Chapter 4
advertisement

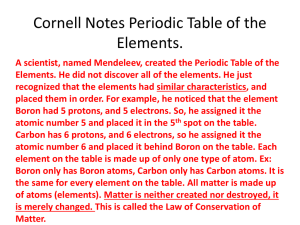
Chapter 4 Elements and the Periodic Table 8th Grade Science Introduction to Atoms • Greek philosopher named __________ Democritus proposed that matter is made up of tiny particles that cannot be made any smaller • ________ “Atomos” - means “uncuttable” Atom - smallest particle of an element • _____ Atomic Theory - formed in the 1600’s as a • ___________ series of models developed from experimental evidence. Atomic Theory • As more experiments were conducted and evidence collected, the theory and models were revised. Dalton’s Atomic Theory - John Dalton, English • ________________ chemist, inferred that atoms had certain characteristics. • Dalton’s atomic theory is still accepted today! • Atoms were like smooth, hard balls that cannot be broken down Summary of Dalton’s Ideas page 103 • All elements are composed of atoms that cannot be ______. divided • All atoms of the same element are exactly alike and have the same ____. mass changed • An atom of one element cannot be _________ into an atom of a different element – only rearranged. • Every ________ compound is composed of atoms of elements different _________ combined in a specific ________. ratio Thomson Model JJ Thomson • ___________ - 1897 atoms have negatively charged electrons embedded in a positive sphere. • _______ electrons - negatively charged particles Rutherford and the Nucleus • 1911 - ____________ Ernest Rutherford - a student of Thomson, found evidence that contradicted Thomson’s model. • ______________ Gold Foil Experiment - beam of positively charged particles aimed at a thin sheet of gold foil. Most of the particles passed through the foil as expected. However, a few particles were deflected _______. Conclusions from the Foil Experiment • Since like charges _____ repel each other, Rutherford concluded that an atom’s positive _________ charges must be clustered in the _____ center of the atom. • ______ nucleus - center of the atom • ________ electrons - no mass protons • ________ - positively charged particles that have mass and are located in the nucleus of the atom. Rutherford’s Model Bohr’s Model Neils Bohr • ___________ - 1913, Danish Scientist, student of both Thomson and Rutherford – electrons orbit move around the nucleus in certain _____ based on energy levels. • Bohr’s Model resembles planets orbiting the sun or layers of an onion. Cloud of Electrons • 1920’s – atomic model changed again • Scientists determined that electrons DO NOT orbit the nucleus like planets. • _________ can be anywhere in a cloudlike region Electrons around the __________. nucleus electrons movement is related to its • An _______ _________ Energy level - specific amount of energy that it has. Energy level • ____________ affects the atoms reactions with other atoms. The Modern Atomic Model James Chadwick discovered another particle in • ___________ the nucleus of atoms. • _________ - particle discovered by Chadwick Neutrons that has no electrical charge and nearly the Protons same mass as _______. • _______________ Modern Atomic Model - consists of a nucleus that contains protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloudlike region of moving electrons. Particle Charges • In an tom the number of ________ equals the protons Electrons number of __________. • _________ have a positive charge and a mass ____ Protons • _________ have a negative charge and very electrons mass little _______. • _________ have neutral charge and a mass Neutrons that equals that of protons. Positive Protons • ________ charge of ________ equals the ________ charge of _________. negative Electrons Masses and Charges Particle Symbol Charge Relative Mass (amu) Proton p⁺ 1₊ 1 Neutron n 0 1 Electron e⁻ 1₋ 1/1,836 • Charges balance making the atom neutral • Number of neutrons does not have to equal the number of protons • Neutrons do not affect the charge of an atom because they have no charge • Approximately 2,000 e⁻ equal mass of one proton. Atomic Number • Every atom of an element has the same number of _________. protons Atomic Number • _____________ - number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. • Atomic number identifies an _________. element • _______ Isotopes - atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. Mass number • __________-sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. Patterns in the Elements _____________ Dmitri Mendelev - Russian scientist discovered a set of patterns that applied to all elements. Mendelev arranged the elements