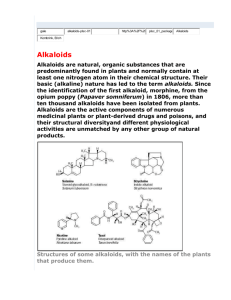
lecture 17
advertisement

Alkaloids derived from Tryotophan by addition of C9 or C10 (Terpenoid Indole Alkaloids ) * They are are distributed in three families which are : - Rubiaceae - Apocynaceae - Loganiaceae * These alkaloids are based on the condesation between tryptamine and secologanine (which is a large structure that possess 9 carbons ) . Note : strictosidine is the parent compound resulted from the condensation , secondary modifications will occur on it to produce the different alkaloids of this class . * The condensation is identical to that used for the production of compounds derived from tryptophan + C2 , but here we are using C9 or C10 instead of C2 . * How secologanine is produced ? --> By splitting of loganine . 1 * Secologanine can occur in the form of Corynanthe group , Aspidosperma and Iboga groups . The exact structure of each type of these groups is not to be memorized. *The typical group is Corynanthe group and the two other groups are resulted by rearrangement of the Corynanthe skeleton . * The simplest way to form beta -carboline and Indolenine is by using the Corynanthe group . * We have two types of cyclization as we mentioned in the alkaloids derived from tryptophan + C2 , which are : - By using the alpha carbon to the (N) atom ( carbon at position 2 ) in tryptamine , and the compound produced will have Beta -carboline structure . - By using the beta carbon to (N) atom ( carbon at position 3 ) in tryptamine , and the compounds produced will have Indoledine structure . * These two carbons ( alpha carbon and beta one ) are the important carbons that are used in the condensation . 2 * The aldehyde group in secologanine is the group which is used in the condensation with the alpha or beta carbons of tryptamine . We will start discussing the plants that have this type of alkaloids : Rauwolfia Serpentina ( Apocynaceae ) : * Its common name is Snakeroot . * Rauwolfia has been used in Africa for hundreds of years, and in India for at least 3000 years. It was used as an antidote to snake-bite, it was used to treat all diseases from snake bite until mental disorders . * Rauwolfia root ecxtract : - Clinical tests showed the drug to have excellent antihypertensive and sedative activity. It was then rapidly and extensively employed in treating high blood pressure and to help mental conditions, relieving anxiety and restlessness, and thus initiated the tranquillizer era. The ‘cure for insanity’ was thus partially justified, and rauwolfia was instrumental in showing that mental disturbance has a chemical basis and may be helped by the administration of drugs. - In the past the root extract was used to lower BP and as sedative tranquilizing agent . Later on the pure compounds ( reserpine , serpentine , rescinnamine ) have been isolated and they started to use pure compounds instead of root extract , but it has been found that when the patients used pure reserpine the suffered from sever depression which may end up by suicidal attempt , so they returned again for the use of root extract rather than the pure compound . * Rauwolfia contains Indole alkaloids which are obtained from roots . * These alkaloids are : Reserpine , Rescinnamine , Deserpidine , Serpentine , Ajmaline , Ajmalicine . 3 * These alkaloids can be subdivided into three groups : Reserpine , Serpentine , Ajmaline , and they can be separated depending on their basicity , the most basic one is serpentine , the intermediate one is the ajmaline , and the least basic are reserpine and rescinnamine . * Serpentine is a beta-carboline , it is yellow in color because it is conjugated , it is a crystalline compounds . * Reserpine has a historical importance because it is the first compound that was used for treatment of different disorders ( hypertension ) . It has known utilization from the clinical point of view for its sedative and tranquilizing activity . * Reserpine has also been suggested to play a role in the promotion of breast cancers . *Ajmaline is the compound which is still used until now as a pure compound ,neither resrpine nor serpentine are of therapeutic use now , ajmaline is used to control cardiac arrhythmia . * Ajmalicine = ( Raubasine ) is used as : spasmolytic , anxiolytic and antihypertensive agent . * These alkaloids are all based on the condensation of tryptamine with secologanine (C9 ) , they are beta-carboline compounds and a few of them are Indolenine alkaloids . Notes about the biosynthesis of these alkaloids : * The biosynthesis will start from the condensation of tryptamine and secologanine and the parent compound will be formed , but the biosynthesis process is not finished by condensation only because you can notice when you look to the structures of these alkaloids that they are huge in structure , so there is secondary modifications to the parent compound which is produced 4 from this condensation which are : hydroxylation , methylation , esterification for the free hydroxyl groups with trimethoxy benzoic acid or trimethoxy cinnamic acid , note that it is not