The Periodic Table
advertisement
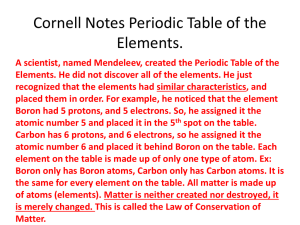
The Periodic Table Section 1 - Organizing the Elements Section 2 - Exploring the Periodic Table Section 3 - Families of Elements State Standards • CLE 3202.1.3 Characterize and classify elements based on their atomic structure • CLE 3202.Inq.1 Recognize that science is a progressive endeavor that reevaluates and extends what is already accepted • CLE 3202.Inq.6 Communicate and defend scientific findings 1 - Organizing The Elements • KEY QUESTIONS : • How did Mendeleev arrange the elements in his periodic table? • How are elements arranged in the modern periodic table? Mendeleev - Recognizing Patterns • By 1860, 60+ elements were known • Dmitri Mendeleev, Russian Chemist, studied properties of the elements • 1869 : he published first Periodic Table of Elements • Arranged by rows of increasing mass number • If chemical properties repeated, new row started – EXAMPLE : Lithium and Sodium are very reactive – Gold and Silver have similar properties, same column Predicting New Elements • Gaps existed in his table - ? • Predicted the properties of Germanium – Description close to what was later found to be Ge • He was the first to use table to predict • Work in Progress – Some predictions did not fit – Te and I fit better in a an inconsistent way – i.e, where the mass number decreased from left - right Changing the Arrangement • Mendeleev’s Periodic Table has been improved – Henry Moseley, ~ 1910 – Elements arranged by atomic number • Resolved problems such as at Tellurium – Iodine – Te has larger average mass, I has 1 more proton – They fit in rows/columns BETTER THAT WAY Mendeleev’s Competition • John Newlands, 1865, Law of Octaves – Every 8th element will mimic each other in The Table • Ordered by Atomic Weights (YET ANOTHER ‘MASS’) • Ridiculed and DISS’ED ( dismissed by peers ) Periodic Law • Metallic properties decrease across PERIODS – Other properties such as reactivity and conductivity • GROUPS have similar properties • Groups – Columns • Periods - Rows • Elements with similar properties appear at regular intervals – The Periodic Law Let’s Describe Some Elements!! • The chemical symbol, C, stands for carbon, which has an atomic number of 6 and an atomic mass [ OR, MASS NUMBER ] of 12.01 – Which value is an average ( average of what? ) – Which value also represents molar mass? • Your turn!! Let’s Describe Some Elements!! • The chemical symbol, C, stands for carbon, which has an atomic number of 6 and an atomic mass [ OR, MASS NUMBER ] of 12.01 • KEY QUESTIONS : • How did Mendeleev arrange the elements in his periodic table? • How are elements arranged in the MODERN periodic table? 2 –Exploring the Periodic Table • KEY QUESTIONS : • Why do elements within a group of the Periodic Table have similar chemical properties? • What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? • What are the three main categories of elements? Role of Electrons • How many electrons in a neutral atom? • Trends in PT are result of electron arrangement • Valence electrons account for similar properties – Example: Lithium and Sodium • Element’s location related to electron arrangement Ion Formation • What is an “ion”? • Once an atom gains/loses electrons, it no longer has a balance between protons/electrons – Charges don’t cancel atom has net electric charge • What is easier – GAIN or LOSE electrons? – Group 1 elements form positive ions ( CATIONS ) – Group 17 elements form negative ions ( ANIONS ) Classifying Elements • Elements in each category have similar properties • Metals • Nonmetals • Semiconductors 2 –Exploring the Periodic Table • KEY QUESTIONS : • Why do elements within a group of the Periodic Table have similar chemical properties? • What happens to an atom that gains or loses electrons? • What are the three main categories of elements? 3 –Families of Elements • KEY QUESTIONS : • What does each element family have in common? • What are the families of metals? • What are some non-metal families? • What are semiconductors Let’s Classify Elements Further • Relate GROUPS of elements to “family” • Elements in family have same # valence electrons • ONLY elements ( not compounds ) are in a family Group Number Number Valence Electrons Name of Family Group 1 1 Alkali Metals Group 2 2 Alkaline-Earth Metals Group 3-12 Varies Transition Metals Group 17 7 Halogens Group 18 8 ( except He – has 2 ) Noble Gases Metals • INCLUDE: Alkali, Alkaline-Earth, and Transition • Alkali metals are very reactive ( Li and Na ) • Alkaline-Earth metals also fairly reactive – Form compounds found in human body/limestone – More solid than Group 1 – Means: harder, denser, higher melting temperature • Transition metals – less reactive than Group 1-2 – Typically more solid than Group 1-2 Transition Metals • Very good catalysts – Catalyst : speeds a reaction up / is not reacted • H2 and O2 explode in presence of Pt catalyst • Some synthetic elements • Technetium and Promethium • Radioactive (nuclei decays into smaller atoms) • Atomic Number > 92 : elements are SYNTHETIC Nonmetals • Families include Noble Gases and Halogens • NOBLE GASES: Group 18 ( Ne, Ar, He ) • HALOGENS: Group 17 ( Cl, F, Br ) – Combine easily with metals to form SALTS • Nonmetals/compounds plentiful on Earth • Carbon – backbone of life ( organic compounds ) – C forms many other compounds Semiconductors • Also called metalloids – B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te • Able to CONDUCT heat and electricity – BUT only under certain conditions – Silicon ( Si ) is found everywhere!! – Boron ( B ) used in steel and glass Hydrogen • Hydrogen is in a class by itself • 1 proton and 1 electron – Reacts with many other elements • Most abundant element in universe – 3 out of every 4 atoms in universe are H 3 –Families of Elements • KEY QUESTIONS : • What does each element family have in common? • What are the families of metals? • What are some non-metal families? • What are semiconductors