Ionic Compounds
advertisement

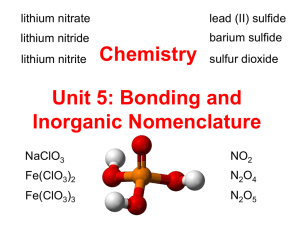
Ionic Compounds Lewis Dot Diagrams Chemical Interactions Occur between the Valence Electrons Dots: represent valence electrons When atoms combine to make molecules, they form chemical bonds. Valence electron interaction • Octet Rule Atoms will form bonds by: Forming Chemical Bonds – Sharing – Giving or – Taking electrons to complete their octet Higher energy farther away from nucleus Atoms form ions to have stable electron configurations (similar to noble gases) hh Ionic Bonds • Ionic Bonds form when one atom (nonmetal) gains electrons and the other atom (metal) loses electrons in order to gain stability. • Ionic Bonds form between a metal (cation) and a nonmetal (anion). To form an ion, lithium will most likely: Gain 1 electron Gain 2 electrons Lose 1 electron Lose 2 electrons 91% 3 4 5% 0% 2 5% 1 1. 2. 3. 4. Forming Chemical Bonds • Lithium –Better to lose 1 electron or to gain 7 electrons? X Therefore, as an ion lithium will have what charge? 73% 27% 4 0% 3 0% 2 1+ 2+ 12- 1 1. 2. 3. 4. Ionic Bonds • Atoms gain or lose its electrons + NaCl salt Chemical Interactions Occur between the Valence Electrons Lewis structures are simpler to do & see Formation of MgCl2 Formation of Na2S • Write down the chemical formula for Aluminum Flouride Formation of AlF3 Today is a practice Day! • We need to be able to name ions given chemical formula • We need to be able to determine the chemical formula given the name Valence Electrons Noble Gas Structure = Octet 1,2 3,4,5,6,7,8 IONIC BONDS / Cations and Anions Cation – positive ions Transition Metals use Roman Numerals to tell you the ox # Anion – negative ions Oxidation Numbers • Oxidation Numbers - indicated # of e’ lost, gained or shared. Ex. Oxidation number of chlorine is -1 Halogens will have an oxidation number of: 0% 0% -2 0% 2 0% -1 +1 +2 -1 -2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. Alkaline earth metals will have an oxidation number of: 0% 0% -2 0% 2 0% -1 +1 +2 -1 -2 1 1. 2. 3. 4. We will name binary compounds together • Using pages 156- 158 • Describe how to name cations and anions when they are by themselves Naming Binary Ionic Compounds • Write the name of the ionic compound, Ca2N3. • Write the name of the ionic compound, K2O. What is the name of BeBr2? Boron bromine Beryllium bromine Bromide beryllide Beryllium bromide Beryllide bromide m lid e br o liu m 0% br om ... ... 0% l.. . Be ry l id e Br om liu m ry l Be be br o ry l m in e m br o n 0% Be ry l 0% ... 0% Bo ro 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Metals with Variable Charges • Many transition metals can form more than one type of cation. • For this reason, you must show the oxidation number in the name using Roman Numerals Naming Binary Ionic Compounds with Transition Metal Cations • Write the name of the ionic compound, Cu2O.. • Write the name of the ionic compound, NiS. What is the name for SnBr2? Bromide Tin Tin Bromide Tin (I) Bromide Tin (II) Bromide Tin (III) Bromide Tin (IV) Bromide 0% 0% 0% 0% 0% Br om id Ti e n (I) Br om id Ti . .. n (II )B ro m i.. Ti . n (II I) Br om Ti . .. n (IV )B ro m i.. . n Ti id e Ti n 0% Br om 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. What is the name for FeI3? Iron iodide Iron (I) iodide Iron (II) iodide Iron (III) iodide (I I I) i Iro n (I I )i od io (I ) Iro n Iro n di d di de io 0% od ... 0% i.. . 0% ... 0% Iro n 1. 2. 3. 4. What is the name for MnS? Manganese sulfide Manganese (I) sulfide Manganese (II) sulfide Manganese (III) sulfide 0% II I ... 0% e( ne s M an ga M an ga ne se (II (I) .. . ).. . 0% ne se an ga M an ga ne se su lf. .. 0% M 1. 2. 3. 4. Exceptions: • Some of the transition metals have only one ionic charge: –Do not need to use roman numerals for these: –Silver is always 1+ (Ag1+) –Cadmium and Zinc are always 2+ (Cd2+ and Zn2+) Writing Formulas for Binary Ionic Compounds • Write the formula for barium iodide. • Write the formula for sodium oxide. • Write the formula for aluminum nitride. • Write the formula for copper (I) sulfide. Criss-Cross Method for Writing Formulas - You can write the oxidation number and criss-cross them 3+ Al 2 as subscripts. 2S - Note – if not in lowest terms = Al2S3 you must reduce the subscripts (ex. Magnesium oxide) 3 What is the formula for aluminum bromide? AlBr AlBr2 Al3Br Br3Al AlBr3 r3 0% Al B 0% Br 3A l 0% Al 3B r r2 0% Al B r 0% Al B 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is the formula for magnesium oxide? MgO Mg2O2 MgO2 Mg2O OMg g 0% OM M M 0% g2 O 0% gO 2 0% M g2 O2 gO 0% M 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Write the formula for titanium (II) chloride. TiCl Ti2Cl TiCl2 Ti2Cl2 2C l2 0% Ti Cl 2 0% Ti 2C l 0% Ti Cl 0% Ti 1. 2. 3. 4. Write the formula for tin (IV) oxide. SnO SnO4 SnO2 Sn4O Sn2O 0% Sn 2O 2 0% Sn 4O Sn O 0% Sn O 0% 4 0% Sn O 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. POLYATOMIC IONS • Not all compounds are made of only 2 types of atoms • poly – “many” Memorize the polyatomic ions from p. 170. Tricks for Polyatomic Naming Perchlorate chlorate chlorite Hypochlorite per+root+ate root+ate root+ite hypo+root+ite ClO4-1 ClO3-1 ClO2-1 ClO-1 Prefixes and suffixes designate number of oxygens Naming Polyatomic Ionic Compounds • Polyatomic ionic compounds are named just like binary ionic compounds. • Exception: be sure to enclose the polyatomic ion in parentheses before writing the subscript (only necessary if subscript is not 1). • Ex. Barium hydroxide = Ba(OH)2 Write the formula for Calcium Nitrate. CaNO2 Ca(NO2)2 Ca2NO3 Ca2NO2 Ca(NO3)2 0% Ca ( NO 3) 2 0% Ca 2N O2 0% Ca 2N O3 NO 2) 2 0% Ca ( O2 0% Ca N 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Write the formula for Magnesium Phosphate. MgPO4 Mg3(PO4)2 Mg4(PO3)2 MgPO3 Mg(PO4)2 0% O4 )2 g( P M gP O 3 0% M O3 )2 0% M g4 (P O4 )2 0% M g3 (P gP O 4 0% M 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Naming Ionic Compounds