necessary to have all types of modification in the same compound . Yohimbe bark (Pausinystalia yohimbe; Rubiaceae) : * The active ingredient Yohimbine has an importance until now in the treatment of male impotence specially in diabetic patients , it is not a safe drug because it has dose dependent hypotensive or hypertensive activity . * From the recent studies , it has been found that yohimbine has effect on adipose tissue so it can be useful for the treatment of obesity . These studies are only trials which are trying to discover that this compound has activity on adipose tissue but it is not utilized yet . Nux-vomica : * Nux-vomica consists of the dried ripe seeds of Strychnos nux-vomica (Loganiaceae) . * The active ingredients are Strychnine and Brucine (Indolenine alkaloids ) , from medicinal point of view they have low interest . They are toxic and bitter , Strychnine is very very bitter and it is more toxic than brucine . * 100 mg of strychnine is fatal to 70 Kg adult . 60 mg can be fatal depending on the body weight . * Its only medicinal use is in very small doses as an appetite stimulant and general tonic, sometimes with iron salts if the patient is anaemic . * Strychnine can be used in a very small doses as an appetite stimulant because it is very bitter and in a very small doses it can stimulate the secretion of the gastric juices . * Nowadays its only use is as a poison for the rats (vermin killer ). * Loss of All body hair is one of its toxicities when it is used bu humans . *Brucine is less toxic than Strychnine , and its used in some countries for the denaturation of alcohol . *Strychnin is very toxic , and it’s a derivative of Brucin , also Strychnin is used as vermin killer especially for moles . 5 *Strychnous toxifira and its constituent Toxifirine are very toxic , but Toxifirine has the activity similar to D.tuberculin (as muscle relaxant) *toxicity of Strychnine is similar to tetranol toxicity paralysis, CV events, noise, headache. *Toxifirine is dimeric compound of Wieland Gumlich aldehyde. *there are more than one type of Toxifirin ( Toxifirin 1 , 2 , 3 ) *Aleuronium is semi-synthetic muscle relaxant produced from Toxifirin . *Toxifirin are ingredients of Loganicaeous curare also . Venca Alkaloids *Viniblastine and Vincristine are anti-cancer compounds from Catharanthus raserus and Venca rosera . they are antimitotic agents , but they cause serious neurotoxicity . *other disadvantage of them is their low concentration in nature (we need 5000 Kg of their leaves to produce 1 g of them !!) *Venicristine has more pharmacological activity than Viniblastine. *************************** *** NOTE *** When we say Dimeric alkaloids , this means that the alkaloid composed of two IDENTICAL units . while when we say Binary alkaloids , this means that its composed of two NON IDENTICAL units . ************************** *Vincristine is obtained from oxidation of N-methyl of Vinblastine. *they and other primary important Venca alkaloids are composed of two monomeric units (Catharantine and Vendoline) .. notice that these two dimmers are not identical they’re binary alkaloids. *Different anhydroderevatives can be formed also , they are biologically active but they posses a lot of side effects especially cytotoxixity . 6 *Vendisine is semi-synthetic derivative of Viniblastine , and used for acute lymphoid leukemia . *Venorelbine is a semi-synthetic derivative also , but the most important thing about it is that its an oral anticancer agent (unlike other anticancer agents which are IV drugs). The side chain of it is shortened by one carbon unit from the original amino acid for its synthesis “tryptophan” .. and its used for childhood leukemia. *Vinca rosea and Vinca minor , both are close in their shape , they are from same genus but different species. Vinka The Madagascar periwinkle Catharanthus roseus (= Vinca rosea) (Apocynaceae) is a small herb or shrub originating in Madagascar, but now common in the tropics and widely cultivated as an ornamental for its shiny dark green leaves and pleasant five-lobed flowers. Drug material is now cultivated in many parts of the world. The plant was originally investigated for potential hypoglycaemic activity because of folklore usage as a tea for diabetics. Although plant extracts had no effects on blood sugar levels in rabbits, test animals succumbed to bacterial infection due to depleted white blood cell levels (leukopenia), though no other adverse effects were apparent. The selective action suggested anticancer potential for the plant, and an exhaustive study of the constituents was initiated. The activity was found in the alkaloid fraction, and more than 150 alkaloids have since been characterized in the plant. These are principally terpenoid indole alkaloids, many of which are known in other plants, especially from the same family. Useful antitumour activity was demonstrated in a number of dimeric indole alkaloid structures (more correctly, bisindole alkaloids, since the ‘monomers’ are different), including vincaleukoblastine, leurosine, leurosidine, and leurocristine. Vinka rosea and Vinka minor are very similar to each other same genius but different species (Apocynaceae) Independent of vinka minor vinka rosea is cultivated as an ornamental plant. Vinca minor is another representative of the strains vinka and main constituent is vincamine. Vincamine is a monoterpen indole alkaloid (min 35:56) it’s used in the treatment of the difficult feeding bonds. Because it’s processing astringent activity. vincamine also improve the cerebral blood flow by increasing the oxygen and glucose consumption so it’s used primarily in the treatment of samility (min 36:25) it delay not improve the disease. Vincamine is not a safe compound. 