KIST cooperation meeting Bern - Science & Technology Office Seoul
advertisement

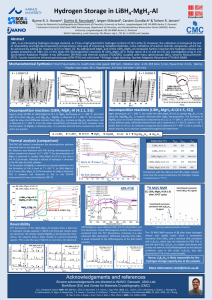
Innovation in Material Science and Technology Cooperation with KIST Gian-Luca Bona, www-empa.ch Empa’s Research Focus Areas Nanostructured Materials Health & Performance Analytical Methods Measurement Techniques Instruments & Tools 20.38% Assessment of Sustainability, Reliability & Safety Computational Modelling Material Synthesis Natural Resources & Pollutants Energy Sustainable Built Environment 2 Example: Ongoing Collaboration on H2 Storage Dr. CHO Young Whan Principal Research Scientist Materials Science and Technology Research Division Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) History of Collaboration on Hydrogen Storage 2008 Ji Woo KIM (1. 2. 2008 - 31. 1. 2009) as PhD student at EMPA Div. Hydrogen & Energy. Investigation of the reaction mechanism of the destabilized LiBH4 system with Al additive, so called reactive composite hydrides. 2008 KOREAN- SWISS INTER-GOVERNMENTAL COOPERATION PROGRAM “Novel complex metal hydrides for hydrogen storage”, 2 years, between Young Whan Cho, Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and Andreas Züttel EMPA Div. Hydrogen & Energy. [4, 5, 6] 2012 Collaborative research agreement “Properties of Nanosized Hydrides” between Young Whan Cho, Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) and Andreas Züttel EMPA Div. Hydrogen & Energy for 2 years. So far a total of 7 joint publications in this area Next Step: Stability of adsorbed C-H species Cluster synthesis, DFT calculations, Hydrides 3 RESULTS Towards room temperature, direct, solvent free synthesis of tetraborohydrides, e.g. LiBH4 Due to their high hydrogen content, tetraborohydrides are discussed as potential synthetic energy carriers. On the example of lithium borohydride LiBH4, we discuss current approaches of direct, solvent free synthesis based on gas solid reactions of the elements or binary hydrides and/or borides with gaseous H2 or B2H6. The direct synthesis from the elements requires high temperature and high pressure (700°C, 150bar D2). Using LiB or AlB2 as boron source reduces the required temperature by more than 300 K. Ref.: A. Remhof, Y. Yan, O. Friedrichs, J. W. Kim, Ph. Mauron, A. Borgschulte, D. Wallacher, A. Buchsteiner, A. Hoser, K. H. Oh, Y. W. Cho, A. Züttel, , Journal of Physics: Conference Series 340 (2012) 012111 Ref.: Friedrichs, O; Kim, JW; Remhof, A; Wallacher, D; Hoser, A; Cho, YW; Oh, KH; Zuttel, A, Physical 4 Chemistry Chemical Physics 12:18 (2010), pp. 4600 - 4603. 5