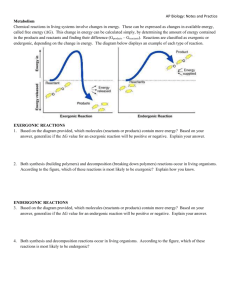
Metabolism Class Work Define metabolism. Define catabolic
advertisement

Metabolism Class Work 1. Define metabolism. 2. Define catabolic pathway. 3. Define anabolic pathway. 4. Give an example of a living system and its surroundings. 5. State the first law of thermodynamics. 6. Give an example of an endothermic system. 7. Give an example of an exothermic system. 8. Define entropy. 9. True of False: Spontaneous reactions occur quickly but only in one direction. Explain Homework 10. What role do enzymes play in metabolic pathways? 11. True of False: The energy of the Universe is not constant. Explain. 12. Give an example of a nonliving system and its surroundings. 13. Define endothermic. 14. Define exothermic. 15. As entropy decreases in an organism, what happens to the entropy of the Universe? 16. State the second law of thermodynamics. 17. What is a spontaneous reaction? Class Work 18. Do endergonic reactions have a positive or negative ∆G? 19. Which type of reaction occurs spontaneously? Exergonic or endergonic. 20. Does a spontaneous reaction increase or decrease the entropy of the universe? 21. What is the ∆G of a reaction that occurs spontaneously? 22. What is the ∆G of a reaction that does not occur spontaneously? Homework 22. Describe how Gibbs Free Energy and the spontaneity of reactions are related. 23. Do exergonic reactions have a positive or negative ∆G? 24. Which type of reaction does not occur spontaneously? Exergonic or endergonic. 25. Which type of reaction releases energy? Exergonic or endergonic. 26. In which kind of reaction do the products have more free energy than the reactants? Exergonic or endergonic. Class Work 27. How are biological systems able to get endergonic reactions to occur? 28. What is the ∆G of a coupled reaction? 29. Name one type of energy used in living organisms? 30. How many phosphate groups are in one molecule of ATP? 31. When ATP is changed to ADP, is Gibbs Free Energy raised or lowered? 32. What type of endergonic reactions does ATP power? Homework 33. Do endergonic processes always directly follow exergonic processes? 34. What are the three types of work done by cells? 35. When changing from AMP to ADP to ATP is energy consumed or released? Explain why. 36. What process is used to break the bond between the second and third phosphate group? 37. True or False: Life is not in equilibrium. Explain. Free Response 1. The constant flow and exchange of materials is one of the driving forces that allow life to proceed. a. Explain how the terms enthalpy, endothermic, and exothermic are related. b. Give an example of an exothermic system. 2. Gibbs free energy is a defining factor in whether or not a reaction will occur spontaneously. a. Explain the relationship between ∆G and the spontaneity of a reaction. b. Explain why living organisms need to couple reactions. 3. ATP is the currency of energy in living things. a. Explain the process of formation of ATP from ADP. b. Explain how ATP is used to provide energy for other reactions in the cell. Metabolism- Answer Key 1. All the chemical reactions that happen in living organisms to maintain life. 2. Break down complex molecules into simpler ones by releasing energy 3. Build complex molecules from simpler ones while consuming energy 4. Multiple answers acceptable. Ex. System: plant Surroundings: dirt, air, sun 5. Energy is neither created nor destroyed. 6. A turkey in the oven 7. A cup of hot coffee sitting on a table. 8. Measure of disorder 9. False: Spontaneous does not mean quickly, but means without outside intervention. Spontaneous reactions do only occur in one direction though because in the other direction the reaction is not spontaneous. 10. Enzymes catalyze the individual reactions in a metabolic pathway 11. False: The energy of the universe is constant; this is the first law of thermodynamics. 12. System: a tea kettle Surroundings: stove, air, kitchen 13. Heat is absorbed by the system 14. Heat is released by the system 15. The entropy of the universe increases; the second law of thermodynamics 16. The entropy of the universe is continually increasing 17. A reaction that occurs without outside forces 18. Positive 19. Exergonic 20. Increase 21. ∆G is negative 22. ∆G is zero or positive 23. When Gibbs free energy is a negative value, then the reaction is spontaneous. When Gibbs free energy is zero or positive, then the reaction does not occur spontaneously. 24. Endergonic 25. Exergonic 26. Endergonic 27. By coupling spontaneous exergonic reactions with endergonic reactions so that the total Gibbs Free Energy between the two reactions still has a negative value. 28. A negative value 29. ATP 30. Three 31. Lowered 32. Phosphorylation reactions 33. No, the energy from exergonic processes can be stored to power endergonic reactions at a later time. 34. Mechanical, transport, chemical 35. Energy is consumed because it takes work to overcome the repulsion of the negative charges on each phosphate group in order to add another phosphate group. 36. Hydrolysis 37. True: Life is not in equilibrium. Life requires a constant flow and exchange with the environment making it an open system. Free Response Answers 1. a. Enthalpy is the measure of heat in a system. When heat is absorbed by the system, or the enthalpy increases, the process is endothermic. When heat is lost by the system, or the enthalpy decreases, the process is exothermic. b. Multiple answers are acceptable: Mug of hot chocolate placed on the table. 2. a. If Gibbs free energy or ∆G is negative for a particular reaction, then the reaction will occur spontaneously. If ∆G is positive or zero, then the reaction will not occur spontaneously. b. Living organisms have specific endergonic reactions that they need to perform. Since these endergonic reactions do not occur spontaneously, the endergonic reaction will couple with a exergonic reaction therefore using the energy released from the exergonic reaction to power the endergonic reaction. In these coupled reactions the total ∆G is negative indicating that the coupled reactions occur spontaneously or without the input of other outside energy. 3. a. ADP is a molecule that has only two phosphates; in order to form ATP, which has three phosphates, energy is put into the reaction. Energy is needed to overcome the electrostatic repulsion provided by the negative charge that each phosphate group carries. ADP undergoes phosphorylation to form ATP. b. When ATP is hydrolyzed to form ADP and a phosphate, energy is released. This energy can then be used to power endergonic reactions in the cell.