in order of increasing __________. Atomic mass Periodic table ____________ - organization of the elements where the properties of the elements repeat in each row of the table. ___________ Henry Moseley - Brittish scientist discovered a way to measure the positive charge on an atom’s nucleus – the atomic number. Periodic Table of Elements • After Moseley’s discovery, the periodic table was rearranged from Atomic ________ _________. mass toAtomic number • Properties of an element can be predicted based on its place in the ___________. Periodic table • Periodic table is arranged according to ___________ Atomic number increasing from left to right. periods • ________ - horizontal rows on the periodic table where the properties of the elements change in a set pattern. Organization of the Periodic Table • Elements on the left side of the periodic table are _______________. Highly reactive metals • Elements in the middle of the periodic table are ______________. Less reactive metals • Elements on the right side of the periodic table are _________________. Metalloids and non-metals • ______ Groups - 18 vertical columns or “families” on the periodic table with similar characteristics such as rate of reaction. (except lanthanides and actinides). Reading the Periodic Table • Each element in the periodic table has all of the following: – ____________ Atomic Number - number of protons in the nucleus Chemical Symbol - 1 or 2 letter representation – _____________ – ____________ Element Name – __________ Atomic Mass - average mass of all of the isotopes of the element. Metals • Physical properties of metals: – ________ shininess – __________ malleability - material can be hammered or rolled into flat sheets and other shapes. ductility - material can be pulled out or drawn – _______ into a thin wire – __________ conductivity - ability of an object to transfer heat or electricity to another object. – ___________ Mercury (Hg) - metal that is liquid at room temperature Chemical Properties of Metals • _________ - the ease or speed of an element reactivity to combine or react to other elements and compounds. elements • Metals usually react by losing ________ to other atoms. • Sodium (Na) is very reactive where gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) are much less reactive. • __________ - the destruction of a metal corrosion because of its reactivity. Metals in the Periodic Table • _______ reactivity of metals decreases from left to right on the periodic table. • ____________ - metals in Group 1 on the Alkali Metals periodic table that react with other elements by losing one ______. electron • Alkali metals are never found in __________ uncombined elements in nature – only in compounds. • ___________________ Sodium(Na) and potassium (K) - two most important alkali metals – important for life processes. Alkali Earth Metals Alkali Earth Metals - Group 2 on the periodic • ______________ table that react with other metals by losing two electrons. • Not as reactive as metals in __________ but Group 1 more reactive than ,most other metals. • Never found uncombined in nature. • ______________________ Magnesium (Mg) and Calcium (Ca) - two most common alkali earth metals. Other Elements on the periodic table • ____________ Transition Metals - elements in Group 3 through 12. These metals are hard and shiny, good conductors of electricity, less reactive than metals in Groups 1 and 2. ________ is an Iron (Fe) example of a very important transition metal. • _______________ Groups 13, 14, and 15 - only some are metals such as aluminum, tin and lead • _________ Lanthanides - two rows of elements at the bottom of the periodic table. Lanthanides • __________ - soft, malleable shiny metals Lanthanides with high conductivity. • Lanthanides mix with other metals to form _____. alloys • _____ alloy - mixture of a metal and at least one other element, usually another metal. Actinides • _________ - only four occur naturally on earth – all others were created artificially. These elements are VERY unstable. Ex. Uranium Synthetic Elements Synthesized • ____________ - elements that follow uranium that are not found naturally on Earth – when nuclear particles are forced to crash into one another. • _____________ Particle accelerator - powerful machines used by scientists to move atomic nuclei to very high speeds. Non-metals and Metalloids • Physical properties of non-metals: Poor conductors – ______________ – _____________________ Reactive with other elements – ______________ Dull and brittle – Many non-metals