7 ***Vincamine sometimes are used in the treatment of disorders of the vascular origin …………. Certain disease having vascular origin processing vasodilator (vincamine is vasoconstrictor). They do not produce anticancer agent*** (min 36:41 – 37:27) Ellipticine (Apocynaceae) Another anticancer agent is the Ellipticine or orchrosia ellptica it’s a βcarbonate type of compound. Clinical trials with these alkaloids and a number of synthetic analogues showed them to be potent inhibitors of several cancerous disorders, but preclinical toxicology indicated a number of side-effects, including haemolysis and cardiovascular effects. Ellipticines are planar molecules that intercalate between the base pairs of DNA and cause a partial unwinding of the helical array. Recent research suggests they also inhibit the enzyme topoisomerase. Ellipticine is oxidized in vivo mainly to 9-hydroxyellipticine, which has increased activity, and it is believed that this may in fact be the active agent. Poor water solubility of ellipticine and derivatives gave problems in formulation for clinical use, but quaternization of 9-hydroxyellipticine to give the water-soluble 9-hydroxy-2-N-methylellipticinium acetate (elliptinium acetate). It’s under clinical investigation. Cinchona (Rubiaceae) Very known representor of the amino acid tryptophan are quinine, quinidine, cinchonidine, and cinchonine. They make up to 60% of the alkaloid among them quinine is the major compound. 8 Quinine: C#8 is S and C#9 is R //// Quinidine C#8 is R and C#9 is S (quinine and quinidine have opposite stereochemistry) Quinine and cinchonidine are different in the presence of the methoxy group with same stereochemistry Quinidine and cinchonine also have the same stereochemistry and differ in the presence of methoxy group in quinidine. Cinchonidine and cinchonine are demethoxy analogues of quinine and quinidine respectively; unfortunately, use of the -id- syllable in the nomenclature does not reflect a particular stereochemistry. Quinine is usually the major component (half to two-thirds total alkaloid content), but the proportions of the four alkaloids vary according to species or hybrid. The two epimers cinchonidinone and cinchoninone equilibrate readily in the plant through keto–enol tautomerism. Finally, reduction of the ketone group gives cinchonidine or cinchonine. Hydroxylation and methylation at some stage allows biosynthesis of quinine and quinidine. Quinine and quinidine, or cinchonidine and cinchonine, are pairs of diastereoisomers, and have opposite chiralities at two centres, C-8 and C-9 .The stereochemistry at C-8 is easily reversed by tautomerism in cinchonidinone and cinchoninone as described above. The stereochemistry adjacent to the quinoline ring (C-9) is controlled by the reduction step. An enzyme catalysing the reduction of cinchoninone produces an unequal mixture of cinchonine and cinchonidine, showing that the stereochemistry of reduction may somehow depend upon the substrate. Cinchona 9 and its alkaloids, particularly quinine, have been used for many years in the treatment of malaria About a dozen different Cinchona species have been used as commercial sources, but the great variation in alkaloid content and the range of alkaloids present has favoured cultivation of three main species, together with varieties, hybrids, and grafts. Cinchona succirubra provides what is called ‘red’ bark (alkaloid content 5–7%), Cinchona ledgeriana gives ‘brown’ bark (alkaloid content 5–14%), and Cinchona calisaya ‘yellow’ bark with an alkaloid content of 4–7%. Selected hybrids can yield up to 17% total alkaloids. Quinine administered as free base or salts, continues to be used for treatment of multidrug-resistant malaria. larger amounts of the alkaloid are consumed in beverages, including vermouth and tonic water. It is amusing to realize that gin was originally added to quinine to make the bitter antimalarial more palatable. Quinine also has a skeletal muscle relaxant effect with a mild curare-like action. It thus finds use in the prevention and treatment of nocturnal leg cramps, a painful condition affecting many individuals, especially the elderly. Until recently, quinidine was used to treat cardiac arrhymias. It inhibits fibrillation, the uncoordinated contractionof muscle fibres in the heart. However, it is rapidly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract and