvent • Easy Separation after Extraction • High Efficiency Cons • High Pressure System requires High Pressure Vessel • High Pumping Cost – High Initial Cost