are common elements on Earth 10 of 16 gases at room – ________non-metals are ______ temperature. Bromine (Br) - only non-metal that is liquid at – ___________ room temperature Chemical Properties of Non-Metals gain share • Atoms of non-metals usually _____ or ______ electrons with atoms that they react with. • When metals and non-metals react, _________ move from the metal atoms to the electrons non-metal atoms. • Non-metals can also form compounds with other non-metals. Families of Non-metals • 1. _______________ - Group 14 only carbon The Carbon Family is a non-metal. atoms that gain, lose, or share four ____electrons when reacting with other elements. • 2. ______________ The Nitrogen Family - Group 15 contains two non-metals, nitrogen and phosphorous. These atoms usually gain, lose or share _______ three electrons when reacting with other elements. • 80% of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas (N₂) Families of Non-Metals continued The Oxygen Family - Group 16 contains three • 3. _____________ non-metals – oxygen, sulfur and selenium. Elements in the oxygen family usually gain or share ___ two electrons. • _________ is highly reactive – it can combine oxygen with nearly any other element. most most abundant element in • Oxygen is the ____ the atmosphere (Nitrogen is first) The Halogen Family • 4. ______________ The Halogen Family - Group 17 contains flourine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and astatine (not a non-metal). Halogen _______ means “salt forming”. Halogen atoms usually gain or share ____ one electron when it reacts with other elements. • All halogens are __________ Very reactive and can be dangerous to humans. • Many compounds that contain halogens can be useful to humans – salt, flourine in water, calcium chloride. Noble Gases • __________ Noble Gases - elements in Group 18 that do not ordinarily form compounds because atoms of noble gases do not usually gain, lose, or share electrons. unreactive • These gases are usually ___________. • All of the noble gases exist in the Earth’s atmosphere ___________. • Noble gases were not discovered until late 1800’s because they are _______ unreactive and ________. scarce Hydrogen Hydrogen (H) - in the upper left corner of the • __________ periodic table. • Hydrogen makes up more than 90% ___ of the atoms in the universe. Pure element • Hydrogen is rarely found as a ___________. Metalloids • ____________ - along the border between Metalloids metals and non-metals. 7 • There are ___ metalloids and they have characteristics of both metals and non-metals. • All metalloids are solid ____ at room temperature. • Metalloids are also brittle, hard, somewhat reactive, varying ability to conduct heat and electricity Silicon (Si) - most common metalloid • ________ Semiconductors Semi-conductors - substances that conduct • ____________ electricity under some conditions but not under others. • ________ metalloids are used as semiconductors because of their physical properties. • Semiconductors are used to make _________, lasers Computer chips transmitters _____________, and ___________. Radioactive Elements • _____________ Radioactive Decay - the atomic nuclei of unstable isotopes release fast moving particles and energy. Henri Becquerel • _____________ - French scientist in 1896 discovered the effects of radioactive decay while he was studying a mineral that contained uranium. Marie Curie is the • ___________ - named after __________ radioactivity spontaneous emission of radiation by an unstable nucleus such as uranium. Types of Radioactive Decay • Natural radioactive decay can produce ___________, ____________, and Alpha particles Beta particles Gamma rays ___________. • _________ Alpha decay - an alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons and is positively charged. The release of an alpha particle by an atom is decreases the atomic number by __ 2 4 and the atomic mass by __ Beta Decay • __________ - a neutron inside of the nucleus Beta Decay of an unstable atom changes into a negatively charged beta particle and a proton. • __________ Beta particle - fast moving electron given off by a nucleus during radioactive decay. • Nucleus has one _____ neutron and one ____ less more proton – therefore, the atomic mass stays the same but the atomic number increases by __ 1 Gamma Radiation Gamma Radiation - consists of high-energy • _____________ waves – has no charge and does not cause a change in either atomic mass or atomic number. Effects of Nuclear Radiation Radioactive Isotopes