Energy and Enzymes
advertisement

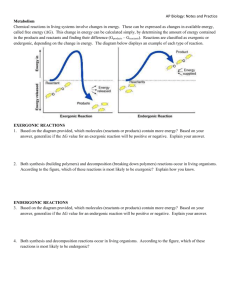
Energy and Enzymes identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic. Things Mr. Lottes would say Something Mr. Gordon would wear Things a Referee does Things you find in the Gym Things you find at the snack bar Things in a class room Catabolic vs. Anabolic • Talk to your neighbor. • What is the difference. • Which uses energy, which makes energy? identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic Identify anabolic and catabolic identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic Energy forms • Identify the picture as either kinetic or potential energy identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic • Identify the picture as either kinetic or potential energy identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic • Identify the picture as either kinetic or potential energy identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic • Identify the picture as either kinetic or potential energy • Heat, or thermal energy identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic What do they have in common Chemical Energy identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic Free Energy • G • Portion of energy able to do work • What does a - G • Exergonic • Endergonic identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic Identify endergonic and exergonic identify reactions as endergonic or exergonic Energy Coupling • What are three types of work that cells can do? • Chemical work • Transport work • Mechanical work describe the key role of ATP in energy coupling Energy Coupling • • • • Vocab words: Phosphorolation ATP ADP describe the key role of ATP in energy coupling Energy Coupling describe the key role of ATP in energy coupling Free Energy catalyst endergonic catabolic ATP Potential Amino acids • 20 amino acids • Joined together by peptide bonds • Amino acid polymer = peptide • Structure determines function • What element is added in proteins? • • • • Primary Structure Secondary Structure Tertiary Structure Quaternary Structure • What is the difference between tertiary and secondary structures? explain how the catalytic cycle of an enzyme that results in the production of a final product Enzymes • Use your book to define the following • Catalyst• Enzyme• Substrate• Active site explain how the catalytic cycle of an enzyme that results in the production of a final product Enzymes • Work by decreasing the amount of energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur. • If less energy is necessary, what do you predict will happen to the speed of the reaction? Activation Energy substrate reactant Active site catalase enzyme Enzyme Properties • They are proteins • Make chemical reaction happen faster • Are not used up in chemical reaction (reused many times) • Specific to only one kind of substrate • Names usually end in ase • Ex: lipase, Catalase, lactase Proteins and enzymes are affected by the following: analyze and predict the effect of enzymes in reactions • Predict why pH and temperature affect enzymatic activity analyze and predict the effect of enzymes in reactions • Competitive and noncompetitive inhibitor analyze and predict the effect of enzymes in reactions