PHG 322 lecture 2
advertisement

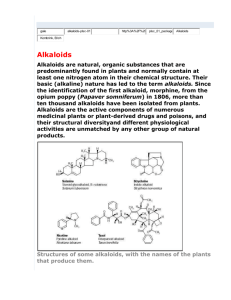
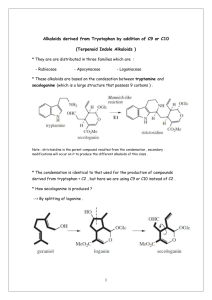
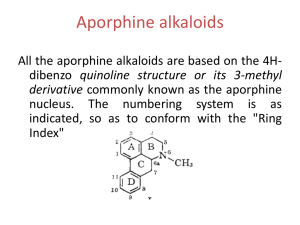
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم PHG 322 PHARMACOGONSY II LECTURE 2 PRESENTED BY ASSISTANT PROF. DR. EBTESAM ALSHEDDI Stability: Generally alkaloids are decomposed by heat except: caffeine sublimes without decomposition Effect of Acids: hot dil. acids or conc. mineral acids may cause: O-demethylation e.g. codeine apoalkaloids e.g. morphine apomorphine Next page ! conc HCl or HI morphine + CH3Cl or CH3I 2 Dehydration Stability: (cont.) Effect of Acids: (cont.) hot dil. acids or conc. mineral acids may cause: Hydrolysis of e.g. atropine - glucoalkaloids: e.g. solanine 3 - ester alkaloids: Stability: (cont.) Effect of Alkalies: Effect of weak alkalies Effect of strong alkalies liberate most alkaloids from their salts Effect of hot dil. alkalies form salts with alkaloids containing carboxylic group e.g Narceine + NaHCO3 Na salt b) Effect of strong alkalies: phenolic alkaloid salt (phenates) + aq. NaOH or KOH c) Effect of hot dilute alkalies: hydrolysis of ester alkaloids e.g. atropine cleavage of lactone ring corresponding acid e.g. pilocarpine Pilocarpic acid Tests for identification: include two types of reactions: Precipitation reactions Colour reactions 1) Precipitation reactions: aqueous soln. of alkaloidal salts precipitating reagent + (contains heavy metals e.g. Hg, Cd, Bi, …) Coloured ppts N.B. (amorphous or crystalline) certain alkaloids do not react e.g. caffeine • false positive results are possible 6 most reagents precipitate: proteins, tannins, … Classification of Alkaloidal precipitating agents: 1- Reagents that form double salts: a- Mayer’s Reagent: Potassium Mercuric Iodide. b- Dragendorff’s Reagents: Potassium Iodobismethate. c- Gold Chloride. 2- Reagents Containing Halogens: a- Wagner’s Reagent: Iodine/ Potassium Iodide. 3-Organic Acids: a- Hager’s Reagent: Picric Acid b- Tannic Acid. 4- Oxygenated High Molecular Weight Acids: a- Phosphomolybdic acid b- Phosphotungestic acid c- Silicotungestic Acid Colour Reagents: solid (free base) + colour reagent (contain conc H2SO4 + an oxidizing agent) characteristic colour 1- Froehd’s Reagent: Phosphomolybdic acid 2- Marqui’s Reagent: Formaldehyde/ Conc. H2SO4 3- Mandalin’s Reagent: Sulphovanidic acid 4- Erdmann’s Reagent: Conc. HNO3/Conc. H2SO4 5- Mecke's Reagent: Selenious acid / conc. H2SO4 6- Shaer's Reagent: Hydrogen peroxide / conc. H2SO4 7- Rosenthaler's Reagent: Potassium arsenate / conc. H2SO4 8- Conc. HNO3 These tests are sensitive to micro amounts used for colourimetric determination (quantitative) - specific for one alkaloid or a group of related alkaloid: 1) Vitalis test for solanaceous alkaloids: + conc HNO3 & alc. KOH violet colour 2) Van-Urks test for ergot alkaloids: blue colour 9 + PDAB in conc H2SO4 Pharmacological activity: wide range of pharmacological activities Pharmacological activity Alkaloid Analgesic & narcotics Morphine Anti-tussive Codeine CNS stimulant Mydriatic Anticancer Caffeine & strychnine Atropine Vincristine, vinblastine, taxol 10 Chemical classification:• = Atypical alkaloids (Protoalkaloids) Heterocyclic = typical alkaloids 14 major groups according to ring structure 11 Non-heterocyclic I. Alkaloids of the Pyridine nucleus: classified according to building nucleus into: Pyridine nucleus only Pyridine nucleus + another nitrogenous ring Tetrahydropyridine nucleus N Piperidine nucleus Pyridone nucleus N H 12 1) Pyridine alkaloids containing another nitrogenous ring: e.g. Tobacco alkaloids H H N (-)-nicotine (major) N CH3 H H N N nor-nicotine CH3 N nicoteine 13 N Volatile liquids non-volatile liquid Nicotine Properties: Colourless or pale yellow oily liquid air or light brown H N less basic N CH3 2 basic N atoms Tests: nicotine picric + acid Crystals 14 form salts with acids Pharmacological actions & uses: Little use in medicine In small doses In larger doses due to high toxicity respiratory stimulant respiratory depressant Increases incidence of abortion Insecticide & anthelmintic in veterinary medicine 15 Main use: 2) Piperidine alkaloids: e.g. alkaloids of: a) Black pepper c) Lobelia b) Conium d) Pomogranate a) Pepper alkaloids: Occurrence: fruits of Piper species e.g. P. nigrum Major alkaloid: piperine + acid Colour tests+ H2SO4 No salt Red colour 16 It is very weak basic soluble in:• CHCl3 & EtOH insoluble in:• Piperine • H2O + alc KOH Piperidine + Piperic acid Crystal tests blue crystals 17 alc. soln. + Wagner`s reag. Uses: Mainly as condiment Used in rubefacient preparations Little use in medicine Chronic toxicity: Prologed use at high doses 18 loss of taste buds in tongue C- LOBELIA ALKALOIDS Occurrence: the dried aerial parts of Lobelia inflata.