H + - Weebly
advertisement

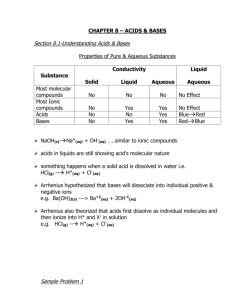
Introduction to Acids and Bases The earliest definition was given by Arrhenius: •An acid contains a hydrogen atom and dissolves in water to form a hydrogen ion, H+. HCl(g) H+(aq) + Cl−(aq) acid •A base contains hydroxide and dissolves in water to form −OH. NaOH(s) Na+(aq) + −OH(aq) base 1 Introduction to Acids and Bases •The Arrhenius definition correctly predicts the behavior of many acids and bases. •However, this definition is limited and sometimes inaccurate. 2 Introduction to Acids and Bases The Brønsted–Lowry definition is more widely used: •A Brønsted–Lowry acid is a proton (H+) donor. •A Brønsted–Lowry base is a proton (H+) acceptor. This proton is donated. HCl(g) + H2O(l) H3O+(aq) + Cl−(aq) •HCl is a Brønsted–Lowry acid because it donates a proton to the solvent water. •H2O is a Brønsted–Lowry base because it accepts a proton from HCl. 3 Introduction to Acids and Bases Brønsted–Lowry Bases •A Brønsted–Lowry base is a proton acceptor, so it must be able to form a bond to a proton. •A base must contain a lone pair of electrons that can be used to form a new bond to the proton. This e− pair forms a new bond to a H from H2O. H N H + H Brønsted–Lowry base H2O(l) + H H N H + −OH(aq) H 4 A Lewis acid is defined to be any species that accepts lone pair electrons. A Lewis base is any species that donates lone pair electrons. Thus, H+ is a Lewis acid, since it can accept a lone pair, while OH− and NH3 are Lewis bases, both of which donate a lone pair. 5 Dissociation of Water 6 The pH Scale Calculating pH pH = −log [H3O+] The lower the pH, the higher the concentration of H3O+. •Acidic solution: pH < 7 [H3O+] > 1 x 10−7 •Neutral solution: pH = 7 [H3O+] = 1 x 10−7 •Basic solution: pH > 7 [H3O+] < 1 x 10−7 7