U9D4 Double Replacement
advertisement

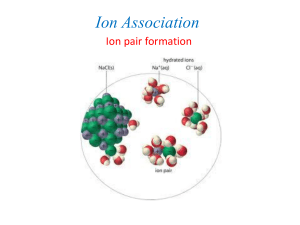
Ion Exchange Reactions Different Motivation = Different Results! U9D4: Double Replacement Rxn HW: see schedule; Type of Reaction cartoon due tomorrow Do Now: 1. HW out for check/answers 2. Complete Work Packet p. 6 A. Be prepared to defend your answers Today: 1. HW answers 2. Redox Check 3. Double Replacement Rxn notes 4. Practice 5. Will They Won’t They Announcements Unit 9 Practice test is online Testwizard.com Class codes were sent home via SchoolTool Period 1: CCQF-ASIM-S3 Period 2: CCQB-ASIM-R6 Period 3: CCQN-ASIM-WQ Quarterly Topic Sheet was sent home via SchoolTool Chemthink.com is a great website for review Student code: 4679-7503-9706 Hwk #3) REDOX Reactions Homework A) Multiple Choice Questions: Place your answer in the space in front of each question. C _____1) In the reaction 2 Na + 2 HCl 2 NaCl + H2, which species is the spectator ion? a) Na0 b) H+1 c) Cl-1 d) Na+1 Why is this the spectator ion? Explain, in terms of ion charge. Cl- has the same ion charge as a reactant and product. It is not involved in the reaction. A _____2) In the reaction Zn + 2 HNO a) Zn(NO3)2 A b) (NO3)2Zn 3 _________ + H2, the missing product is c) ZnNO3 d) NO3Zn _____3) In the reaction 2________ 2 Pb + O2, the missing product is a) PbO b) OPb c) PbO2 d) O2Pb B) Identify the type of reaction shown: Use the key S for synthesis, D for decomposition, SR for single replacement Reaction KBr + Na à NaBr + K 2 LiNO3 + Ca à Ca(NO3)2 + 2 Li 2 Fe + 3 Cl2 à 2 FeCl3 2 Li2O à 4 Li + O2 What Type? How Did You Know? (Clue) SR SR “May I cut in” S D 2 reactant 1 product “May I cut in” 1 reactant 2 product C) Write the charges of each species, then identify which species are oxidized, reduced and spectator ions in the following reactions: (for polyatomic ions, use the charge on the polyatomic ion) +1 -2 0 0 1) Ag2S 2 Ag + S -2 +1 S Ag none OXIDIZED:________ Reduced:_________ Spectator Ion:____________ 0 +1 -1 0 +1 -1 2) KBr + Na Na Br + K Na 0 K +1 -1 Br OXIDIZED:___________ Reduced:____________ Spectator Ion:____________ +1 -1 0 +2 -1 0 3) 2 Li NO3 + Ca Ca (NO3)2 + 2 Li 0 +1 -1 Ca Li NO3 OXIDIZED:___________ Reduced:____________ Spectator Ion:___________ 0 0 +3 -1 4) 2 Fe + 3 Cl2 2 Fe Cl3 0 none 0 Cl2 Fe OXIDIZED:__________ Reduced:____________ Spectator Ion:___________ +1 -2 0 0 5) 2 Li2 O 4 Li + O2 -2 +1 O Li none OXIDIZED:__________ Reduced:____________ Spectator Ion:__________ D) Complete the following reactions by writing the appropriate formula(s) (Remember BrINClHOF ‘s come in pairs when alone!) NaBr a) 2 Na + Br2 à2 __________ Cl2 b) Mg + ______________________ à MgCl2 O2 c) 2 BaO à 2 Ba + ___________ N2 d) 2 NO2 à _____________ + 2 O2 Li3N e) 2 ______________à 6 Li + N2 Cu f) 2 Sc + 3 CuSO4 à Sc2(SO4)3 + 3 ___________________ KNO2 g) Cu + 2 _________________à Cu(NO2)2 + 2 K Check : Write your answers on the white board For your reaction: 1) assign the oxidation #s 2) Determine what is oxidized or reduced 3) Identify the spectator ion (write “none” if no spectator ion) 4) Identify the type of REDOX reaction: ___ A. 4Al + 3 FeO2 2 Al2O3 + 3 Fe ox # __________ red# __________ spectator ion: _______ ___ B. Zn + 2 HCl ZnCl2 + H2 ox # ________ red# _______ spectator ion: _______ Double Replacement Reactions Relevant Vocabulary Soluble: able to be dissolved into a solvent Insoluble: Dissolves only to a small degree into a solvent Solute: the material whose IMAF are overcome by and breaks up into a solvent. Solvent: the material into which a solute may be dissolved Precipitate: an insoluble product that exits the solution. In terms of today, the precipitate will be a SOLID. Ion Exchange (Double