overdose can be hazardous, leadingto diastolic arrest. This has effectively curtailed its use. Quinidine, cinchonine, and cinchonidine also have antimalarial properties, but these alkaloids are not as effective as quinine. The cardiac effect makes 10 quinidine unsuitable as an antimalarial. However, mixtures of total Cinchona alkaloids, even though low in quinine content, are acceptable antimalarial agents. This mixture, termed totaquine, has served as a substitute for quinine during shortages. Cinchona and its alkaloids, particularly quinine, have been used for many years in the treatment of malaria, , it was used as safe analgesic up to the 50s or 60s “for common headache” with the safe drugs now its not used as analgesic anymore , Until recently, quinidine was used to treat cardiac arrhymias. Quinine is not a synthetic compound it’s a natural compound , it’s the secondary metabolite of the cinchona bark , that was first found in south America , it wascultivated world wide especially in china and the eastern part of asia . When this source was cut off by Japan in the Second World War, a range of synthetic antimalarial drugs was hastily produced as alternatives to quinine. Many of these compounds were based on the quinine structure. They took the quinline and substituted it with an amino group , a wide range of compounds was produced, chloroquine, primaquine, and mefloquine. Primaquine is exceptional in having an 8-aminoquinoline structure, whereas chloroquine and mefloquine retain the 4-substituted quinoline as in quinine. The ability of Plasmodium falciparum a” protozoa “ to develop resistance to modern drugs means malaria still remains a huge health problem, and is probably the major single cause of deaths in the modern world. It is estimated that 200– 500 million people are affected by malaria, So it’s a come back to the nature , to the natural quinine. Quinine also has a skeletal muscle relaxant effect with a mild curare-like action. It thus finds use in the prevention and treatment of nocturnal leg cramps, a painful condition affecting many individuals, especially the elderly. Vastly larger amounts of the alkaloid Quinines are consumed in beverages industry , including vermouth and tonic water. Long time use of quinines cause hearing impairment, particularly high-frequency loss. Although some studies suggest that this high-frequency hearing impairment is reversible, it has not been conclusively established whether such impairment is temporary or permanent . 11 Camptothecin It’s obtained from Camptothecaacuminata (Nyssaceae) , it is a further example of a quinoline-containing structure that is derived in nature ,it grows in high altitudes “Himalayas”, all parts of the tree “ bark ,leaves ,roots” contain Campatothecin. Camptothecin derivatives have provided some useful anticancer drug in china , in many clinical trials its used to treat different kinds of carcinomas. Camptothecin is a nature compound originated from the Chinese tree Camptotheca acuminate of the family (Nyssaceae) , all parts of this tree obtain alkaloids seeds , leaves, barks … This plant was used in china for the treatment of cancer In limited clinical trials, camptothecin showed broad-spectrum anticancer activity, but toxicity and poor solubility were problems it is s quinoline based alkaloid Semi-synthetic analogues (9-aminocamptothecin) and the water-soluble derivatives topotecan and irinotecan showed good responses in a number of cancers; topotecan and irinotecan are now available for the treatment of ovarian cancer and colorectal cancer respectively about the structure we are dealing with the amino acid tryptophan to yield our b-cabonyl derivative ,, it is a 6-membered ring all carbons are linked together that includes a pyrrolo[3,4-β]-quinoline moiety (rings A, B and C), conjugated pyridone moiety (ring D) and one chiral center at position 20 within the alpha-hydroxy lactone ring , it is (6-5-6) b-carbonyl compound when we have an indole derivative it is changing from (6-5-6) to a (6-6-5) so we are obtaining a pyrolidine ring (5-membered ring) and the quinoline ring ,, has a very potent biological activity 12 The clinical utilized ones Irinotecan is a carbamate pro-drug by physostigmine , when it is administered in the liver it will be converted to the active drug of the 10-hydroxy camptothecin topotecan is a substituted derivative of camptothecin , and can be used clinically for the treatment of cancers something interesting to say that camptothecin and it's derivatives can be obtained from fungi (endophiles ) not a parasitic type , they cope with the production of the secondary metabolites that are living in the plant itself not in sea ,, as Low concentrations of camptothecin have also been detected in cultures of an unidentified fungus isolated from the inner bark of Nothapodytes foetida 13 If something about the last plant (camptothecin) is not clear you can refer to the below information from the book . 14 15 16 GOOD LUCK Done By : Deema Mohammed, Rokaya Shroukh Ghoujal, Yasmin Abuali, Naffin Yanal, Lina Zahran 17