(indian tobacoo) Major alkaloid: Lobeline crystalline) Uses: -Asthma -Chronic bronchitis -Anti-smoking preparations -Injection of lobeline hydrochloride is used in the resuscitation of newborn infants. Caution: Toxic doses the herb has a paralytic effect D- POMEGRANATE ALKALOID Occurrence: the fruit rind, root bark and stem bark of Punica granata Major alkaloid: pelltierine (liquid) pelletierine tannate (mixture, solid) Alkali decompose it to give free alkaloids Pomegranates have astringent properties because of the alkaloids (pelletierine tannate) present in the bark of the stems and roots and have been used for many years as an anthelmintic: removing tapeworms II. Alkaloids of the Quinoline group Most important → Cinchona alkaloids Cinchona alkaloids Present in the bark Cinchona species - Cinchona ledgeriana & C. calisaya (yellow Cinchona) - C. succirubra (red Cinchona) F. Rubiaceae e.g. of alkaloids: two groups of stereoisomers: Quinine (l) & Quinidine (d) > 50% Cinchonidine (l) & Cinchonine (d) Quinine (Cinchonidine epimer at C-9) Quinidine (Cinchonine epimer at C-9) Structure: CH CH2 CH2 CH2 9 HO H C N R Alkaloid H Cinchonine & cinchonidine OCH3 Quinine & quinidine R N Quinine: 23 Intensely bitter solid Quinine (l) gives amyl alcohol Cinchonine & quinidine Quinidine (d) among other products when warmed with KOH in Cinchonidine are less soluble in H2O than quinine & Test: 1) Fluorescence test: + dil H2SO4 Fluorescence + ve for quinine & quinidine 2) Thalleoquine test: aq. soln of alkaloidal salt + Br2/H2O + NH4OH 24 Emerald green colour Uses: Quinine used as as Quinine sulphate or other salts anti-malarial has febrifuge effect (contra indicated in pregnancy as it causes abortion) Quinidine used as cardiac depressant (anti-arrythmic) 25 Cinchonine and Cinchonidine are used as anti-rheumatic Structure activity relationship: For antimalarial activity (Quinine): loss of activity - Removal of vinyl group - Replacement of CHOH by: - CHCl, CH2, CO decreases activity Vinyl group CH CH2 CH2 CH2 9 HO H C N N 26 CH3O III. Alkaloids of the Isoquinoline group N Opium (Papaverine type) 27 Ipecacuanha ISOQUINOLINE ALKALOIDS 1- IPECACUANHA ALKALOIDS Occurrence: Ipecac is the dried roots and rhizomes of Cephalis ipecacuanha (Brazilian ipecacuanha) or Cephalis acuminata (Cartagena or Panama ipecacuanha) Fam. Rubiaceae. It contains several alkaloids (2 –2.5 %), mainly emetine (50- 70 % of total alkaloids), with cephaline and psychotrine. MeO RO MeO OMe N H OMe H N R = Me Emetine R=H Cephaline HO OMe OMe N H N Psychotrine Emetine: It is non phenolic and levorotatory. It contains 2 basic nitrogens. Cephaline: It is phenolic and levorotatory. It gives emetine on methylation with (CH3)2 SO4. Psychotrine: Occurs as yellow prisms. It is phenolic and gives cephaline on reduction. It gives emetine on reduction followed by methylation. TESTS FOR IDENTIFICATION OF IPECA ALKALOIDS: Alkaloidal solution in HCl + Ca hypochlorite orange color. Emetine and cephaline + Froehd's reagent: dirty green color (the color with emetine fades by addition of HCl). Psychotrine + Froehd's reagent: pale green color. Cephaline and psychotrine + p-nitrodiazobenzene dye soluble in NaOH purple color. Psychotrine + conc. H2SO4 + HNO3 cherry red color. Emetine + Liebermann's reagent black color. USES: Emetine and cephaeline have antitumour and antiviral activity, but are too toxic for therapeutic use. Emetine and psychotrine are mainly used as emetic drugs. The crude drug is used as expectorant (due to its saponin content) . Emetine HCl has an antiamoebic effect, and are used for the treatment of amoebic dysentry and Fasciola. Ipeca alkaloids are diaphoretic, alone or in combination with opium (e.g. Dover's powder).