Summary of Biochemical Tests in Microbiology
advertisement

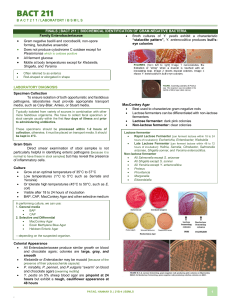
Summary of Biochemical Tests in Microbiology “Better living through chemistry” Catalase Test Summary Tests for presence of catalase. Background Catalase is an enzyme that breaks down hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen gas. Evolution of oxygen gas bubbles is positive. All + except EF – Methods Loop of bacteria added to a drop of Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Blood Agar Test Summary Tests for presence of hemolysin. Background Hemolysin is an enzyme that destroys red blood cells. Methods Bacteria streak and loop stabs to blood agar. 3 Types of Blood Agar Results Summary Alpha – Partial hemolysis Beta – Complete hemolysis Gamma – No hemolysis Background Alpha hemolysis partially oxidizes hemoglobin changing it to green. All B+ except SE and EF Beta hemolysis lyses RBC completely making a clear zone Gamma hemolysis – no activity Mannitol Salts Agar (MSA) Test Summary Selective for gram + Differential for fermentation of mannitol sugar. Background Gram + bacteria tolerate sodium chloride (NaCL) salt. SA + EF + SE - and others – Methods Streak surface of MSA Agar. Watch for change from pink to yellow as a + McConkeys Test Summary Tests for fermentation of lactose. Background Selects for gram - , Crystal violet inhibits gram + Lactose and neutral red produce a dark pink differentiating lactose + EC, CLO, KP are + Methods Loop of bacteria streaked on Mac agar EMB Agar Test Summary Tests for fermentation of lactose. Background Selects for gram - , Eosin and methylene blue inhibit gram + Lactose and dyes produce a dark pink differentiating lactose + in CLO and a green sheen in EC EC, CLO, KP are + Methods Loop of bacteria streaked on EMB agar Nitrate Reduction Test Summary Tests for nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase. Background Potassium Nitrate KNO3 as substrate. Nitrate Nitrite N2 Methods . Add Nitrate A & B and cherry red means + for nitrate reductase All + Follow up with Zinc = grey = + for nitrite reductase PA + Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) Test Summary Differentiates gram – enterics by fermentation patterns. Background Lactose and glucose are substrates. Phenol red is the indicator. pH of 6.8 or lower turns yellow. Methods Stab and streak TSI slant. Red slant & yellow but = glucose fermentation. ST SF PA Yellow slant and yellow butt = lactose and glucose fermentation. SA SE EF BS EC CLO KP PV(false) Red slant & red butt = no fermentation. Black butt = Hydrogen sulfide production Urease Test Summary Differentiates organisms using urease to break down urea into ammonia Background Substrate is urea. pH indicator is phenol red (pH 6= yellow, 6.8 topaz, 8 = fuchsia) Methods Loop inoculation of urea broth. SA SE KP PV are + IMViC Indole Test Summary and Background Differentiates enteric organisms such as EC and PV which are able to metabolize the amino acid tryptophan into indole and pyruvic acid. This test also detects motility of bacteria and H2S2 production. Methods Needle inoculation of SufideIndole-Motility (SIM) media. Substrate is tryptophan. Add Kovac’s indole reagent. A red color is + for indole production. Black = + for H2S2 Motility is observed as turbidity radiating out from the inoculation line. IMViC Methyl Red Summary and Background Differentiates enteric organisms such as EC from CLO using the timing of glucose fermentation products. Both produce acids but CLO further converts to non acidic ethanol and then elevates the pH. Methods Loop inoculation of MR VP broth. Add methyl red indicator. Red = + for acid conditions. SA SE BS EC KP PV ST SF Yellow is – indicating more basic conditions. EF CLO PA Citrate Test Summary Differentiates organisms using citrate as a carbon source. Background Organisms using citrate must also have nitrogen found in the medium as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate. Citrate fermentation produces ammonia causing the indicator (bromothymol blue) to turn deep blue. Methods Loop inoculation of citrate slant. Prussian blue = + for citrate fermentation and alkaline conditions. Green or yellow = - (low pH)