Replacement) Reactions Reactions in which two aqueous solutions are mixed resulting in a solid precipitate. The cation of one solution and the anion of the other solution attract so strongly that water cannot break the ionic bond and the ionic compound formed “falls out” of solution as a solid precipitate. AB (aq) + CD (aq) AD (s) + CB (aq) Solubility Use Reference Table F to determine solubility Soluble: can be used as a reactant in the reaction Insoluble: is the precipitate product of the reaction Do Now Work packet p. 6A A) Use TABLE F to determine if the following ionic compounds are soluble or insoluble 1. Determine the cation and the anion in the compound given 2. Look up the anion on Reference Table F: it should fall in the soluble or insoluble column 3. Determine if there are any exceptions to the rule that apply a) Al(OH)3 _______ c) CaCl2 _______ b) (NH4)(NO3) _______ d) Mg(CO3) _______ Dissolving Example Double Replacement Reaction +1 -1 +1 -1 AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq) Ag Cl (s) + Na NO3 (aq) AB + + CD Example Double Replacement Reaction +1 +2 -1 -3 3 Ca(NO3)2 (aq) +2 K3PO4 (aq) 6 K NO3 (aq) + Ca 3 ( PO4 ) 2 (s) AB + CD + Animation Pb(NO3)2 (aq) + 2 KI (aq) 2 KNO3 (aq) + PbI2 (s) Making A Desired Precipitate +2 -1 +1 -2 +1 -1 Ca ( NO3)2 (aq) + K 2CO3 (aq) 2 K NO3 (aq) + CaCO3 (s) 4)The 1) Write reactants the formula are two of the solutions, productone (made containing from the the +2 -2 2) 3) 5) Find Balance a +– ion the that reaction. will be soluble with CO Ca 3 . . Ca+2 ion , the spectator ions). other containing the CO3-2 ion. Differences Between Redox Reactions and Ion Exchange Reactions REDOX ION EXCHANGE Charges of species changes from one side to the other Spectator ion is the species that does not change charge from one side to the other Both take reactants and turn them into products Both require writing formulas based on the charges found on the Periodic Table Charges of species do not change from one side to the other Spectator ion is the species that remains in solution from one side to the other Your turn…work packet p. 6B B) With Reference Table F, predict the products and determine which is the soluble (aq) and which is the insoluble (s) product. a) CuCl2 (aq) + Na2(CO3) (aq) b) 3 K2(CrO4) (aq) s + CuCO3 __________ (___) + 2 Fe(NO3)3 (aq) aq 2 NaCl (___) __________ KNO3 (____) aq + 6_________ Fe2(CrO4)3 s _________ (____) NaNO3(____) aq + c) Na2(CO3) (aq) + 2 Ag(NO3) (aq) 2_________ Ag2CO3 s _________ (____) KNO3 (____) aq + d) KCl (aq) + Ag(NO3) (aq) _________ AgCl (____) s _________ Up for More? Demo: Use solubility Reference Table F to predict if a ppt. will form or not? Compounds Mixed CoCl2 NaOH K(NO3) NaCl Ag(NO3) NaCl Fe(NO3)3 Na(OH) Fe(NO3)3 Ag(NO3) Will a ppt. form? (Y or N) If yes, which ions will form the ppt? Prediction correct (C) or incorrect (I) New Challenge… 1. Each of you has an ion card. (Blue : Cations. Yellow: Anions) 2. Pair up with a person with a card to form an ionic compound. (one blue/one yellow) 3. Determine if new compound is soluble or insoluble. 4. Write your new compound on the appropriate board (remember to write chemical formula correctly) 5. Return to your seat and await further instructions. You have 2.5 minutes GO! Challenge Part 2 1. Choose one compound from the insoluble column and one from the soluble column. 2. Write these compound on your white board. Be sure to write in the phase for each compound. Answer: What were the reactants for your reaction? What are the spectator ions in the reaction? Will They Won’t They You will work alone on this sheet You are to do only the questions circled on your WS. Turn over when complete. If time begin HW.