Chemical Reactions
advertisement

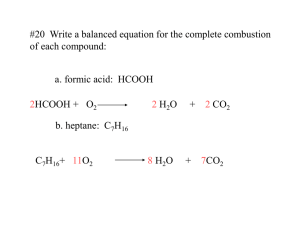
Reaction Types Chemistry Dr. May Single Displacement Reaction A Compound and an element form a compound and an element C + AB CB + A Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 May I Have This Dance ? Dancer C steps in to dance with B replacing A C + AB CB + A Single Displacement Reactions Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + 2 Al + 6 HCl 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2 Mg + 2 HNO3 Mg(NO3)2 + H2 Zn + H2SO4 ZnSO4 H2 + H2 Single Displacement Reactions Cu + 2 AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag 2 Fe + 2 CuSO4 Fe2(SO4)3 + 2 Cu 3 Al + 2 CuCl2 3 AlCl3 + 2 Cu Mg CuSO4 MgSO4 + Cu + Will React With Acid Activity Series Most Active HCl + Zn ZnCl2 + H2 Li, K, Ca, Na, Mg, Al, Zn, Cr, Fe,Ni, Sn, Pb H Acid Cu, Hg, Ag, Pt, Au Least Active Will Not React With Acid Driving Force A single displacement reaction is driven by the electron affinity of the elements 2 AgNO3 + Cu Cu(NO3)2 + 2 Ag 2 Ag+1 + 2 NO31 + Cu0 Cu+2 + 2 NO31 + 2 Ag0 Silver wants electrons more than copper 2 Ag+1 + Cu0 Cu+2 + 2 Ag0 Copper is oxidized and silver is reduced Double Displacement Reaction Two compounds form two different compounds AB + CD AD + CB HCl + KOH KCl + HOH Let’s Trade Partners Dancer A takes D and dancer C takes B C AB + CD B + D CB + AD A Double Displacement Reactions HCl NaCl + HOH 2 HCl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 + 2 HOH 2 KI + Pb(NO3)2 PbI2 + 2 KNO3 NH4Cl + NaOH + KOH KCl + NH4OH Driving Double Displacement Formation of a precipitate (AgCl ) Formation of a non-ionized material (H2O) Formation of a gas (CO2 ) Formation of a precipitate AgNO3 + KCl AgCl + KNO3 Silver chloride precipitates from solution and drives the reaction to the right Formation of a non-ionized material HNO3 + KOH HOH + KNO3 Water is covalently bonded and does not ionize, driving the reaction to the right. Formation Of A Gas 2 HNO3 + K2CO3 2 KNO3 + H2CO3 HOH + CO2 Carbonic Acid is unstable and decomposes to form water and carbon dioxide, driving the reaction to the right No Reaction If there is no driving force, Then there is no reaction NaCl + KNO3 No Reaction Na+1 + Cl1 + K+1 + NO31 Na+1 + Cl1 + K+1 + NO31 Synthesis Reaction Two or more materials combine to form a new compound A + B 2 H2 + O2 AB 2 H 2O Materials Combine Two or more materials combine to form a new compound Hydrogen is oxidized (Loses electrons) 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O Oxygen is reduced (Gains electrons) Synthesis Reactions Na + Cl2 2 NaCl N2 + 3 H2 2 NH3 4 Na + O2 2 Na2O 4 Fe + 3 O2 2 Fe2O3 Oxidized Reduced New Compound Decomposition Reactions A compound breaks apart to form two or more new materials AB 2 KClO3 2 KCl A + B + 3 O2 Compounds Break Apart A compound breaks apart to form two or more new materials 2 KClO3 2 KCl + 3 O2 Decomposition Reactions H2CO3 H2O + CO2 NH4OH H2O + NH3 H2O H2 + O2 CaCO3 CaO + CO2 H2SO4 H2O + SO3 Combustion Reactions A hydrocarbon compound combines with oxygen to form CO2 plus H2O CxHy + O2 CO2 + H2O C3H8 + 5 O2 3 CO2 + 4 H2O Green House Gas Burning gasoline gives CO2 and H2O C7H16 + 11 O2 7 CO2 + 8 H2O Combustion Reactions CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O 4 CO2 + 6 H2O 3 CO2 + 4 H2O 8 CO2 + 10 H2O 5 CO2 + 6 H2O Natural Gas 2 C2H6 + 7 O2 Propane C3H8 + 5 O2 Butane 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 Jet Fuel C5H12 + 8 O2 Hydrocarbon Vs. Hydrogen Fuel 2 H2 + O2 2 H2O Water is the only product C5H12 + 8 O2 5 CO2 + 6 H2O Forms lots of greenhouse gas The End This presentation was created for the benefit of our students by the Science Department at Howard High School of Technology Please send suggestions and comments to rmay@nccvt.k12.de.us